Sites: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
topic: Water Crisis
Social media activity version | Lean version
An ancient Indigenous lagoon system brings water back to a dry town in Ecuador
- The town of Catacocha, located in the south of Ecuador, is in a province known for being almost a desert: dry forest, barren soil and rains that only appear two months in the year.
- A historian discovered the water collection system long ago used by Palta Indigenous people and persuaded locals in Catacocha to apply it.
- By building 250 artificial lagoons, the inhabitants of this region have succeeded in managing rainwater.
- The change that has happened in nine years is visible: They sowed 12,000 plant,s and UNESCO has included the area in its list of ecohydrology demonstration sites.
Indigenous Bolivians flee homes as backlash to mining protest turns explosive
- Indigenous communities have been threatened and attacked for protesting mining pollution, water scarcity and land use change in the community collective of Acre Antequera.
- The collective, or ayllu, is an Indigenous territorial structure made up of eight Quechua communities traditionally devoted to pastoralism and agriculture.
- But open-pit mining for silver, copper, lead, zinc, tin and other minerals has used up a lot of their freshwater.
- While protesting earlier this month against the harmful impacts of mining, several women in the community said dynamite was thrown into their homes and their children weren’t allowed to attend school.
Indigenous community fights to save its lands on Indonesia’s historic tin island
- The Lanun Indigenous community of Indonesia’s Belitung Island have responded to increasing environmental damage by building their capacity in skills such as advocacy and mediation.
- At issue is the growth in illegal mining and forest clearing by the plantation industry on land that the Lanun consider to have long been theirs.
- In 2021, UNESCO announced this area of Indonesia would become an international geopark, which required joint applications by government and local communities to conserve a landscape of global significance.
Rainwater reserves a tenuous lifeline for Sumatran community amid punishing dry season
- Kuala Selat village lies on the coast of Indragiri Hilir district on the Indonesian island of Sumatra.
- In the first half of the year, residents of the village arrange buckets and drums to collect rainwater to meet their daily needs.
- They will then stockpile water to last through the dry months from June-September, but a longer dry spell has led to an acute shortage of water.
- Residents say they believe the water crisis in the village was linked to bouts of diarrhea, and that many fled the village during an outbreak.
Critics fear catastrophic energy crisis as AI is outsourced to Latin America
- AI use is surging astronomically around the globe, requiring vastly more energy to make AI-friendly semiconductor chips and causing a gigantic explosion in data center construction. So large and rapid is this expansion that Sam Altman, the boss of OpenAI, has warned that AI is driving humanity toward a “catastrophic energy crisis.”
- Altman’s solution is an audacious plan to spend up to $7 trillion to produce energy from nuclear fusion. But even if this investment, the biggest in all of history, occurred, its impact wouldn’t be felt until mid-century, and do little to end the energy and water crises triggered by AI manufacture and use, while having huge mining and toxic waste impacts.
- Data centers are mushrooming worldwide to meet AI demand, but particularly in Latin America, seen as strategically located by Big Tech. One of the largest data center hubs is in Querétaro, a Mexican state with high risk of intensifying climate change-induced drought. Farmers are already protesting their risk of losing water access.
- As Latin American protests rise over the environmental and social harm done by AI, activists and academics are calling for a halt to government rubber-stamping of approvals for new data centers, for a full assessment of AI life-cycle impacts, and for new regulations to curb the growing social harm caused by AI.
Java rice farmers suffer crop failure as copper mine pollutes local irrigation
- Rice farmers in Cokrokembang village, East Java province, suspect contamination from a nearby copper mine operated by PT Gemilang Limpah Internusa is to blame for recent crop failures.
- Water pollution from the mine is visible in the Kedung Pinihan River, while tests conducted by the local government reveal levels of copper compounds far exceeding environmental standards.
- Despite attempts to address the issue, including government involvement and remedial measures by the company, farmers like Parno continue to suffer declining yields, prompting calls for compensation for affected farmers.
Pollution poses big risks to global clean water supplies, study shows
- Nitrogen pollution could intensify global water scarcity threefold by 2050, scientists warn in a recently published paper. In addition, “newly emerging pollutants,” such as microplastics, heavy metals, pathogens and pharmaceuticals, emitted into waterways could cause “severe water degradation in the future.”
- Modeling the escalating impact of nitrogen pollution on water quality, the scientists found that more than 3,000 river basins globally are at risk of water scarcity by 2050 in one future scenario. That finding comes along with concern that climate change could exacerbate water quality decline and increased scarcity.
- Nitrogen pollution and water contamination by heavy metals and pathogens have serious known public health consequences, while health impacts from microplastics and pharmaceuticals need far more research.
- The researchers suggest solutions that include curbing nitrogen pollution through better fertilizer management practices and improved wastewater treatment.
Harsh dry season sours harvest prospects for Java coffee farmers
- Indonesia is the world’s fourth-largest producer of coffee, after Brazil, Vietnam and Colombia, but the archipelago’s farmers are less productive than their competitors.
- In East Java province, farmers have seen yields plummet as a protracted water deficit shrinks fruit and introduces pests.
- Total output is expected to drop by more than 20% this season, while increasingly frequent extreme weather may pose challenges to the viability of some smallholders in lowland areas of Indonesia.
Locals at the mouth of the Amazon River get a salty taste of climate change
- Ocean rise and changes in the Amazon River are ruining the way of life in an archipelago close to where the Amazon River runs into the Atlantic.
- In Bailique, locals are experiencing longer periods of salty water, a natural phenomenon that is becoming more usual due to climate change.
- Açaí berries, the prime economic drive of the community, are becoming saltier, and palm trees are being eaten by the erosion caused by changes in the Amazon River’s flow.
- Part of the population has already left the region, as others struggle to adapt to the new landscape.
Controversy brews over proposed dam on Kathmandu’s Bagmati River
- A proposed dam on Kathmandu’s Bagmati River aims to collect rainwater during the wet season and release it in the dry season to rejuvenate the river, but skeptics question its viability and safety.
- Concerns include environmental impact, potential destruction of trees, pollution and the risk of dam failure in earthquake-prone Nepal.
- Political, ecological and community-related questions remain unanswered, with some advocating for alternatives and further analysis before proceeding.
Andes community-led conservation curbs more páramo loss than state-protected area: Study
- In the central highlands of Ecuador, land managed by Indigenous peoples and local communities is associated with improved outcomes for drought adaptation and páramo conservation, according to a new study.
- The study finds that páramo areas managed by communities in this region are better protected than those under the care of the state.
- Due to the advance of the agricultural frontier in the highlands, approximately 4 hectares (9.9 acres) of páramo are lost every day, which threatens the water supply of the entire region.
- Community-led land management that incorporates inclusive participation, traditional knowledge and the cultural values of those who inhabit the areas, coined by reseachers as “social technology,” can aid in the conservation of the páramo.
Maluku farmers sweat El Niño drought as Indonesia rice prices surge
- Rice prices surged across Indonesia during the second half of 2023 as the effects of El Niño led to widespread crop failures.
- In December, President Joko Widodo ordered military personnel to help farmers plant rice in a bid to boost domestic production, and curb food price inflation.
- On Buru Island, Mongabay Indonesia spoke with farmers who described risks of conflict as water scarcity forced farmers to queue for access to water.
Java’s crumbling coastline and rising tide swamp jasmine flower trade
- Growers of jasmine flowers in lowland areas of Indonesia’s Central Java province are vulnerable to coastal erosion and rising sea levels.
- Research published in 2022 showed Central Java’s Semarang was among the fastest-sinking major cities in the world.
- Jasmine grower Sobirin has altered his home on three occasions since 2010, raising the floor to adapt to increasing tidal surges.
In Mexico, Xalapa’s chronic water scarcity reflects a deepening national crisis
- Residents of Xalapa, the capital of Veracruz, Mexico, have been struggling with a worsening water shortage that often leaves people without daily access to household water for washing.
- The problem is nationwide, in 30 of 32 states, forcing residents to purchase and recycle water and postpone bathing.
- Experts have blamed climate change and extreme heat for the country’s water shortages; others also blame corruption that allows companies to pay for unlimited water use.
- Deforestation for development, an increase in construction and building and population increases are also factors.
Why the Amazon’s small streams have a major impact on its grand rivers
- An unprecedented time-series study in the basin of the Tapajós River, a major tributary of the Amazon, assesses the level of degradation of small rivers threatened by agribusiness expansion.
- Researchers from several universities will assess the conservation status of 100 streams spread between the municipalities of Santarém and Paragominas, at the confluence of the Tapajós and the Amazon, which were first analyzed in 2010.
- The impact of dirt roads and their network of river crossings, which causes sediment load, siltation, erosion and changes in water quality, was one of the factors that caught researchers’ attention in the initial time-series study.
- Experts say that local development models should ideally start from water to land, rather than the other way around, given the importance of water for the rainforest, its biodiversity, and the inhabitants who depend on both.
New AI model helps detect and identify microplastics in wastewater
- A new model developed by researchers at the University of Waterloo in Canada uses advanced spectroscopy and artificial intelligence to identify the presence of microplastics in wastewater.
- Researchers trained PlasticNet to detect microplastics based on how they absorb and transmit different wavelengths of light that they’re exposed to.
- The tool successfully classified 11 types of common plastics with an accuracy of more than 95%; it could potentially be used by wastewater treatment plants and food producers to identify microplastics.
- The team is currently working to make the model work faster and more efficiently, and to also streamline the process of gathering data.
A Mekong island too tiny for industrial farming now points to Vietnam’s future
- In the decades following the U.S. war in Vietnam, the Vietnamese government championed intensive farming methods that boosted rice harvests and turned the country into an export powerhouse.
- While much of the Mekong Delta was reshaped to support intensive farming, the coastal island of Con Chim was deemed too small to be worth installing the necessary dikes and sluice gates, leaving farmers there to continue traditional patterns of wet and dry season agriculture and fishing.
- Now, in an era dominated by climate concerns, Vietnam plans to scale back rice farming and shift to more nature-based agricultural practices. Once a forgotten backwater, Con Chim now stands as a rare guidepost to a more sustainable agricultural future.
- This story was produced in partnership with the Global Reporting Program at the University of British Columbia’s School of Journalism, Writing, and Media.
Extreme drought in western Pará pushes family farmers into agroforestry
- Lost crops, reduced fish numbers, low water levels in rivers and difficult access to potable water have all led to a state of disaster declared in many municipalities in the state of Pará.
- Severe drought, the result of increasing climate changes and El Niño, is resulting in a more flammable Amazon rainforest. Farmers and technicians are seeking out more sustainable alternatives to the traditional slash-and-burn system.
- Agroforestry systems (AFS) and native honeybee apiculture cooperatives are increasing in the region.
With half its surface water area lost, an Amazonian state runs dry
- Water bodies across the Brazilian state of Roraima have shrunk in area by half over the past 20 years, according to research from the mapping collective MapBiomas.
- Today, locals are facing even drier times amid a severe drought in the Amazon, which has led to record-low levels of water in the rainforest’s main rivers.
- Since 1985, Roraima’s agricultural area has grown by more than 1,100%, with experts pointing to crops as one of the state’s main drivers of water loss.
Salty wells and lost land: Climate and erosion take their toll in Sulawesi
- Coastal erosion on the west coast of Indonesia’s Sulawesi Island is so advanced that seawater has penetrated the groundwater supply that tens of thousands use for drinking water.
- The communities have yet to be served by utility water provision, so families are resorting to costly supplies of water from private distributors.
- Research shows that rising seas and more frequent and powerful storms will accelerate coastal abrasion, raising burdens shouldered by the world’s coastal communities.
New study pushes for protection of one of Africa’s ‘least understood treasures’
- A new study reveals the extent of a tropical water tower in Angola, which performs the same role as snow-capped mountains in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The Angolan Highlands Water Tower contains peatlands and freshwater lakes that supply major rivers in the region, and the wildlife-rich Okavango Delta in Botswana.
- Despite this vital hydrological role, the water tower currently has no formal protection.
- The team behind the study hopes it will help to strengthen the case for recognition of a vast portion of the water tower as a Ramsar Site of International Importance.
The Cloud vs. drought: Water hog data centers threaten Latin America, critics say
- Droughts in Uruguay and Chile have led residents to question the wisdom of their governments allowing transnational internet technology companies to build water-hungry mega-data centers there.
- As servers process data, they need lot of water to keep them cool. But if demand grows as expected, the world will need 10-20 times more data centers by 2035, and they’ll be using far more water. Many will likely be built in economically and water-challenged nations already facing climate change-intensified droughts.
- Latin American communities fear that this “data colonialism” will consume water they desperately need for drinking and agriculture, and are critical of their governments for giving priority treatment to transnational tech giants like Google and Microsoft, while putting people’s access to a basic human necessity at risk.
- Surging digital data use by 2030 may cause each of us in the developed world to have a “digital doppelganger,” with our internet use consuming as much water as our physical bodies. But much of the stored data is “junk.” Critics urge that nations insist on tougher regulations for transnational companies, easing the crisis.
More action needed to protect freshwater ecosystems, report says
- A recent report from the international conservation NGO WWF argues that freshwater ecosystems are too valuable to go overlooked as new conservation policies are created.
- Freshwater underpins global food security, the economy and public health, putting the total value of water in 2021 at around $58 trillion, or 60% of the global GDP, the report estimates.
- WWF urged governments to revitalize efforts to conserve 30% of rivers, lakes and wetlands by 2030 and for the private sector to develop better risk assessments that eliminate pollution from their supply chains and consider how they contribute to water scarcity.
A tale of two biomes as deforestation surges in Cerrado but wanes in Amazon
- Brazil has managed to bring down spiraling rates of deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest in the first half of this year, but the neighboring Cerrado savanna has seen a wave of environmental destruction during the same period.
- The country’s second largest biome, the Cerrado is seeing its highest deforestation figure since 2018; satellite data show 3,281 hectares (8,107 acres) per day have been cleared since the start of the year through Aug. 4.
- The leading causes of the rising deforestation rates in the Cerrado are a disparity in conservation efforts across Brazil’s biomes, an unsustainable economic model that prioritizes monocultures, and escalating levels of illegal native vegetation clearing.
- Given the importance of the Cerrado to replenish watersheds across the continent, its destruction would affect not just Brazil but South America too, experts warn, adding that the region’s water, food and energy security are at stake.
Vietnamese rice farmers go high-tech to anticipate a low-water future
- Since the 1970s, Vietnam’s “rice-first” policy facilitated the construction of an elaborate series of dikes and dams that allowed farmers in the Mekong Delta to flood their fields to allow for multiple harvests per year.
- Now, in the face of climate change impacts, seawater intrusion, upstream dams and new government policies that mandate water conservation, farmers in the delta need to find ways to reduce their water consumption.
- In one pilot project, university researchers have teamed up with local farmers to implement a technique called alternate wetting and drying (AWD), supported by a smartphone application that allows farmers to save water and reduce emissions.
Award-winning community group in Sumatra cleans up lake
- A group of locals have since 2013 tried to clean up the trash pooling in Lake Sipin in the Sumatran province of Jambi.
- Their efforts have received national attention, with their leader, Leni Haini, awarded the country’s highest environmental award in 2022 by the government.
- Indonesia has announced a plan to restore 15 lakes (Sipin isn’t included) across the country by 2024, citing their high degree of degradation, chiefly sedimentation, which has resulted in their rapid shrinking and a decline in the biodiversity they host.
- These lakes are crucial in supporting the livelihoods of millions of Indonesians, serving as a source of freshwater, a form of flood control, and a site for fish-farming and tourism.
Crud-to-crude: The global potential of biofuels made from human waste
- Creating liquid biofuels from human waste shows promise as a way to meet one of alternative energy’s greatest challenges: reducing the transportation sector’s heavy carbon footprint. The good news is there is a steady supply stream where waste is treated.
- Humanity produces millions of tons of sewage sludge annually via wastewater treatment. Existing disposal methods include landfilling, application on agricultural land, and incineration; each with social and environmental consequences.
- Harnessing the carbon-rich potential of sludge as a transportation fuel for planes, ships and trucks is part of a drive toward zero waste and creating a circular economy, say experts. A host of projects are underway to prove the effectiveness of various methods of turning all this crud into biocrude.
- Some techniques show promise in lab and pilot tests, but large-scale industrial plants have yet to be built. Using pollutant-laden sewage sludge as a biofuel comes with its own environmental concerns, but lacking a silver-bullet solution to the human waste problem, it could be part of a suite of best alternatives.
Dhaka faces manifold problems as water bodies diminish
- A study by the Bangladesh Institute of Planners, or BIP, says the capital has lost 36% of its water bodies since 2010.
- Dhaka city has experienced water scarcity during dry months, which puts a strain on firefighters as they battle large fire; during monsoon months, the city experiences regular waterlogging as water retention points fill up.
- The disappearance of water bodies has created multifaceted problems like rising water levels, airborne disease, and mosquito-related diseases.
- In 2000, the government passed the Natural Water Reservoir Conservation Act, which mandates that natural water bodies be kept intact.
Madagascar: What happens to villagers when a graphite mine comes knocking?
- When representatives of an Australian mining firm arrived in Ambohitsy Haut village in southern Madagascar, they told residents they wanted to drill holes looking for graphite in their village. The villagers agreed, but they were clear; you can dig, but away from our ancestral tombs.
- In November, the company, BlackEarth Minerals (BEM), told investors it was ready to move to the next stage, exploitation, and planned to start construction of a mine this year, which could mean resettling the villagers and moving their tombs. But villagers said they haven’t given the company permission to do so.
- BEM, now known as Evion Group, is touting Madagascar as an alternative to China , currently the world’s leading graphite supplier, but experts and activists say the graphite mining rush is coming to a country and communities ill-prepared for it: obsolete mining laws, a brittle land rights regime, and limp environmental and social protections.
- A top Evion executive told Mongabay that the villagers had no private claims to the land, but the company would respect their traditional rights.
Drying wetlands and drought threaten water supplies in Kenya’s Kiambu County
- Prolonged drought in Kenya has caused a water crisis, threatening local livelihoods and biodiversity; one of the badly affected areas is Kiambu County, a region normally known for its high agricultural productivity.
- Human activities such as dumping, encroachment and overgrazing coupled with dire effects of climate change exacerbate the degradation of wetlands, worsening the water crisis.
- Scientists say that conservation efforts must center around local communities to ensure the restoration of natural resources and combat the impacts of climate change.
At the U.N. Water Conference, food security needs to take center stage (commentary)
- This week at the United Nations Water Conference, the growing level of global food insecurity from a lack of water should be addressed.
- “We urgently need a worldwide evaluation of water-related food risks that offers immediate and practical solutions,” a new op-ed argues.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors, not necessarily of Mongabay.
‘During droughts, pivot to agroecology’: Q&A with soil expert at the World Agroforestry Centre
- As the unabating drought in Kenya persists, pastoralists in the region are struggling as millions of their livestock perish and vast swaths of crops die. About 4.4 million people in the country are food insecure.
- International food agencies are calling it a dire humanitarian situation and highlight the vital need to build communities’ resilience to adapt and cope with drought.
- Mongabay speaks with David Leilei, a Kenyan soil biologist at the World Agroforestry Centre, on the agroecological techniques and strategies pastoralists and the government can use to restore healthy soils to promote productive farming.
- Mary Njenga, a research scientist at the World Agroforestry Centre who works with 1,200 households in northern Kenya, also speaks with Mongabay on climate-resilient strategies.
Herders turn to fishing in the desert amid severe drought, putting pressure on fish population
- As Northern Kenya’s unabating drought continues, a growing wave of pastoralists are finding it challenging to keep their livestock alive and are switching to fishing in Lake Turkana, the world’s largest desert lake.
- However, environmentalists, fishing authorities, and some fishers worry that potential overfishing and increased pressures on fish populations will cause a collapse in fish stocks and the lake’s ecosystem.
- Authorities are also concerned about the rampant use of illegal fishing gear, such as thin mesh nets that catch undersized fish in shallow breeding zones, and an illegal tilapia smuggling network draining the lake by the tons.
- Though no studies have yet been done to assess fish populations, some environmentalists and fishers are calling for better enforcement of regulations to keep livelihoods afloat.
Tobacco: Vaping and smoking drive environmental harm from farm to fingertip
- Electronic cigarettes heavily marketed via single-use flavored products are increasingly popular. These products require disposal of large amounts of hazardous waste, including huge quantities of lithium, a resource in demand for electric car batteries and rechargeable electronics for laptops and mobile phones.
- Even as vaping use grows, an estimated 6 trillion “traditional” cigarettes are still smoked annually; 4.5 trillion are thought to be discarded into the environment each year. Researchers and activists emphasize that the tobacco industry is responsible for considerable harm to nature and human health.
- Traveling along the supply chain, tobacco production and consumption has consequences for forests, oceans, the climate, and for farmers and their families who produce the crop — all to an extent not yet fully known or understood.
- Efforts are underway to rein in some of these negative impacts against the backdrop of an industry accused of consistently greenwashing to conceal an environmental footprint that is harming both nature and public health.
Blue jeans: An iconic fashion item that’s costing the planet dearly
- The production of blue jeans, one of the most popular apparel items ever, has for decades left behind a trail of heavy consumption, diminishing Earth’s water and energy resources, causing pollution, and contributing to climate change. The harm done by the fashion industry has intensified, not diminished, in recent years.
- The making of jeans is water intensive, yet much of the world’s cotton crop is grown in semiarid regions requiring irrigation and pesticide use. As climate change intensifies, irrigation-dependent cotton cultivation and ecological catastrophe are on a collision course, with the Aral Sea’s ecological death a prime example and warning.
- While some major fashion companies have made sustainability pledges, and taken some steps to produce greener blue jeans, the industry has yet to make significant strides toward sustainability, with organic cotton, for example, still only 1% of the business.
- A few fashion companies are changing their operations to be more sustainable and investing in technology to reduce the socioenvironmental impacts of jeans production. But much more remains to be done.
Avocado farming is threatening Colombia’s natural water factory
- To satisfy the world’s ever-increasing appetite for the popular fruit, Colombia is risking the páramo, one of its key ecosystems.
- These rare environments provide fresh water to tens of millions of people — the majority of the Colombian population.
- The country is now second to Mexico as the world’s top avocado producer, with a significant uptick in production in the last year, resulting in socioeconomic and environmental impacts for communities downstream.
In temperate Nepal, climate change paves way for tropical dengue fever
- Nepal is experiencing its worst outbreak of dengue fever in recorded history, which health experts attribute in part to a changing climate.
- Wetter monsoons and warmer temperatures have made for ideal breeding conditions for the mosquitoes that carry the virus.
- Poor water and waste management are also factors, allowing for water to stagnate for long periods and giving the mosquitoes a place to lay their larvae.
- Experts say it will take a combination of personal responsibility — to eradicate mosquito-breeding grounds — and government leadership — to coordinate the public health response — if dengue is to be eradicated in Nepal.
Putting a price on water: Can commodification resolve a world water crisis?
- In 2018, a trader listed water on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and then in 2020 introduced a futures market so consumers can factor the cost of water into their investment plans. After a slow start, traders expect the market to grow more strongly in 2023.
- Some analysts see this as a positive step, allowing market adjustments to provide consumers with the cheapest and most efficient way of buying water. Others disagree, saying that water, like air, should not be commodified as it is a fundamental human right and must be available to all.
- Critics fear that creating a water market is a first step toward a future in which just a few companies will be able to charge market rents for what should be a free natural resource. Huge questions remain over water allocations for industry, agribusiness and smallholders, cities, and traditional and Indigenous peoples.
- The clash between these economic and socioenvironmental worldviews isn’t just occurring internationally. The conflict over water regulation is evident in many nations, including Brazil, which lays claim to the world’s biggest supply of freshwater, and Chile, currently suffering from its most severe drought ever.
Haiti: An island nation whose environmental troubles only begin with water
- As Haiti plunges into the worst social unrest the nation has seen in years, shortages abound. One of these is water. But in Haiti, water scarcity has deeper roots, that connect to virtually every other aspect of the environment. Haiti’s ecosystems today, say some, are under stress due to regional and global transgressions of the nine planetary boundaries.
- The planetary boundary framework originated in 2009 to define required limits on human activities to prevent collapse of vital Earth operating systems. They include biodiversity loss, freshwater, air pollution, climate change, high phosphorus and nitrogen levels, ocean acidity, land use changes, ozone layer decay, and contamination by human-made chemicals.
- Scientists defining the global freshwater boundary warn that tampering with the water cycle can affect the other boundaries. Haiti, as a small isolated island nation, suggests a laboratory case-study of these many interconnections, and offers a graphic example of the grim results for humanity and wildlife when freshwater systems are deeply compromised.
- Haiti today is plagued by an extreme socioeconomic and environmental crisis. As it fights climate change, freshwater problems, deforestation and pollution, it may also be viewed as a bleak bellwether for other nations as our planetary crisis deepens. But scientists warn that research on applying planetary boundary criteria on a regional level remains limited.
On the frontlines of drought, communities in Mexico strive to save every drop of water
- Sixteen Indigenous Zapotec communities in Mexico have created over 579 water infrastructure projects, including absorption wells, small dams and water pans, to conserve water in the Oaxaca Valley – a region impacted by recurrent droughts.
- Significant success in harvesting water has been realized, however, farmers still struggle to have enough water due to lack of rain – making water conservation efforts largely fall to dust.
- Last year, the Mexican government recognized their efforts and gave communities a concession to manage water resources locally. Communities are still waiting to know when they will officially receive the concession.
- Just a few women hold leadership positions in these communities, including Josefina, Esperanza and María. They have been involved in water conservation projects since a severe drought hit the region 17 years ago and hope to enhance gender equality in the region.
Climate change hits northern Mexico, as officials look to solve water crisis
- Water scarcity in northern Mexico has gotten worse over the last several years, especially in the state of Nuevo León and its capital city of Monterrey.
- The crisis is a result of a combination of declining rainfall, increasing deforestation of natural aquifers and government mismanagement of climate change readiness policies.
- Officials are investing in new dams and aquifers to address the problem through 2050. They’ve also “bombed” the sky to make it rain and implemented temporary water cutoffs for residents in urban areas.
Java communities rally as clock ticks on cleanup of ‘world’s dirtiest river’
- A national program to transform Java’s Citarum River into a source of drinking water expires in 2025.
- A reforestation program in uplands near the source of the river is drawing on community volunteers.
- West Java Governor Ridwan Kamil tells Mongabay that residents will see improved water quality by 2025 and that there is political will to tackle the crisis.
As their land and water turns saline, Kenyan communities take on salt firms
- Between 1977 and the 1990s, the Kenyan government allocated thousands of hectares of land to salt mining companies along the country’s north coast.
- People had been living on that land for generations, despite its being officially gazetted as public land by the government.
- Following the allocation of land, local people have complained of harassment and violent evictions by the salt companies, as well as soil and waters rendered too salty to farm, drink, or fish.
- In 2020 groups representing these communities filed a lawsuit against the companies and government that consolidates many complaints and aims to provide recourse for loss of land and livelihoods and damage to the environment. The case is due before a judge in October.
Drought-beset South African city taps aquifer, shirks long-term solutions: Critics
- A major coastal city located in South Africa’s Eastern Cape province is facing a total water cutoff for about 500,000 residents, almost half its population, following a prolonged drought.
- Disaster relief hydrologists have begun drilling boreholes to access groundwater so that hospitals and schools can stay open during the emergency in Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality.
- But critics say the city administration has failed to develop a long-term plan to support water harvesting from intermittent rains and construction of desalination plants.
- They also point out that overreliance on boreholes drilled near the sea could lead to saline water intrusion into the aquifer, contaminating groundwater and rendering borehole water undrinkable.
Water-stressed Bangladesh looks to recharge its fast-depleting aquifers
- Water management authorities in Bangladesh have drawn up a plan to recharge, or refill, the aquifers serving Dhaka and other areas, which are being depleted by one of the highest groundwater extraction rates in the world.
- The plan calls for injecting storm water, reclaimed water, desalinated water and potable water into the aquifers, which, in the case of Dhaka, is falling by up to 3 meters (nearly 10 feet) a year.
- The country withdraws an estimated 32 cubic kilometers (7.7 cubic miles) of groundwater annually, 90% of which is used for irrigation and the rest for domestic and industrial purposes.
- Even though four of South Asia’s largest rivers run through Bangladesh, the country struggles to provide sufficient drinking water for its inhabitants, in large part because of pollution.
Podcast: ‘Water always wins,’ so why are we fighting it?
- On this week’s episode of the Mongabay Newscast we examine humanity’s approach to harnessing water, and how the current “us-first” mindset is actually exacerbating our water access problems.
- Journalist and author Erica Gies joins us to discuss the concept of ‘slow’ solutions to water shortages presented in her new book “Water Always Wins: Thriving in an Age of Drought and Deluge,” and how communities can work with water rather than against it.
- Gies discusses how hydrologists, engineers, and urban planners are creating ‘slow’ water projects with traditional hydrological knowledge, which are less invasive ways of harnessing water, in places such as Chennai, India.
Beyond boundaries: Earth’s water cycle is being bent to breaking point
- The hydrological cycle is a fundamental natural process for keeping Earth’s operating system intact. Humanity and civilization are intimately dependent on the water cycle, but we have manipulated it vastly and destructively, to suit our needs.
- We don’t yet know the full global implications of human modifications to the water cycle. We do know such changes could lead to huge shifts in Earth systems, threatening life as it exists. Researchers are asking where and how they can measure change to determine if the water cycle is being pushed to the breaking point.
- Recent research has indicated that modifications to aspects of the water cycle are now causing Earth system destabilization at a scale that modern civilization might not have ever faced. That is already playing out in extreme weather events and long-term slow-onset climate alterations, with repercussions we don’t yet understand.
- There are no easy or simple solutions. To increase our chances of remaining in a “safe living space,” we need to reverse damage to the global hydrological cycle with large-scale interventions, including reductions in water use, and reversals of deforestation, land degradation, soil erosion, air pollution and climate change.
Indigenous agroforestry dying of thirst amid a sea of avocados in Mexico
- A rich tradition of cultivating and collecting medicinal plants in Mexico’s Michoacán state is at risk, as the Indigenous community behind it loses access to water.
- Avocado farms–mostly supplying the U.S. market–dominate water resources in the town of Angahuan, forcing Indigenous P’urhépecha healers to buy clean water by the gallon from shops to keep their medicinal plants alive.
- These healers, known as curanderas, have for generations grown a wide variety of such plants in agroforestry gardens that also combine fruits and vegetables, timber trees, and flowers.
- The P’urhépecha healers are resisting the impacts of avocado farms by planting trees in the hills to build up water resources while launching a natural pharmacy business in town, efforts for which the collective has already won an award from the state government.
In Bangladesh, a community comes together to save a life-giving forest
- Several tribal settlements are spread across Bangladesh’s Chittagong Hill Tracts (CHT) region, each with its own communally managed forest that residents can use.
- But the unchecked exploitation of the once-rich forests, a consequence of population growth, has led to local water holes drying up, forcing many residents to leave the villages.
- In one village, however, residents started an initiative with various programs aimed at conserving their forest and providing funding for alternative livelihoods to reduce members’ reliance on forest resources.
- The initiative in the village of Kamalchhori, which includes prohibitions on hunting and slash-and-burn farming, has seen local water sources restored and vegetation conserved.
Better deep-bore wells aim to stop Indonesia’s groundwater waste
- Farmers in Pasuruan have long dug deep wells for irrigation, relying on the region’s volcanic aquifer to keep supplying plentiful water.
- But the wells are crude structures that lack a shutoff valve, meaning they discharge water nonstop.
- Researchers have developed an improved well system that can be shut off when not needed, but its cost is a potential downside for local farmers.
Freshwater planetary boundary “considerably” transgressed: New research
- Earth’s operating systems have stayed in relative balance for thousands of years, allowing the flourishing of civilization. However, humanity’s actions have resulted in the transgressing of multiple planetary boundaries, resulting in destabilization of those vital operating systems.
- This week scientists announced that humanity has transgressed the freshwater planetary boundary. Other boundaries already crossed are climate change, biosphere integrity, biogeochemical cycles (nitrogen and phosphorous pollution), land-system change, and novel entities (pollution by synthetic substances).
- In the past, the freshwater boundary was defined only by “blue water” — a measure of humanity’s use of lakes, rivers and groundwater. But scientists have now extended that definition to include “green water” — rainfall, evaporation and soil moisture.
- Scientists say soil moisture conditions are changing from boreal forests to the tropics, with abnormally dry and wet soils now common, risking biome changes. The Amazon, for example, is becoming far dryer, which could result in it reaching a rainforest-to-savanna tipping point, releasing large amounts of stored carbon.
The world’s dams: Doing major harm but a manageable problem?
- Dam construction is one of the oldest, most preferred tools to manage freshwater for various uses. The practice reached a peak internationally in the 1960s and ’70s, but in recent years dam construction has faced increasing global criticism as the hefty environmental price paid for their benefits piles up.
- The flows of most major waterways have been impacted by dams globally. Only 37% of rivers longer than 1,000 km (620 mi) remain free-flowing, and just 23% flow uninterrupted to the sea. Natural flows will be altered for 93% of river volume worldwide by 2030, if all planned and ongoing hydropower construction goes ahead.
- This global fragmentation of rivers has led to severe impacts. Dams have contributed to an 84% average decline in freshwater wildlife population sizes since 1970. More than a quarter of Earth’s land-to-ocean sediment flux is trapped behind dams. Dams also impact Earth’s climate in complex ways via modification of the carbon cycle.
- But dams are needed for energy, agriculture and drinking water, and are an inevitable part of our future. Lessons on how to balance their benefits against the environmental harm they do are already available to us: removing some existing dams, for example, and not building others.
Pharmaceutical water pollution detected deep in the Brazilian Amazon
- Major rivers in the Amazon Basin of Brazil are contaminated with a wide range of pharmaceuticals as well as with sewage and wastewater, largely coming from urban centers in the region, according to recent research.
- Water samples taken along the Amazon, Negro, Tapajós and Tocantins rivers, and small urban tributaries that pass through the region’s cities, including Manaus, Santarém, Belém and Macapá contained 40 pharmaceuticals out of 43 in concentrations that have the potential to affect 50-80% of the local aquatic species.
- Experts explain that a major cause of freshwater contamination is the Amazon Basin’s rapidly growing population along with the government’s failure to provide adequate sanitation infrastructure — even though that has long been promised. Most of the region’s sewage is untreated, a solvable problem if properly funded.
Caffeine: Emerging contaminant of global rivers and coastal waters
- Caffeine is the most consumed psychostimulant in the world, and a regular part of many daily lives, whether contained in coffee, chocolate, energy drinks, or pharmaceuticals.
- Partially excreted in urine, it is now ubiquitous in rivers and coastal waters. So much so that its detection is used to trace wastewater and sewage pollution. A new study found it to be in more than 50% of 1,052 sampling sites on 258 rivers around the globe. Another new study enumerates caffeine harm in coastal and marine environments.
- This continual flow of caffeine into aquatic ecosystems is causing concern among scientists due to its already identified impacts on a wide range of aquatic life including microalgae, corals, bivalves, sponges, marine worms, and fish. Most environmental impacts — especially wider effects within ecosystems — have not been studied.
- Soaring global use of products containing caffeine means the problem will worsen with time. Untreated sewage is a major source. And while some sewage treatment facilities can remove caffeine, many currently can’t. Far more study is needed to determine the full scope and biological impacts of the problem.
Tiny plastic particles accumulating in river headwaters: Study
- Researchers modeled the journey of microplastics released in wastewater treatment plant effluent into rivers of different sizes and flow speeds, focusing on the smallest microplastic fragments — less than 100 microns across, or the width of a single human hair.
- The study found that in slow-flowing stream headwaters — often located in remote, biodiverse regions — microplastics accumulated quicker and stayed longer than in faster flowing stretches of river.
- Microplastic accumulation in sediments could be the ‘missing plastic’ not found in comparisons of stream pollution levels with those found in oceans. Trapped particles may be released during storms and flood events, causing a lag between environmental contamination and release to the sea.
- A few hours in stream sediments can start to change plastics chemically, and microbes can grow on their surfaces. Most toxicity studies of microplastics use virgin plastics, so these environmentally transformed plastics pose an unknown risk to biodiversity and health.
Innovative sewage solutions: Tackling the global human waste problem
- The scale of the world’s human waste problem is vast, impacting human health, coastal and terrestrial ecosystems, and even climate change. Solving the problem requires working with communities to develop solutions that suit them, providing access to adequate sanitation and adapting aging sewage systems to a rapidly changing world.
- Decentralized and nature-based solutions are considered key to cleaning up urban wastewater issues and reducing pressure on, or providing affordable and effective alternatives to, centralized sewage systems.
- Seeing sewage and wastewater — which both contain valuable nutrients and freshwater — as a resource rather than as pollutants, is vital to achieving a sustainable “circular economy.” Technology alone can only get us so far, say experts. If society is to fully embrace the suite of solutions required, a sweeping mindset change will be needed.
In Kathmandu, a struggle for water amid worsening floods
- In Kathmandu, residents face the dual challenges of freshwater aquifers running dry, and increasingly unpredictable monsoons causing flash floods.
- The combination of climate change and a rapidly growing urban population is straining an already overwhelmed municipal water system, forcing many residents to have to buy water by the tank at high prices.
- An ambitious project to pipe water to the city from a nearby river was shut down within months of its long-delayed start — a victim of the monsoon floods that destroyed a dam and water treatment plant.
- Another solution being explored is rainwater harvesting, which proponents say should be complemented by restoration of Kathmandu’s green areas and restrictions on drawing groundwater.
The thick of it: Delving into the neglected global impacts of human waste
- Though little talked about, our species has a monumental problem disposing of its human waste. A recent modeling study finds that wastewater adds around 6.2 million tons of nitrogen to coastal waters worldwide per year, contributing significantly to harmful algal blooms, eutrophication and ocean dead zones.
- The study mapped 135,000 watersheds planetwide and found that just 25 of them account for almost half the nitrogen pollution contributed by human waste. Those 25 were pinpointed in both the developing world and developed world, and include the vast Mississippi River watershed in the United States.
- Human waste — including pharmaceuticals and even microplastics contained in feces and urine — is a major public health hazard, causing disease outbreaks, and putting biodiversity at risk. Sewage is impacting estuary fish nurseries, coral reefs, and seagrasses, a habitat that stores CO2, acting as a buffer against climate change.
- Waste is often perceived as mostly a developing world problem, but the developed world is as responsible — largely due to antiquated municipal sewage systems that combine rainwater and wastewater in the same pipes. As a result, intense precipitation events regularly flush raw sewage into waterways in the U.S., U.K. and EU.
Sinkholes emerge in rural Kenya after series of floods, droughts
- In recent years, a number of sinkholes have emerged in Baringo county, a geologically active region in western Kenya’s Great Rift Valley.
- According to geologists, their appearance can be linked both to the worsening impacts of climate change through floods and droughts, and local communities drilling boreholes along precarious fault lines to access more water.
- According to members of the community, the sinkholes have yet to spur the county or the government into action, with food aid currently provided by local human rights organizations.
- Increases in floods are driving human-wildlife conflict for space, and pastoralists are having difficulty adapting to environmental changes.
As climate-driven drought slams farms in U.S. West, water solutions loom
- Drought in the U.S. West has been deepening for two decades, with no end in sight. Unfortunately for farmers, water use policies established in the early 20th century (a time of more plentiful rainfall), have left regulators struggling with their hands tied as they confront climate change challenges — especially intensifying drought.
- However, there is hope, as officials, communities and farmers strive to find innovative ways to save and more fairly share water. In Kansas and California, for example, new legislation has been passed to stave off dangerous groundwater declines threatening these states’ vital agricultural economies.
- Experts say that while an overhaul of the water allocation system in the West is needed, along with a coherent national water policy, extreme measures could be disruptive. But there are opportunities to realize incremental solutions now. Key among them is bridging a gap between federal water programs and farmers.
- A major concern is the trend toward single crop industrial agribusiness in semi-arid regions and the growing of water-intensive crops for export, such as corn and rice, which severely depletes groundwater. Ultimately, 20th century U.S. farm policies will need to yield to flexible 21st century policies that deal with unfolding climate change.
In Colombia, threatened women of the Wayuú community continue to fight rampant mining
- The Wayuú Women’s Force, founded in 2006, is an Indigenous organization that denounces the coal mining that has dammed and contaminated rivers, leaving much of La Guajira without water.
- Members of the organization have received death threats but continue to train women to stand up for their human rights.
- In addition to their work in La Guajira, the Wayuú women are developing ways of holding companies all over the world accountable for their negative environmental impact.
From flood to drought, Brazil’s Acre state swings between weather extremes
- Extreme weather conditions, from massive flooding to severe water shortages, have rocked cities and small communities alike in the heart of the Brazilian Amazon this year, a trend experts attribute to climate change and human actions.
- The Acre River, which crosses the state of same name in the western Brazilian Amazon, is experiencing its second-worst drought in recorded history, with water levels close to record lows.
- The water shortage comes just months after the same region experienced widespread flooding as the Acre River overflowed its banks and forced hundreds of thousands of people to flee their homes.
- Brazil as a whole is facing its worst dry spell in nearly a century, which is affecting water supplies for people, agriculture and electricity generation, and is part of a global pattern of increased water stress.
Children born in 2020 will see spike in climate disasters, study says
- The study used climate modeling to determine specialized impacts by region, finding that at the current level of carbon reduction pledges, people born in 2020 will experience many more extreme climate events in comparison to those born in 1960.
- On the world’s current course, those children will experience twice as many wildfires overall, three times as many crop failures, and seven times as many heat waves.
- At a geographical scale, children born in low-income countries that are least responsible for the climate crisis will confront significantly higher spikes in extreme events than in wealthier countries.
- If the world takes a more aggressive approach to limiting warming to 1.5°C (2.7°F) by 2100, the number of climate disasters experienced by younger generations would drop substantially, with the model predicting 45% fewer heat waves, 39% fewer droughts, and 28% fewer crop failures.
Dam builder denies responsibility as logjam chokes river in Malaysian Borneo
- Tons of wood debris has clogged up the Baleh and Rajang rivers in Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo.
- The logjam originated in the headwaters of the Baleh, where a hydroelectric dam is currently under construction and logging activity is being carried out nearby.
- The logjam originated in the headwaters of the Baleh, where a hydroelectric dam is currently under construction and logging activity is being carried out nearby.
- But the state-owned utility building dam denies responsibility, pointing to logging upstream.
As populations grow, how will thirsty cities survive their drier futures?
- The world’s rapidly expanding cities are on a collision course with climate change, presenting unprecedented challenges to municipal and national governments as they work to continue providing residents with access to safe and sufficient water.
- Increasingly, calls are made to rethink the way we develop urban watersheds and the way we live in them — with water sourcing, transport, use and reuse planning key to the process. One approach, water-sensitive urban design (WSUD) entails a complete reimagining of the role and use of water in urban areas.
- WSUD embraces the water cycle, and considers the entire watershed where cities are located. It uses green infrastructure such as permeable pavements, green roofs and rain gardens, to greatly reduce stormwater runoff. Conscious design allows water to be recycled and reused repeatedly for various purposes. Waste is greatly reduced.
- Some cities are already changing their development pathways to be more resilient to inevitable future climate extremes, with Singapore and Cape Town leading the way. Future water stress can be overcome, but work needs to start now before extreme weather events, including mega droughts and floods, hit.
Mexico devises revolutionary method to reverse semiarid land degradation
- Land degradation is impacting farmlands worldwide, affecting almost 40% of the world’s population. Reversing that process and restoring these croplands and pastures to full productivity is a huge challenge facing humanity — especially as climate change-induced drought takes greater hold on arid and semiarid lands.
- In Mexico, a university-educated, small-scale peasant farmer came up with an innovative solution that not only restores degraded land to productivity, but also greatly enhances soil carbon storage, provides a valuable new crop, and even offers a hopeful diet for diabetics.
- The process utilizes two plants commonly found on Mexico’s semiarid lands that grow well under drought conditions: agave and mesquite. The two are intercropped and then the agave is fermented and mixed with the mesquite to produce an excellent, inexpensive, and very marketable fodder for grazing animals.
- The new technique is achieving success in Mexico and could be applied to global degraded lands. Experts with World Agroforestry warn, though, that agave and mesquite are highly invasive outside their region, but suggest that similar botanical pairings of native species are potentially possible elsewhere.
Coastal Indonesian village adapts to life amid rising tidal floodwaters
- Cars once drove along the road in front of residents’ homes in coastal Timbulsloko village on the northern coast of Indonesia’s Java Island. Now, only canoes can pass; when the tide recedes, the water is knee-deep.
- Timbulsloko experiences severe tidal flooding caused by land subsidence, abrasion, nearby major construction, and climate change.
- Residents are starting to respond: A network of interlocking boardwalks now connects the submerged hamlets to dry land, and the village has designated a protected coastal area and prohibited the clearing of mangroves.
- The goal is to prevent further coastal damage and ensure the safety of residents’ settlements. The community is also beginning to discuss sustainable aquaculture.
A world of hurt: 2021 climate disasters raise alarm over food security
- Human-driven climate change is fueling weather extremes — from record drought to massive floods — that are hammering key agricultural regions around the world.
- From the grain heartland of Argentina to the tomato belt of California to the pork hub of China, extreme weather events have driven down output and driven up global commodity prices.
- Shortages of water and food have, in turn, prompted political and social strife in 2021, including food protests in Iran and hunger in Madagascar, and threaten to bring escalating misery, civil unrest and war in coming years.
- Experts warn the problem will only intensify, even in regions currently unaffected by, or thriving from the high prices caused by scarcity. Global transformational change is urgently needed in agricultural production and consumption patterns, say experts.
Cerrado desertification: Savanna could collapse within 30 years, says study
- Deforestation is amplifying climate change effects in the Brazilian Cerrado savanna biome, making it much hotter and drier. Researchers observed monthly increases of 2.24°C (4.03°F) in average maximum temperatures between 1961 and 2019. If this trend persists, temperature could be 6°C (10.8°F) higher in 2050 than in 1961.
- Cerrado air moisture is decreasing partly due to the removal of trees, which bring water up from as much as 15 meters (nearly 50 feet) underground to carry on photosynthesis during the dry season. Replacement of native vegetation by crops also reduces the absorption of sunlight by wild plants and leads to an increase in temperature.
- Even dew, the only source of water for smaller plants and many insects during the dry season, is being reduced due to deforestation and deepening drought. The demise of pollinators that rely on dew may prompt a cascading effect adversely impacting the biome’s biodiversity, which could collapse in the next 30 years.
- The Cerrado is often called Brazil’s “water tank,” as it is the source of eight of 12 Brazilian river basins. Its looming biome collapse and deepening drought mean less water for rural and urban populations and for agriculture. Low flows in rivers will also affect hydropower, likely causing energy shortages.
Study puts 2050 deadline on tipping point for Mekong Delta salinity
- The increasing salinity in Mekong Delta is currently being driven by the building of dams upstream and sand mining downstream, but climate change will likely be the predominant factor by 2050, a new study shows.
- The Mekong Delta is a key farming region, and already more frequent and extensive saltwater intrusion is killing off large swaths of crops with greater frequency.
- The study’s authors say regional stakeholders need to address the anthropogenic drivers of saltwater intrusion in the delta now, before climate change makes it a global problem.
- The study also has implications for other delta systems across Asia, which face similar pressures, both anthropogenic and climate change-driven.
Amazon and Cerrado deforestation, warming spark record drought in urban Brazil
- Southern and central Brazil are in the midst of the worst drought in nearly 100 years, with agribusiness exports of coffee and sugar, and the production of hydroelectric power, at grave risk.
- According to researchers, the drought, now in its second year, likely has two main causes: climate change, which tends to make continental interiors both hotter and drier, and the deforestation of the Amazon rainforest and Cerrado savanna biomes.
- Deforestation has caused the loss of almost half of the Cerrado’s native vegetation, which helps hold vast amounts of water underground, maintaining aquifers that supply the nation’s rivers with water. In the Amazon, rainforest loss is preventing billions of tons of water vapor from reaching the atmosphere.
- President Jair Bolsonaro acknowledges neither climate change nor deforestation as sources of the drought, but attributes it instead to the country and himself being “unlucky.” The administration’s drought response so far is to reactivate fossil-fuel power plants, which pollute heavily and are costly to operate.
Amazon dams: No clean water, fish dying, then the pandemic came
- Villagers living near the Teles Pires and São Manoel dams in Brazil’s Mato Grosso state — including the Apiaká, Kayabí and Munduruku peoples — attest to poor water quality, lack of potable water, increased malaria and rashes since the dams were built on their river. They also say there has been little response from the dam companies.
- Indigenous peoples say the Brazilian hydroelectric projects have altered river ecology along with thousands of years of cultural practice, especially their fishing livelihood. Migratory fish and other game fish have been greatly diminished, so residents must now resort to fishing at night.
- Once the COVID-19 pandemic arrived in the region, lack of clean water for bathing became even more urgent, while disappearing fish in daily diets made it harder to get food or isolate in riverside villages. Only under judicial order did dam companies recently improve water supply infrastructure.
- Experts trace these adverse impacts back to the dams’ planning stages: with the construction companies skipping legally mandated steps, not consulting Indigenous peoples as required, and failing to calculate cumulative impacts of multiple dam projects. Villagers are now monitoring impacts — and some are studying the law.
After two collapses, a third Vale dam at ‘imminent risk of rupture’
- Vale, the Brazilian mining company responsible for two deadly dam collapses since 2015, has another dam that’s at “imminent risk of rupture,” a government audit warns.
- The Xingu dam at Vale’s Alegria mine in Mariana municipality, Minas Gerais state, has been retired since 1998, but excess water in the mining waste that it’s holding back threatens to liquefy the embankment and spark a potentially disastrous collapse.
- Liquefaction also caused the collapse of a Vale tailings dam in 2019 in Brumadinho municipality, also in Minas Gerais, that killed nearly 300 people; the 2015 collapse of another Vale dam, in Mariana in 2015, caused extensive pollution and is considered Brazil’s worst environmental disaster to date.
- Vale has denied the risk of a collapse at the Xingu dam and says it continues to monitor the structure ahead of its decommissioning; regulators, however, say the company still hasn’t carried out requested measures to improve the structure’s safety, and have ordered an evacuation of the immediate vicinity.
As the world’s biggest users of water, business must act to save it (commentary)
- Water is a problem that has historically been overlooked, but the conversation around water is growing, and companies no longer have the excuse to turn a blind eye.
- The World Bank has found that failure to tackle the current water crisis by implementing better water management practices could cause 6% regional GDP losses by 2050.
- Investors who want to consider water could make decisions on companies based on how those companies address the value of water throughout their operations by, for example, reporting on and managing their water-related risks.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors, not necessarily Mongabay.
Humanity’s challenge of the century: Conserving Earth’s freshwater systems
- Many dryland cities like Los Angeles, Cairo and Tehran have already outstripped natural water recharge, but are expected to continue growing, resulting in a deepening arid urban water crisis.
- According to NASA’s GRACE mission, 19 key freshwater basins, including several in the U.S., are being unsustainably depleted, with some near collapse; much of the water is used indiscriminately by industrial agribusiness.
- Many desert cities, including Tripoli, Phoenix and Los Angeles, are sustained by water brought from other basins by hydro megaprojects that are aging and susceptible to collapse, while the desalination plants that water Persian Gulf cities come at a high economic cost with serious salt pollution.
- Experts say that thinking about the problem as one of supply disguises the real issue, given that what’s really missing to heading off a global freshwater crisis is the organization, capital, governance and political will to address the problems that come with regulating use of a renewable, but finite, resource.
Water crisis in Indonesia’s East Nusa Tenggara linked to mining, observers say
- Many parts of Indonesia’s East Nusa Tenggara province have experienced a shortage of clean water shortage since last year.
- Environmental activists attribute the problem to environmental degradation in forested water catchment areas, including by mining companies.
- Women and children in several areas have to walk up to 10 kilometers (6 miles) to get water from privately run tanker trucks.
- Even in the provincial capital, Kupang, 36% of households reportedly lack access to clean water.
Ecuadoran water fund transforms consumers into conservationists
- The Regional Water Fund of Southern Ecuador (FORAGUA) operates in 14 municipalities, serving 500,000 residents, and has restored 1,500 hectares (3,700 acres) of land and put an additional 337,000 hectares (833,000 acres) under conservation.
- By 2030, the fund aims to work in 39 municipalities, serving 1 million people and conserving 600,000 hectares (1.48 million acres) of land.
- A pilot project to incentivize landowners to rewild their properties and take up alternative livelihoods shows that where landowners could earn 50 times more per hectare cultivating guanabana, a local fruit, than raising cattle.
- Municipal residents pay on average $1 per month to FORAGUA for their water consumption, with 90% of funds raised going to conservation projects.
Scientists warn of looming water crisis with millions of wells at risk
- A recent study in Science has found that up to a fifth of wells worldwide are at risk of running dry.
- The researchers analyzed data about 39 million wells and estimated that between 6 and 20% of the wells were at risk of drying if the water table dipped a few meters.
- Digging deeper is not always feasible because water quality may be poorer and deeper wells are more expensive to build.
- As groundwater reserves diminish, wealthier sections of societies would be better positioned to access them, leading to deepening inequalities, a related commentary in the journal said.
Podcast: Though humanity exceeds key ‘planetary boundaries’ there are many solutions
- On this episode of the Mongabay Newscast, we speak with two recent contributors to our “Covering the Commons” special reporting project who wrote pieces that deal with the concept of Planetary Boundaries and how we can build a more sustainable future.
- Claire Asher tells us about her recent article detailing the nine Planetary Boundaries, the four environmental limits we’ve already exceeded, and the chances 2021 offers us to make transformative change.
- Andrew Willner discusses his recent article on how a “New Age of Sail” might soon transform the international shipping industry, the sixth-largest source of carbon emissions in the world.
The nine boundaries humanity must respect to keep the planet habitable
- All life on Earth, and human civilization, are sustained by vital biogeochemical systems, which are in delicate balance. However, our species — due largely to rapid population growth and explosive consumption — is destabilizing these Earth processes, endangering the stability of the “safe operating space for humanity.”
- Scientists note nine planetary boundaries beyond which we can’t push Earth Systems without putting our societies at risk: climate change, biodiversity loss, ocean acidification, ozone depletion, atmospheric aerosol pollution, freshwater use, biogeochemical flows of nitrogen and phosphorus, land-system change, and release of novel chemicals.
- Humanity is already existing outside the safe operating space for at least four of the nine boundaries: climate change, biodiversity, land-system change, and biogeochemical flows (nitrogen and phosphorus imbalance). The best way to prevent overshoot, researchers say, is to revamp our energy and food systems.
- In 2021, three meetings offer chances to avoid planetary boundary overshoot: the Convention on Biological Diversity meeting in Kunming, China; the U.N. Climate Summit (COP26) in Glasgow, U.K.; and the U.N. Food Systems Summit in Rome. Agreements with measurable, implementable, verifiable, timely and binding targets are vital, say advocates.
Dusty winds exacerbate looming famine in Madagascar’s deep south
- At least 1.27 million people need humanitarian assistance in Madagascar’s drought-hit deep south, according to a Jan. 18 request by the U.N. and the Malagasy government for $75.9 million in international aid to cope with the crisis.
- The area is also experiencing dust and sand storms, a natural phenomenon known as a tiomena that is exacerbating the crisis by smothering crops, forests, buildings and roads.
- Tiomenas may be increasingly common as southern Madagascar undergoes a long-term drying trend.
- Experts say upgrading the area’s water supply system is an urgent priority and recommend massive tree planting to provide wind breaks, protect soils from erosion and create more humidity.
At-risk Cerrado mammals need fully-protected parks to survive: Researchers
- A newly published camera trap study tracked 21 species of large mammal in Brazil’s Cerrado savanna biome from 2012-2017.
- The cameras were deployed in both fully protected state and federal parks and less protected mixed-use areas known as APAs where humans live, farm and ranch.
- The probability of finding large, threatened species in true reserves was 5 to 10 times higher than in the APAs for pumas, tapirs, giant anteaters, maned wolves, white-lipped and collared peccaries, and other Neotropical mammals.
- With half the Cerrado biome’s two million square kilometers of native vegetation already converted to cattle ranches, soy plantations and other croplands, conserving remaining habitat is urgent if large mammals are to survive there. The new study will help land managers better preserve biodiversity.
Communities on Brazil’s ‘River of Unity’ tested by dams, climate change
- The Pixaim Quilombo is one of many traditional communities made up mostly of Afro-Brazilian descendants of runaway slaves. It sits at the mouth of the São Francisco River, one of Brazil’s most important waterways.
- Once a thriving community, it has been struggling for decades due to the impacts of upriver dams which reduce the river’s flow and alter aquatic migrations. As a result, one of the community’s two chief livelihoods has been sharply curtailed — the river’s fishery is in steep decline.
- Now, climate change threatens to make those struggles even greater, further changing fish populations, reducing river flow even more, and dangerously elevating the salinity of the stream as seawater intrudes. Rice, which once provided Paixim’s second major livelihood, can no longer be grown in the delta’s saltier marshes.
- Pixaim is seeing a major outmigration as subsistence livelihoods becomes more difficult. Residents there count among 18 million people residing in the São Francisco River watershed, impacted by a steadily dwindling water resource.
China held water back from drought-stricken Mekong countries, report says
- Eyes on Earth studied data from a 28-year period to determine the extent that dams in China on the Upper Mekong River impact natural water flow.
- While these dams have disrupted the river’s natural systems for years, 2019 saw a particularly damaging situation, as downstream countries faced a severe drought while the Upper Mekong received above-average rainfall.
- China’s water management practices and lack of data-sharing with neighboring countries threaten the livelihoods of roughly 60 million people.
A Philippine tribe that defeated a dam prepares to fight its reincarnation
- The Dumagat-Remontado indigenous group has ancestral domain claims in an area where the Philippine government plans to build a dam to supply water to Metro Manila and nearby urban areas.
- The Kaliwa Dam is part of the New Centennial Water Source (NCWS), a project for which President Rodrigo Duterte has secured with a $235.9 million loan deal from China.
- The indigenous community defeated a previous iteration of this project, when a much larger dam was proposed in 2009, but the project has since been revised to call for nine smaller dams — an approach that observers say will undermine the resistance to the project.
- Five out of six community clusters voted to reject the Kaliwa Dam project, but the environment department still issued an environmental compliance certificate to the contractors; Duterte has also warned of the use of “extraordinary powers” to push the project through, raising the prospect of another show of mass resistance.
Controversial dam gets green light to flood a Philippine protected area
- The environment department has issued an environmental compliance certificate that allows the contested Kaliwa Dam project in the Sierra Madre mountain range to go ahead, part of a wider push to secure water supplies for Manila and surrounding areas.
- The certificate is one of the last sets of documents required by the developers for the project being funded by a $238.3 million loan from the Export-Import Bank of China.
- Yet its issuance comes despite a government-conducted environmental impact assessment showing that the dam’s reservoir alone will endanger endemic wildlife and plants, drive massive species migration, and pose risks to lowland agricultural and fishing communities with a history of flash flooding.
- The site of the planned dam falls within the Kaliwa watershed forest reserve, which has been designated a natural wildlife park sanctuary and game refuge, and an IUCN Category V Protected Landscape/Seascape.
Reforesting a village in Indonesia, one batch of gourmet beans at a time
- Deforestation in the village of Cibulao on the outskirts of the Indonesian capital, Jakarta, left it prone to droughts in the dry season and landslides in the rainy season.
- That changed in the early 2000s when a local tea plantation worker named Kiryono began replanting the slopes with seeds foraged from the nearby forest.
- Among those seeds were coffee seeds taken from wild coffee trees, and with training and the help of his family, Kiryono today produces some of the most prized coffee in Indonesia.
- The village is also greener now, thanks to Kiryono’s replanting efforts, and the local farmers’ cooperative hopes to expand on that work by applying for the right to manage a larger area of land.
Climate adaptation begins with how we manage water (commentary)
- Some 70 percent of the world’s freshwater is used for agriculture, but cities and other sectors have growing demands on the same water resources. To adapt to climate change without undermining food security and farmers’ livelihoods, we will have to fundamentally rethink agricultural water usage, our food systems, and our diets.
- A major new report from the Global Commission on Adaptation (GCA) makes this case loud and clear. The report urges us to face the fact that climate change will require ‘massive’ adaptation. It urges us to meet this challenge with urgency and resolve.
- The GCA report paints a sobering picture of our water and food security futures. We can and must adapt more quickly and effectively. Adaptive water management is an important place to start.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
For Indonesia’s Kendari Bay, silting is a death sentence
- Researchers say the Kendari Bay, on the island of Sulawesi, is rapidly disappearing.
- The main culprit is land clearing for development projects around the bay and the rivers the feed it. The land clearing releases sediment into the water that eventually settles on the bottom of the bay.
- The bay may be decades from filling up completely, but studies suggest hope of saving its plant and animal life may already be lost.
As climate chaos escalates in Indian Country, feds abandon tribes
- South Dakota’s Pine Ridge Oglalla Sioux Indian Reservation is one of the most impoverished places in the U.S. But in 2018 and 2019, the reservation was struck by two horrific storms — with economic harm to their homes and livelihoods that the community’s low income residents have found it extraordinarily difficult to absorb.
- High Plains weather has been getting more variable, erratic and destructive: in 2011 came severe drought and wildfires, followed in 2012 by severe flooding. Sometimes these oscillations take the form of high-powered storms, with a rash of tornadoes in 2016, a destructive ice storm in 2018, and a bomb cyclone in 2019.
- According to the National Climate Assessment issued at the end of 2018, “Climate change is expected to exacerbate these [extreme weather] challenges.” But starting with Bill Clinton and continuing under Donald Trump, the federal government has severely slashed federal aid to Indian reservations and their low income residents.
- As a result, Pine Ridge is increasingly forced to rely on its own resources and on creative solutions, including crowdfunded local and national volunteer teams who have risen to the challenge and helped the communities repair storm damage. But as extreme weather intensifies on the High Plains, surviving there will get tougher.
Deforestation diminishes access to clean water, study finds
- A recent study compared deforestation data and information on household access to clean water in Malawi.
- The scientists found that the country lost 14 percent of its forest between 2000 and 2010, which had the same effect on access to safe drinking water as a 9 percent decrease in rainfall.
- With higher rainfall variability expected in today’s changing climate, the authors suggest that a larger area of forest in countries like Malawi could be a buffer against the impacts of climate change.
Cloud seeding bears no rain in Sri Lanka
- An experimental attempt by Sri Lanka to induce artificial rain amid a prolonged drought fell short of expectations when the anticipated rain materialized a day late.
- Despite the setback, the government appears committed to exploring the technology further as it seeks to address power cuts caused by low water levels in its hydropower reservoirs.
- Scientists have called for comprehensive studies on cloud microphysics, meteorology and observational studies to ensure that such an expensive endeavor is backed by adequate scientific data.
- With no cost-benefit analysis, climatologists fear that artificial rainmaking may cause adverse impacts over the long term.
Environmental issues among top priorities of urban Indian voters: Report
- With India just a few weeks away from the general elections, a new survey has found that clean drinking water and agriculture-related governance issues feature prominently in the Indian voters’ list of priorities.
- High levels of water and air pollution, which have been plaguing Indian cities over the past few years, were not a top priority nationally but were of importance to the urban voters.
- Some other environment-related concerns that found a place in the overall list of the voters’ priorities include sand and stone quarrying, traffic congestion, river and lake pollution, and noise pollution.
Days of darkness: Venezuelan national emergency is also environmental crisis
- Venezuela, once a shining star of economic prosperity in Latin America, continues its plummet into chaos — a cauldron of human suffering in which the environment is also a victim.
- This month’s nationwide blackout, according to eyewitness accounts, saw courageous Venezuelans coming together to help each other as their government failed to respond effectively. It was the nation’s most recent crisis, though likely not its last.
- News reports from inside the country remain sketchy. But with the lights back on, his Internet connection restored, Venezuelan contributor Jeanfreddy Gutiérrez Torres offers Mongabay readers an exclusive firsthand account of Venezuela’s days of darkness.
Colombia: Dying of thirst, Wayuu blame mine, dam, drought for water woes
- The struggle for access to safe and sufficient water for drinking and irrigation defines life for the indigenous Wayuu of La Guajira, Colombia’s northernmost department.
- Activists have described the Wayuu as being in the throes of a humanitarian crisis, with Wayuu children suffering high rates of malnutrition and death as a result of water and food scarcity.
- The Wayuu blame their thirst mainly on the Cerrejón coal mine, which they say drains water from the local river and groundwater and pollutes what’s left. A dam built by the government to provide water in times of drought has only made matters worse, they say.
- However, Cerrejón disputes the notion that it is seriously affecting the tribe, while the government defends decisions that have compromised the Wayuu’s water access.
As India’s Ganges runs out of water, a potential food shortage looms
- In the last three decades, the groundwater input to the Ganges River in India has declined by 50 percent during the summer, a new study has found, leading to the river losing water during those dry months.
- The dwindling of the river’s water flow could severely affect the availability of water for surface water irrigation, with potential declines in food production in the future.
- The low river flows could also prevent effective dilution of pollutants in the Ganges, which is already one of the most contaminated transboundary rivers in the world, the researchers say.
More companies sign on to Cerrado Manifesto
- APG and Robeco are two of the most recent companies to sign on to the Cerrado Manifesto, which calls for an end to deforestation in Brazil’s Cerrado biome.
- The Manifesto is a two-page document that puts the onus on soy and meat producers and traders, as well as other companies in the commodities supply chain, to prevent runaway destruction of the Cerrado savannah.
- According to experts, about half of the biome’s native forests and vegetation have already been cleared for agricultural expansion.
- While more than 70 companies have signed the Cerrado Manifesto, including large fast food companies and supermarkets like McDonalds and Walmart, experts say the initiative won’t likely be successful without participation by large commodities firms, such as Cargill, ADM and Bunge.
Pay more attention to forests to avert global water crisis, researchers urge
- According to a new report, the growing human population and climate change are exacerbating a looming global water crisis that has already hit home in places like Australia’s Murray Darling basin — but the crisis could potentially be averted if humans paid more attention to the links between forests and water.
- Despite the links between the global climate, forests, people, and water, international bodies like the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) have tended to view carbon sequestration as the chief role of forests and trees.
- Report co-editor Meine van Noordwijk, chief scientist at the World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF) in Indonesia and a professor of agroforestry at Wageningen University in the Netherlands, warns that we ignore the importance of water in the climate debate at our own peril.
A wish list for an environmentally friendly NAFTA
- The renegotiation of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) has been progressing along a very rocky path, with the U.S., Canada and Mexico all threatening at one point or another to exit the pact. But slow progress is being made toward a new agreement.
- However, experts warn that the resulting trade treaty is unlikely to benefit the environment and the general public, unless major changes are made. These proposed NAFTA alterations, as outlined in this story, could also provide a template for future enviro-friendly international trade agreements.
- Among the changes needed: remove NAFTA Chapter 11 or reform the ISDS, remove any reference to water as a common commodity, remove the energy proportionality rule, include the Paris Climate Agreement and Sustainable Development Goals, and protect supply management and sustainable agriculture.
- Also, axe regulatory cooperation and harmonization, fully fund the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) and give it some teeth, Acknowledge indigenous and native rights (not free trade incentives), and most importantly: make a place at the bargaining table for the people and the planet.
Analysis: U.S. call to drill off all coasts, economic and ecological folly?
- 90 billion barrels of recoverable oil, plus 327 trillion cubic feet of natural gas lie untapped offshore on the U.S. continental shelf. In January, the Trump administration ordered that the entire coast, in the Pacific, Atlantic, Gulf, and Arctic, be opened to drilling.
- Environmentalists and the coastal states fear oil spills that could devastate tourism. They also are concerned about the massive infrastructure (pipelines, terminals, refineries, pumping stations and more) that would be needed to support the industry.
- The executive branch has moved forward with efficiency to create a surge in U.S. oil and gas production: the Interior and Energy departments, and the Environmental Protection Agency have all worked to slash regulations and open additional lands and seas to oil and gas exploration, with the plan of achieving U.S. “energy dominance” around the globe.
- Most coastal states are resisting the federal oil and gas offshore drilling plan; Florida has already been exempted, while other states are likely to fight back with lawsuits. The irony is that a flood of new U.S. oil could glut the market and drive prices down, resulting in an economic disaster for the industry.
Gaza City residents’ water problems continue to compound
- Locked between increasingly-polluted seascape and the borders of one of the most tightly-controlled enclaves in the world, Gaza City residents say the water has become so polluted they can no longer go swimming.
- Situated at the borders of Egypt, Israel, and the Mediterranean Sea, Gaza’s 2 million residents fear that an ongoing electricity crisis has pushed their maritime ecosystem past the brink.
- 80 percent of Gaza’s Mediterranean Sea coastline is thought to be polluted and families who used to rely on it for livelihoods and leisure now fear its waters.
Mexico City dwellers shoulder future of their urban ‘Water Forest’
- The territory, which conservationists and area residents are working to preserve, includes a large swath of southern Mexico City.
- The term “urban forest” typically describes public parkland or a collection of shade trees, but Mexico City’s Water Forest is an actual forest.
- The Water Forest also hosts endangered volcano rabbits (Romerolagus diazi) and Sierra Madre Sparrows (Xenospiza baileyi) as well as pumas, bobcats, white-tailed deer, and at least 10 percent of the bird species known in Mexico.
So long, UNESCO! What does U.S. withdrawal mean for the environment?
- Since 2011, the U.S. has refused to pay its agreed to share to UNESCO as a Member Nation who has participated in and benefited from the organization’s scientific, environmental and sustainability programs. Now, President Trump has announced U.S. withdrawal from UNESCO, effective at the end of 2018.
- Experts say the pullout won’t in fact do any major damage to the organization, with most of the harm done to UNESCO when the U.S. went into arrears starting in 2011, with unpaid dues now totaling roughly $550 million. However, America’s failure to participate could hurt millions of Americans.
- UNESCO science initiatives are international and deal multilaterally with a variety of environmental issues ranging from basic earth science, climate change, freshwater, oceans, mining, and international interrelationships between indigenous, rural and urban communities.
- Among the most famous of UNESCO science programs are the Man and the Biosphere Programme and the World Network of Biosphere Reserves, now including 669 sites in 120 countries, including the United States.
As Northwest salmon economy teeters on brink, Trump gives it a push
- Northwest salmon fisheries are in trouble, impacted by warming oceans and overdeveloped, dammed and silted spawning rivers and streams.
- Pre-contact indigenous groups in the region once organized their societies around sustainable fishing tribal agreements that worked. More recently, under past presidential administrations, Canadian, US and tribal authorities came together to save the declining salmon fisheries.
- Especially successful have been federally funded local, state and tribal programs, administered by NOAA, that protect and restore Northwest spawning streams — an investment in habitat and healthy local economies.
- Trump’s 2018 budget would cut all those programs, though for now Congress has restored them. However, politicians and regulators are concerned that Trump’s abandonment of Northwest fisheries and local economies will persist through his administration.
Trump’s global resorts put profit first, environment last, critics say
- Donald Trump’s negative environmental record in Scotland and elsewhere has conservationists concerned in Bali, where Trump firms are developing a major resort and golf facility known as Trump International Hotel & Tower Bali.
- Another resort under development, the Trump International Hotel & Tower Lido, a 700-hectare facility including a six-star luxury resort, theme park, country club, spa, villas, condos and 18-hole golf course threatens the nearby Gunung Gede Pangrango National Park, one of Java’s last virgin tropical forests.
- Mongabay looked into Trump’s claims that he is an environmentalist, winning “many, many environmental awards.” We were able to locate just two — one a local New York award, and another granted by a golf business association. The Trump Organization did not respond to requests to list Mr. Trump’s awards.
- Trump’s environmental record as president, and as a businessman, is abysmal, say critics. His attempt to defund the U.S. Energy Star program, they say, is typical of a compulsion to protect his self interest: Energy Star has given poor ratings to nearly all Trump’s hotels, which experts note has possibly impacted his bottom line.
Trump budget threatens Zimbabwe climate change resilience programs
- President Trump has threatened to cut U.S. aid to developing nations by a third. This could impact Zimbabwe which receives $150 million annually to decrease food insecurity for 2.1 million people.
- Aid to Zimbabwe is important to rural farmers, victims of escalating drought due to climate change. USAID finances dams and irrigation projects, making agriculture sustainable.
- The 2018 budget isn’t due to be finalized by Congress until October 1, 2017, leaving Zimbabwe’s people in uncertainty as to the direly needed aid.
- What seems certain is that the climate resilience program will not be expanded to meet the needs of yet to be served Zimbabwean communities.
Pressure over water in Brazil puts pulp industry in the spotlight
- Brazil is the world’s largest producer of eucalyptus-derived pulp and the state of Espírito Santo is one of its biggest production centers.
- More than a third of the state, which was once rich in Atlantic Forest, is at risk of becoming desert.
- The region faces one of the worst droughts in its history, which is causing billions in losses.
The cousins from Indonesia who revived an ancient spring
- A major reforestation effort is underway in the eastern part of Indonesia’s Flores island.
- It began when residents Markus Hayon and Damianus Pelada set out to restore an area around an ancestral spring that had all but dried up after an earthquake in the 1980s.
- The cousins proceeded to plant thousands of trees — though not without some challenges along the way.
Mother Nature and a hydropower onslaught aren’t the Mekong Delta’s only problems
- Vietnam’s Mekong Delta, home to nearly 20 million people, is one of the most highly productive agricultural environments in the world, thanks in part to an elaborate network of canals, dikes, sluice gates and drainage ditches.
- On the strength of Delta agriculture, Vietnam has gone from a chronic importer of rice to a major exporter.
- But farmers in the region are critical of the government’s food security policies, which mandate that most of the Delta’s land be devoted to rice production. And many of them are taking measures to circumvent those rules, in ways that aren’t always friendly to the environment.
- That’s just one example of how water and land-use policy in the Delta is undermining efforts to protect the vulnerable region from climate change and upstream development.
Vietnam sweats bullets as China and Laos dam the Mekong
- The Mekong River is the lifeblood of mainland Southeast Asia. It flows through six countries and affects the lives of some 60 million people.
- China and Laos are damming the river in many places. And Thailand is planning a large-scale of diversion of water that could further affect its flow.
- It’s still an open question whether the dams in Laos can be financed. Will Beijing step in?
Rio Doce grassroots response arises out of Fundão mining disaster
- On November 5, 2015, an iron mining tailings dam, owned by the Samarco company, a joint venture of Vale and Austro-British BHP Billiton, collapsed in Brazil killing 19 people and sending a toxic sludge flood into the Rio Doce, polluting its length to the Atlantic Ocean.
- The disaster contaminated the drinking water of thousands of people living in river communities, wrecked the livelihoods of fishermen and small scale gold miners, ruined recreational activities for the region’s children, and disrupted lives across the region.
- Critics say the government and corporate responses have been slow and very uneven in their effectiveness, with aid coming for some who have been impacted, while the needs of others have largely been ignored.
- A strong grassroots movement has arisen, with many existing and newly arising groups taking a wide variety of actions, including the founding of a radio station and newspaper to report on the crisis, acts of civil disobedience, informational workshops and protests, and even a group looking at long-term sustainable solutions.
Two-thirds of the world’s population doesn’t have reliable access to fresh water
- Researchers say two-thirds of the global population — some four billion people, half of them in India or China — live under conditions of severe water scarcity at least one month out of the year.
- As many as half a billion people face severe water scarcity all year.
- The majority of water usage is for food, researchers say, so water scarcity primarily means decreasing or failing crop yields.
Raja Ampat fires destroy livelihoods; Sumatrans suffer from drought amid haze
- Indonesian Vice President Jusuf Kalla called on all Muslims to pray for rain on Wednesday and to ask God for “forgiveness, guidance and mercy.”
- An aide to Kalla said companies could announce force majeur if the government declared a national disaster.
- Malaysia continues to push Indonesia to adopt tube wells in its peatlands in Kalimantan and Riau.
Lima to restore pre-Incan aqueducts to alleviate its water crisis
 Andean community leaders show hydrologists and project developers from Lima damaged amunas. These pre-Incan canals collect excess river water in the wet season so it can recharge pools and groundwater supplies for use in the dry season. Credit: Gena Gammie. To tackle a looming water crisis, the city of Lima, Peru, is planning a series […]
Andean community leaders show hydrologists and project developers from Lima damaged amunas. These pre-Incan canals collect excess river water in the wet season so it can recharge pools and groundwater supplies for use in the dry season. Credit: Gena Gammie. To tackle a looming water crisis, the city of Lima, Peru, is planning a series […]
Kaiduan dam in Borneo meets fierce opposition
 Mt. Kinabalu, in the Crocker Range of Sabah, Malaysia, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Part of the Crocker Range would be flooded if the Kaiduan dam is built. Credit: Shankar S. Activists are calling on the government of Sabah, Malaysia, to reconsider the proposed Kaiduan dam, saying the Infrastructure Development Ministry (IDM) has not considered other […]
Mt. Kinabalu, in the Crocker Range of Sabah, Malaysia, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Part of the Crocker Range would be flooded if the Kaiduan dam is built. Credit: Shankar S. Activists are calling on the government of Sabah, Malaysia, to reconsider the proposed Kaiduan dam, saying the Infrastructure Development Ministry (IDM) has not considered other […]
U.S. Central Plains and Southwest will likely face apocalyptic drought
 Researchers find 80 percent chance of megadrought in American West due to climate change this century Dust storm in Texas during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s. New research finds that the American West is set to face a megadrought, worst than the Dust Bowl, in the next century due to climate change. Photo by: […]
Researchers find 80 percent chance of megadrought in American West due to climate change this century Dust storm in Texas during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s. New research finds that the American West is set to face a megadrought, worst than the Dust Bowl, in the next century due to climate change. Photo by: […]
The price of gold: winners and losers in Latin America’s mining industry
 On a Friday afternoon in June, the Plaza de Armas in Cajamarca is pulsing with life. It’s winter here, and although thick white clouds hover low in the distance, the sun in this northern Peruvian city is warm. Couples sit on benches facing one another. Kids run in the grass between flowerbeds. Men in suits […]
On a Friday afternoon in June, the Plaza de Armas in Cajamarca is pulsing with life. It’s winter here, and although thick white clouds hover low in the distance, the sun in this northern Peruvian city is warm. Couples sit on benches facing one another. Kids run in the grass between flowerbeds. Men in suits […]
Fracking sucks up all the water from Texas town
 Beverly McGuire saw the warning signs before the town well went dry: sand in the toilet bowl, the sputter of air in the tap, a pump working overtime to no effect. But it still did not prepare her for the night last month when she turned on the tap and discovered the tiny town where […]
Beverly McGuire saw the warning signs before the town well went dry: sand in the toilet bowl, the sputter of air in the tap, a pump working overtime to no effect. But it still did not prepare her for the night last month when she turned on the tap and discovered the tiny town where […]
Water crisis widening: 4.5 billion people live near ‘impaired water sources’
 The majority of the 9 billion people on Earth will live with severe pressure on fresh water within the space of two generations as climate change, pollution and over-use of resources take their toll, 500 scientists have warned. The world’s water systems would soon reach a tipping point that “could trigger irreversible change with potentially […]
The majority of the 9 billion people on Earth will live with severe pressure on fresh water within the space of two generations as climate change, pollution and over-use of resources take their toll, 500 scientists have warned. The world’s water systems would soon reach a tipping point that “could trigger irreversible change with potentially […]
What if companies actually had to compensate society for environmental destruction?
 The environment is a public good. We all share and depend on clean water, a stable atmosphere, and abundant biodiversity for survival, not to mention health and societal well-being. But under our current global economy, industries can often destroy and pollute the environment—degrading public health and communities—without paying adequate compensation to the public good. Economists […]
The environment is a public good. We all share and depend on clean water, a stable atmosphere, and abundant biodiversity for survival, not to mention health and societal well-being. But under our current global economy, industries can often destroy and pollute the environment—degrading public health and communities—without paying adequate compensation to the public good. Economists […]
Up for grabs: how foreign investments are redistributing land and water across the globe
 In 2007, the increased human population, increased prices in fuel and transportation costs, and an increased demand for a diversity of food products prompted a Global Food Crisis. Agricultural producers and government leaders world-wide struggled to procure stable food sources for their countries. But the crisis had impacts beyond 2007: it was also the impetus […]
In 2007, the increased human population, increased prices in fuel and transportation costs, and an increased demand for a diversity of food products prompted a Global Food Crisis. Agricultural producers and government leaders world-wide struggled to procure stable food sources for their countries. But the crisis had impacts beyond 2007: it was also the impetus […]
Norwegian Pinot Noir?: global warming to drastically shift wine regions
 In less than 40 years, drinking wine could have a major toll on the environment and wildlife, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study finds that climate change will likely force many vineyards to move either north or to higher altitudes, leading to habitat loss, […]
In less than 40 years, drinking wine could have a major toll on the environment and wildlife, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study finds that climate change will likely force many vineyards to move either north or to higher altitudes, leading to habitat loss, […]
Over $8 billion invested in watersheds in 2011
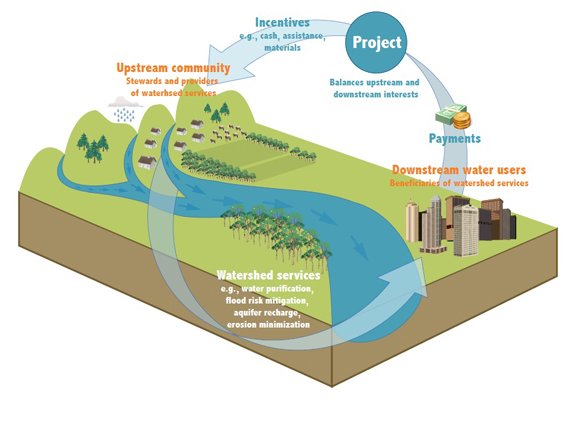 How a sample payment for ecosystem services project works. Click to enlarge. Unlike cars, hamburgers, and computers, clean drinking water is a requirement for human survival. In a bid to safeguard this essential resource, more and more nations are moving toward protecting ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and streams. In fact, according to a new […]
How a sample payment for ecosystem services project works. Click to enlarge. Unlike cars, hamburgers, and computers, clean drinking water is a requirement for human survival. In a bid to safeguard this essential resource, more and more nations are moving toward protecting ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and streams. In fact, according to a new […]
Forests in Kenya worth much more intact says government report
 Loita hills forest in Kenya. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Kenya’s forests provide greater services and wealth to the nation when they are left standing. A landmark report by The Kenyan Government and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) addresses the importance of forests to the well-being of the nation, putting Kenya among a pioneering […]
Loita hills forest in Kenya. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Kenya’s forests provide greater services and wealth to the nation when they are left standing. A landmark report by The Kenyan Government and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) addresses the importance of forests to the well-being of the nation, putting Kenya among a pioneering […]
Climate change melting glaciers in the Andes
 Pastoruri Glacier. Photo by: Edubucher/Wikimedia Commons. Glaciers are melting faster than ever in the tropical Andes, warns a new study published in The Cryosphere, which puts the blame for vanishing glaciers squarely on climate change. The study — the most comprehensive to date — found that since the 1970s glacier melt in the region has […]
Pastoruri Glacier. Photo by: Edubucher/Wikimedia Commons. Glaciers are melting faster than ever in the tropical Andes, warns a new study published in The Cryosphere, which puts the blame for vanishing glaciers squarely on climate change. The study — the most comprehensive to date — found that since the 1970s glacier melt in the region has […]
Improving food and water efficiency a must for the next generation
 Mwamanongu Village water source in Tanzania.. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. This summer, while climate change silence reigned in the U.S. presidential race, the Stockholm International Water Institute’s conference for World Water Week focused on the global initiatives required in order to live with its effects. The report, titled “Feeding a Thirsty World,” garnered the most […]
Mwamanongu Village water source in Tanzania.. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. This summer, while climate change silence reigned in the U.S. presidential race, the Stockholm International Water Institute’s conference for World Water Week focused on the global initiatives required in order to live with its effects. The report, titled “Feeding a Thirsty World,” garnered the most […]
World Bank agrees to fund project related to controversial Gibe III dam
 The Turkana people fear their ecosystem will be gravely impacted by the Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Originally refusing to provide funding to Ethiopia’s controversial Gibe III hydroelectric dam, the World Bank has now announced plans to fund the power lines that will carry generated electricity away from […]
The Turkana people fear their ecosystem will be gravely impacted by the Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Originally refusing to provide funding to Ethiopia’s controversial Gibe III hydroelectric dam, the World Bank has now announced plans to fund the power lines that will carry generated electricity away from […]
Climate change increased the probability of Texas drought, African famine, and other extreme weather
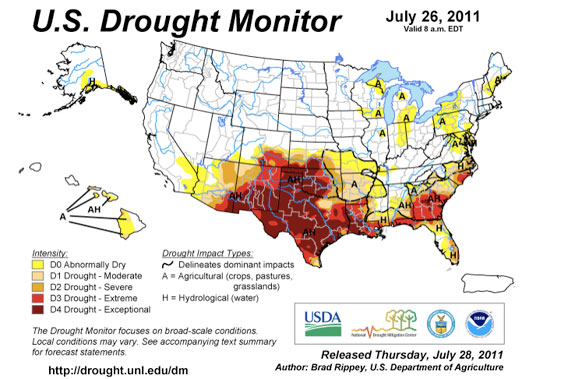 Map shows the level of drought and dryness across the US in July 2011. Map courtesy US Department of Agriculture. Click to enlarge. Climate change is here and its increasing the chances for crazy weather, according to scientists. A prestigious group of climatologists have released a landmark report that makes the dramatic point that climate […]
Map shows the level of drought and dryness across the US in July 2011. Map courtesy US Department of Agriculture. Click to enlarge. Climate change is here and its increasing the chances for crazy weather, according to scientists. A prestigious group of climatologists have released a landmark report that makes the dramatic point that climate […]
The vanishing Niger River imperils tourism and livelihoods in the desert
 Contrary to conception, the Sahara Desert’s most common feature is really the Hamada, or stone plateaus and gravel plains, which cover over three quarters of its surface, and harbors at great distance the barely visible silhouette of the once-majestic Niger River. Photo by: Linda Leila Diatta. Severely affected by recent turmoil across its northern frontiers, […]
Contrary to conception, the Sahara Desert’s most common feature is really the Hamada, or stone plateaus and gravel plains, which cover over three quarters of its surface, and harbors at great distance the barely visible silhouette of the once-majestic Niger River. Photo by: Linda Leila Diatta. Severely affected by recent turmoil across its northern frontiers, […]
Charting a new environmental course in China
 An interview with the Nature Conservancy’s China Program. TNC staff and volunteers repairing signage at Meili Snow Mountain National Park in northwest Yunnan. Community benefits and ecotourism are at the heart of TNC’s program to establish national parks in China. Photo by: Tang Ling. Founded in 1951, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) works in more than […]
An interview with the Nature Conservancy’s China Program. TNC staff and volunteers repairing signage at Meili Snow Mountain National Park in northwest Yunnan. Community benefits and ecotourism are at the heart of TNC’s program to establish national parks in China. Photo by: Tang Ling. Founded in 1951, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) works in more than […]
Turkey’s rich biodiversity at risk
 Turkey’s stunning landscapes and wildlife are under threat due to government ambivalence. Here, the sun sets outside Igdir, Turkey. Photo by: Cagan Sekercioglu. Turkey: the splendor of the Hagia Sophia, the ruins of Ephesus, and the bizarre caves of the Cappadocia. For foreign travelers, Turkey is a nation of cultural, religious, and historic wonders: a […]
Turkey’s stunning landscapes and wildlife are under threat due to government ambivalence. Here, the sun sets outside Igdir, Turkey. Photo by: Cagan Sekercioglu. Turkey: the splendor of the Hagia Sophia, the ruins of Ephesus, and the bizarre caves of the Cappadocia. For foreign travelers, Turkey is a nation of cultural, religious, and historic wonders: a […]
United Nations meets clean water goal
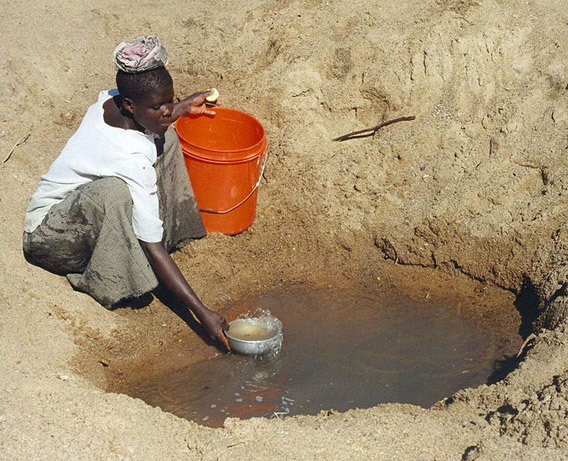 Access to clean water is most difficult in Africa. Here a woman in Tanzania gathers water from a hole in a riverbed. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. Over the past two decades (1990-2010) over two billion people have received access to improved drinking water, bringing the current number of people worldwide who have access to better […]
Access to clean water is most difficult in Africa. Here a woman in Tanzania gathers water from a hole in a riverbed. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. Over the past two decades (1990-2010) over two billion people have received access to improved drinking water, bringing the current number of people worldwide who have access to better […]
Top 10 Environmental Stories of 2011
 Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
The Atlas of Climate Change: Mapping the World’s Greatest Challenge – a book review
 The Atlas of Climate Change: Mapping the World’s Greatest Challenge presents in clear and concise visual form the impacts and effects, solutions and mitigation actions surrounding climate change – which is our greatest global challenge. Dr. Kristin Dow and Dr. Thomas E. Downing provide us with over 200 full-color maps and other illustrative details demonstrating […]
The Atlas of Climate Change: Mapping the World’s Greatest Challenge presents in clear and concise visual form the impacts and effects, solutions and mitigation actions surrounding climate change – which is our greatest global challenge. Dr. Kristin Dow and Dr. Thomas E. Downing provide us with over 200 full-color maps and other illustrative details demonstrating […]
11 challenges facing 7 billion super-consumers
 The Turkana tribe of northern Kenya are buffeted by constant drought and food insecurity, which recent research says may be worsening due to climate change. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Perhaps the most disconcerting thing about Halloween this year is not the ghouls and goblins taking to the streets, but a baby born somewhere in […]
The Turkana tribe of northern Kenya are buffeted by constant drought and food insecurity, which recent research says may be worsening due to climate change. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Perhaps the most disconcerting thing about Halloween this year is not the ghouls and goblins taking to the streets, but a baby born somewhere in […]
What does Nature give us? A special Earth Day article
- Yet we have so disconnected ourselves from the natural world that it is easy—and often convenient—to forget that nature remains as giving as ever, even as it vanishes bit-by-bit.
- The rise of technology and industry may have distanced us superficially from nature, but it has not changed our reliance on the natural world: most of what we use and consume on a daily basis remains the product of multitudes of interactions within nature, and many of those interactions are imperiled.
- Beyond such physical goods, the natural world provides less tangible, but just as important, gifts in terms of beauty, art, and spirituality.
‘Huge reduction’ of water from plants due to higher carbon levels
 As if ocean acidification and a warming world weren’t enough, researchers have outlined another way in which carbon emissions are impacting the planet. A new study shows that higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have taken a toll on how much water vapor plants release, potentially impacting the rainfall and groundwater sources. A study […]
As if ocean acidification and a warming world weren’t enough, researchers have outlined another way in which carbon emissions are impacting the planet. A new study shows that higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have taken a toll on how much water vapor plants release, potentially impacting the rainfall and groundwater sources. A study […]
New organization seeks to make biofuels sustainable, but is it possible?
Not too long ago policy-makers, scientists, and environmentalists saw biofuels as a significant tool to provide sustainable energy to the world. However, as it became clear that biofuels were not only connected to deforestation, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions (sometimes exceeding fossil fuels), but also competed with the global food supply and water sources, biofuels […]
Want water? save forests
 The UN-backed Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF) is urging nations to conserve their forests in a bid to mitigate rising water scarcity problems. “[Forests] reduce the effects of floods, prevent soil erosion, regulate the water table and assure a high-quality water supply for people, industry and agriculture,” said the Forestry Department Assistant Director General, Eduardo […]
The UN-backed Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF) is urging nations to conserve their forests in a bid to mitigate rising water scarcity problems. “[Forests] reduce the effects of floods, prevent soil erosion, regulate the water table and assure a high-quality water supply for people, industry and agriculture,” said the Forestry Department Assistant Director General, Eduardo […]
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
 Andean community leaders show hydrologists and project developers from Lima damaged amunas. These pre-Incan canals collect excess river water in the wet season so it can recharge pools and groundwater supplies for use in the dry season. Credit: Gena Gammie. To tackle a looming water crisis, the city of Lima, Peru, is planning a series […]
Andean community leaders show hydrologists and project developers from Lima damaged amunas. These pre-Incan canals collect excess river water in the wet season so it can recharge pools and groundwater supplies for use in the dry season. Credit: Gena Gammie. To tackle a looming water crisis, the city of Lima, Peru, is planning a series […] Mt. Kinabalu, in the Crocker Range of Sabah, Malaysia, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Part of the Crocker Range would be flooded if the Kaiduan dam is built. Credit: Shankar S. Activists are calling on the government of Sabah, Malaysia, to reconsider the proposed Kaiduan dam, saying the Infrastructure Development Ministry (IDM) has not considered other […]
Mt. Kinabalu, in the Crocker Range of Sabah, Malaysia, a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Part of the Crocker Range would be flooded if the Kaiduan dam is built. Credit: Shankar S. Activists are calling on the government of Sabah, Malaysia, to reconsider the proposed Kaiduan dam, saying the Infrastructure Development Ministry (IDM) has not considered other […] Researchers find 80 percent chance of megadrought in American West due to climate change this century Dust storm in Texas during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s. New research finds that the American West is set to face a megadrought, worst than the Dust Bowl, in the next century due to climate change. Photo by: […]
Researchers find 80 percent chance of megadrought in American West due to climate change this century Dust storm in Texas during the Dust Bowl of the 1930s. New research finds that the American West is set to face a megadrought, worst than the Dust Bowl, in the next century due to climate change. Photo by: […] On a Friday afternoon in June, the Plaza de Armas in Cajamarca is pulsing with life. It’s winter here, and although thick white clouds hover low in the distance, the sun in this northern Peruvian city is warm. Couples sit on benches facing one another. Kids run in the grass between flowerbeds. Men in suits […]
On a Friday afternoon in June, the Plaza de Armas in Cajamarca is pulsing with life. It’s winter here, and although thick white clouds hover low in the distance, the sun in this northern Peruvian city is warm. Couples sit on benches facing one another. Kids run in the grass between flowerbeds. Men in suits […] Beverly McGuire saw the warning signs before the town well went dry: sand in the toilet bowl, the sputter of air in the tap, a pump working overtime to no effect. But it still did not prepare her for the night last month when she turned on the tap and discovered the tiny town where […]
Beverly McGuire saw the warning signs before the town well went dry: sand in the toilet bowl, the sputter of air in the tap, a pump working overtime to no effect. But it still did not prepare her for the night last month when she turned on the tap and discovered the tiny town where […] The majority of the 9 billion people on Earth will live with severe pressure on fresh water within the space of two generations as climate change, pollution and over-use of resources take their toll, 500 scientists have warned. The world’s water systems would soon reach a tipping point that “could trigger irreversible change with potentially […]
The majority of the 9 billion people on Earth will live with severe pressure on fresh water within the space of two generations as climate change, pollution and over-use of resources take their toll, 500 scientists have warned. The world’s water systems would soon reach a tipping point that “could trigger irreversible change with potentially […] The environment is a public good. We all share and depend on clean water, a stable atmosphere, and abundant biodiversity for survival, not to mention health and societal well-being. But under our current global economy, industries can often destroy and pollute the environment—degrading public health and communities—without paying adequate compensation to the public good. Economists […]
The environment is a public good. We all share and depend on clean water, a stable atmosphere, and abundant biodiversity for survival, not to mention health and societal well-being. But under our current global economy, industries can often destroy and pollute the environment—degrading public health and communities—without paying adequate compensation to the public good. Economists […] In 2007, the increased human population, increased prices in fuel and transportation costs, and an increased demand for a diversity of food products prompted a Global Food Crisis. Agricultural producers and government leaders world-wide struggled to procure stable food sources for their countries. But the crisis had impacts beyond 2007: it was also the impetus […]
In 2007, the increased human population, increased prices in fuel and transportation costs, and an increased demand for a diversity of food products prompted a Global Food Crisis. Agricultural producers and government leaders world-wide struggled to procure stable food sources for their countries. But the crisis had impacts beyond 2007: it was also the impetus […] In less than 40 years, drinking wine could have a major toll on the environment and wildlife, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study finds that climate change will likely force many vineyards to move either north or to higher altitudes, leading to habitat loss, […]
In less than 40 years, drinking wine could have a major toll on the environment and wildlife, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study finds that climate change will likely force many vineyards to move either north or to higher altitudes, leading to habitat loss, […] How a sample payment for ecosystem services project works. Click to enlarge. Unlike cars, hamburgers, and computers, clean drinking water is a requirement for human survival. In a bid to safeguard this essential resource, more and more nations are moving toward protecting ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and streams. In fact, according to a new […]
How a sample payment for ecosystem services project works. Click to enlarge. Unlike cars, hamburgers, and computers, clean drinking water is a requirement for human survival. In a bid to safeguard this essential resource, more and more nations are moving toward protecting ecosystems, such as forests, wetlands, and streams. In fact, according to a new […] Loita hills forest in Kenya. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Kenya’s forests provide greater services and wealth to the nation when they are left standing. A landmark report by The Kenyan Government and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) addresses the importance of forests to the well-being of the nation, putting Kenya among a pioneering […]
Loita hills forest in Kenya. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Kenya’s forests provide greater services and wealth to the nation when they are left standing. A landmark report by The Kenyan Government and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) addresses the importance of forests to the well-being of the nation, putting Kenya among a pioneering […] Pastoruri Glacier. Photo by: Edubucher/Wikimedia Commons. Glaciers are melting faster than ever in the tropical Andes, warns a new study published in The Cryosphere, which puts the blame for vanishing glaciers squarely on climate change. The study — the most comprehensive to date — found that since the 1970s glacier melt in the region has […]
Pastoruri Glacier. Photo by: Edubucher/Wikimedia Commons. Glaciers are melting faster than ever in the tropical Andes, warns a new study published in The Cryosphere, which puts the blame for vanishing glaciers squarely on climate change. The study — the most comprehensive to date — found that since the 1970s glacier melt in the region has […] Mwamanongu Village water source in Tanzania.. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. This summer, while climate change silence reigned in the U.S. presidential race, the Stockholm International Water Institute’s conference for World Water Week focused on the global initiatives required in order to live with its effects. The report, titled “Feeding a Thirsty World,” garnered the most […]
Mwamanongu Village water source in Tanzania.. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. This summer, while climate change silence reigned in the U.S. presidential race, the Stockholm International Water Institute’s conference for World Water Week focused on the global initiatives required in order to live with its effects. The report, titled “Feeding a Thirsty World,” garnered the most […] The Turkana people fear their ecosystem will be gravely impacted by the Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Originally refusing to provide funding to Ethiopia’s controversial Gibe III hydroelectric dam, the World Bank has now announced plans to fund the power lines that will carry generated electricity away from […]
The Turkana people fear their ecosystem will be gravely impacted by the Gibe III dam on the Omo River. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Originally refusing to provide funding to Ethiopia’s controversial Gibe III hydroelectric dam, the World Bank has now announced plans to fund the power lines that will carry generated electricity away from […] Map shows the level of drought and dryness across the US in July 2011. Map courtesy US Department of Agriculture. Click to enlarge. Climate change is here and its increasing the chances for crazy weather, according to scientists. A prestigious group of climatologists have released a landmark report that makes the dramatic point that climate […]
Map shows the level of drought and dryness across the US in July 2011. Map courtesy US Department of Agriculture. Click to enlarge. Climate change is here and its increasing the chances for crazy weather, according to scientists. A prestigious group of climatologists have released a landmark report that makes the dramatic point that climate […] Contrary to conception, the Sahara Desert’s most common feature is really the Hamada, or stone plateaus and gravel plains, which cover over three quarters of its surface, and harbors at great distance the barely visible silhouette of the once-majestic Niger River. Photo by: Linda Leila Diatta. Severely affected by recent turmoil across its northern frontiers, […]
Contrary to conception, the Sahara Desert’s most common feature is really the Hamada, or stone plateaus and gravel plains, which cover over three quarters of its surface, and harbors at great distance the barely visible silhouette of the once-majestic Niger River. Photo by: Linda Leila Diatta. Severely affected by recent turmoil across its northern frontiers, […] An interview with the Nature Conservancy’s China Program. TNC staff and volunteers repairing signage at Meili Snow Mountain National Park in northwest Yunnan. Community benefits and ecotourism are at the heart of TNC’s program to establish national parks in China. Photo by: Tang Ling. Founded in 1951, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) works in more than […]
An interview with the Nature Conservancy’s China Program. TNC staff and volunteers repairing signage at Meili Snow Mountain National Park in northwest Yunnan. Community benefits and ecotourism are at the heart of TNC’s program to establish national parks in China. Photo by: Tang Ling. Founded in 1951, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) works in more than […] Turkey’s stunning landscapes and wildlife are under threat due to government ambivalence. Here, the sun sets outside Igdir, Turkey. Photo by: Cagan Sekercioglu. Turkey: the splendor of the Hagia Sophia, the ruins of Ephesus, and the bizarre caves of the Cappadocia. For foreign travelers, Turkey is a nation of cultural, religious, and historic wonders: a […]
Turkey’s stunning landscapes and wildlife are under threat due to government ambivalence. Here, the sun sets outside Igdir, Turkey. Photo by: Cagan Sekercioglu. Turkey: the splendor of the Hagia Sophia, the ruins of Ephesus, and the bizarre caves of the Cappadocia. For foreign travelers, Turkey is a nation of cultural, religious, and historic wonders: a […] Access to clean water is most difficult in Africa. Here a woman in Tanzania gathers water from a hole in a riverbed. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. Over the past two decades (1990-2010) over two billion people have received access to improved drinking water, bringing the current number of people worldwide who have access to better […]
Access to clean water is most difficult in Africa. Here a woman in Tanzania gathers water from a hole in a riverbed. Photo by: Bob Metcalf. Over the past two decades (1990-2010) over two billion people have received access to improved drinking water, bringing the current number of people worldwide who have access to better […] Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […] The Atlas of Climate Change: Mapping the World’s Greatest Challenge presents in clear and concise visual form the impacts and effects, solutions and mitigation actions surrounding climate change – which is our greatest global challenge. Dr. Kristin Dow and Dr. Thomas E. Downing provide us with over 200 full-color maps and other illustrative details demonstrating […]
The Atlas of Climate Change: Mapping the World’s Greatest Challenge presents in clear and concise visual form the impacts and effects, solutions and mitigation actions surrounding climate change – which is our greatest global challenge. Dr. Kristin Dow and Dr. Thomas E. Downing provide us with over 200 full-color maps and other illustrative details demonstrating […] The Turkana tribe of northern Kenya are buffeted by constant drought and food insecurity, which recent research says may be worsening due to climate change. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Perhaps the most disconcerting thing about Halloween this year is not the ghouls and goblins taking to the streets, but a baby born somewhere in […]
The Turkana tribe of northern Kenya are buffeted by constant drought and food insecurity, which recent research says may be worsening due to climate change. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Perhaps the most disconcerting thing about Halloween this year is not the ghouls and goblins taking to the streets, but a baby born somewhere in […] As if ocean acidification and a warming world weren’t enough, researchers have outlined another way in which carbon emissions are impacting the planet. A new study shows that higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have taken a toll on how much water vapor plants release, potentially impacting the rainfall and groundwater sources. A study […]
As if ocean acidification and a warming world weren’t enough, researchers have outlined another way in which carbon emissions are impacting the planet. A new study shows that higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have taken a toll on how much water vapor plants release, potentially impacting the rainfall and groundwater sources. A study […] The UN-backed Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF) is urging nations to conserve their forests in a bid to mitigate rising water scarcity problems. “[Forests] reduce the effects of floods, prevent soil erosion, regulate the water table and assure a high-quality water supply for people, industry and agriculture,” said the Forestry Department Assistant Director General, Eduardo […]
The UN-backed Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF) is urging nations to conserve their forests in a bid to mitigate rising water scarcity problems. “[Forests] reduce the effects of floods, prevent soil erosion, regulate the water table and assure a high-quality water supply for people, industry and agriculture,” said the Forestry Department Assistant Director General, Eduardo […]