Sites: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
topic: United Nations
Social media activity version | Lean version
At its fourth summit, 170 nations strive toward a global plastics treaty by 2025
- Last week, the International Negotiating Committee of the United Nations Environment Programme wrapped up the fourth of five scheduled negotiating sessions to develop an international treaty to control plastic pollution.
- Environmentalists say the atmosphere in Ottawa was better and more cooperative, with more achieved than at the third meeting, which took place in November and bogged down in procedural disagreements. However, there was little forward progress in Ottawa on a proposal to significantly reduce plastic production.
- For the first time ever, the pollution of the world’s oceans by large amounts of “Ghost gear” came under discussion at a treaty summit. This plastic waste includes a variety of fishing equipment, including plastic traps, nets, lines, ropes and artificial bait left floating in the world’s seas which can harm marine life and degrade into microplastics.
- Two committees have been authorized to work during intersessional meetings on draft language for discussion and possible adoption at the next, and potentially final treaty session, scheduled for late November in Busan, South Korea. The goal is to achieve a plastic pollution treaty by 2025.
Tribes turn to the U.N. as major wind project plans to cut through their lands in the U.S.
- Last week a United States federal judge rejected a request from Indigenous nations to stop SunZia, a $10 billion dollar wind transmission project that would cut through traditional tribal lands in southwestern Arizona.
- Indigenous leaders and advocates are turning to the U.N. to intervene and are calling for a moratorium on green energy projects for all U.N. entities “until the rights of Indigenous peoples are respected and recognized.”
- Indigenous leaders say they are not in opposition to renewable energy projects, but rather projects that don’t go through the due process and attend their free, prior and informed consent.
- According to the company, the wind transmission project is the largest clean energy infrastructure initiative in U.S. history, and will provide power to 3 million Americans, stretching from New Mexico to as far as California.
Bioplastics as toxic as regular plastics; both need regulation, say researchers
- Emerging research shows that plant-based plastics — just like petroleum-based plastics — contain many thousands of synthetic chemicals, with large numbers of them extremely toxic. However, the bioplastics industry strongly denies that bio-based plastics contain hazardous substances.
- Scientists are finding that while plant sources for bioplastics, such as corn or cane sugar, may not themselves be toxic or have adverse health impacts, the chemical processes to manufacture bioplastics and the many performance additives needed to give them their attributes (hardness, flexibility, color, etc.) can be quite toxic.
- Those doing the research no longer see bioplastics as a solution to the global plastic pollution crisis and would like to see them regulated. However, a very large number of petroleum-based plastics and the chemicals they contain also lack tough government oversight.
- This week, representatives from the world’s nations gather for a fourth session to hammer out an international treaty to curb the global plastic pollution crisis. The High Ambition Coalition (including 65 countries) hopes to achieve a binding global ban on the worst toxins in plastics. But the U.S., China and other nations are resisting.
Deep-sea mining’s future still murky as negotiations end on mixed note
- Between March 18 and 29, members of the International Seabed Authority (ISA), the U.N.-affiliated regulator of deep-sea mining activities in international waters, met for talks in Kingston, Jamaica.
- One focus of discussion was the ongoing revision of the regulations governing exploitation, which are still in draft form, but which member states are aiming to finalize by July 2025. Seabed mining activities could begin before then, as early as next year.
- ISA officials said “good progress” was made on the regulations. However, one NGO observer pointed out that there were “many areas where these negotiations have not progressed.”
- Delegates to the meetings also didn’t adopt either of two proposals to limit the ability of Greenpeace International to protest deep-sea mining activities at sea.
UN award for Nepal’s tiger range restoration spurs euphoria amid challenges
- Nepal’s Terai Arc Landscape (TAL) initiative, aimed at restoring ecosystems and creating space for tigers, receives global recognition from the U.N. as one of seven World Restoration Flagships.
- Launched in 2004, the TAL initiative restored 66,800 hectares (165,000 acres) of forest and significantly increased the Bengal tiger population in the region.
- The U.N. recognition opens doors for technical and financial support to restore an additional 350,000 hectares (865,000 acres) in both Nepal and India, but overcoming challenges like infrastructure expansion and human-wildlife conflict remains critical for long-term sustainability.
Little achieved for Indigenous groups at U.N. climate summit, delegates say
- At this year’s U.N. climate conference, COP28, Indigenous delegates numbered more than 300, but were left generally disappointed with the outcomes of the event.
- The final agreement had little inclusion of Indigenous rights and excluded an Indigenous representative from sitting on the board of the newly launched loss and damage fund.
- Indigenous groups say two big climate mitigation strategies, the clean energy transition and carbon markets, should include robust protection of Indigenous rights and consent.
- Despite setbacks, Indigenous leaders say they’re working on increasing their presence and influence at the next climate conferences, including upping their numbers to 3,000 delegates, creating a large international Indigenous Commission, and taking part in the summit’s decision-making.
Despite progress, small share of climate pledge went to Indigenous groups: report
- A report from funders of a $1.7 billion pledge to support Indigenous peoples and local communities’ land rights made at the 2021 U.N. climate conference found that 48% of the financing was distributed.
- The findings also show that only 2.1% of the funding went directly to Indigenous peoples and local communities, despite petitions to increase direct funding for their role in combating climate change and biodiversity loss.
- This is down from the 2.9% of direct funding that was disbursed in 2021.
- Both donors and representatives of Indigenous and community groups call for more direct funding to these organizations by reducing the obstacles they face, improving their capacity, and respecting traditional knowledge systems.
Russia, Saudi Arabia, Iran & petrochemical industry stall plastics treaty: Critics
- In March 2022, the world’s nations met to launch negotiations for a global plastic treaty with the goal of achieving final treaty language by 2025. That effort came as the planet drowns in a tidal wave of plastic waste, polluting oceans, air and land.
- That treaty goal and deadline may have been put at risk this month as the United Nations Environment Programme’s Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee on Plastic Pollution (INC) met in Nairobi, Kenya for its third session.
- There, three of the world’s biggest petrostates — Russia, Saudi Arabia, and Iran — began obstructing the process in an attempt to stall the negotiations, according to environmental NGOs that attended the meeting. More than 140 lobbyists at the November conference represented the fossil fuel and petrochemical industries.
- While a coalition of more than 60 high-ambition nations is seeking a binding international treaty that regulates cradle-to-grave plastics production, the resisters argued for treaty language that would focus on recycling rather than production, would not regulate plastic toxins and would allow nations to set individual goals for plastics regulation.
‘Very good progress’ but nothing firm as deep-sea mining rules are hashed out
- Between Oct. 30 and Nov. 8, representatives of the 36 member states of the the International Seabed Authority (ISA) council met in Kingston, Jamaica, to work on a set of regulations that would govern how deep-sea mining activities could proceed.
- Previously, at the ISA meetings that took place in July 2023, delegates agreed to try to finalize the regulations by July 2025.
- However, observers say they believe the regulations are far from being complete, despite continued work on the text.
- The Metals Company (TMC), a Canadian firm that could be the first in the world to begin deep-sea mining, has indicated that it intends to submit an application for exploitation following the July 2024 meeting; if this application is approved, mining could start in the near future without regulations to govern this activity.
World Heritage Site listing for Ethiopian park leads to eviction of farming community
- The new designation of a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Ethiopia will also come with the relocation of the more than 20,000 people living inside Bale Mountains National Park, say park officials.
- Home to a wealth of biodiversity, the park has experienced a dramatic increase in illegal human settlements, which park officials and conservationists say threatens its natural resources, forest cover, and habitat for rare and endemic species.
- Community members have mixed feelings about the planned relocation, with longtime residents mostly opposing it due to attachment to the land and fear over their livelihoods, and others open to receiving fair compensation in exchange.
- The relocation strategy is still in its initial stages and hasn’t officially been shared with communities, though UNESCO and Ethiopian officials underline the importance of consulting the locals and supporting their livelihoods.
Forest conservation ‘off-track’ to halt deforestation by 2030: New report
- The world lost 6.6 million hectares (16.3 million acres) of forest, an area larger than Sri Lanka, and deforestation rates increased by 4% in 2022, according to a report published Oct. 24 that tracks commitments to forest conservation.
- The Forest Declaration Assessment is an annual evaluation of deforestation rates against a 2018-2020 deforestation and forest degradation baseline compiled by civil society and research organizations.
- Much of the forest loss occurred in the tropics, and nearly two-thirds of it was in relatively undisturbed primary forests, while forest degradation, more than deforestation, remains a serious problem in temperate and boreal forests.
- Despite being far off the pace to achieve an end to deforestation by 2030, a goal that 145 countries pledged to pursue in 2021, more than 50 countries have cut their deforestation rates and are on track to end deforestation within their borders by the end of the century.
How nonprofit journalism revealed many problems with the UN’s climate neutrality claims
- Despite claiming to be 95% “climate neutral,” the United Nations — a long-standing and vocal proponent of climate action — isn’t, a new report has found.
- Mongabay teamed up with reporters at The New Humanitarian in a yearlong investigation spanning multiple countries to investigate the U.N.’s claims.
- The investigation found that many projects that issue carbon credits to the U.N. were linked to environmental damage or displacement, and 2.7 million out of 6.6 million credits were linked to wind or hydropower — which experts say don’t represent true emissions reductions.
- Investigative reporter Jacob Goldberg from The New Humanitarian joins the podcast to explain how the team arrived at these surprising findings.
Seventy-plus nations sign historic high seas treaty, paving way for ratification
- As of Sept. 22, 76 nations and the European Union had signed the high seas treaty while gathered at the 78th U.N. General Assembly in New York.
- After signing the treaty, each nation must ratify it. Then, once 60 nations have ratified the treaty, it will come into force after 120 days.
- The high seas encompass two-thirds of the world’s oceans, but only 1% currently has protected status.
U.N. ‘stocktake’ calls for fossil fuel phaseout to minimize temperature rise
- The U.N. climate change agency published a new report Sept. 8 confirming that while there has been progress on climate change mitigation since the landmark Paris Agreement in 2015, more needs to be done to limit the global rise in temperatures at 1.5°C (2.7°F) above pre-industrial levels.
- The report is an element of the global stocktake, a Paris Agreement-prescribed inventory of progress toward climate-related goals.
- The authors of the report called for phasing out fossil fuels and ramping up renewable energy.
- The global stocktake process will conclude at the U.N. climate conference (COP28) beginning Nov. 30 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
Pacific alliance adopts moratorium on deep-sea mining, halting resurgent PNG project
- The Melanesian Spearhead Group put in place a moratorium on deep-sea mining within its member countries’ territorial water in a declaration signed Aug. 24.
- Leaders from Fiji, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and an alliance of pro-independence political parties known as FLNKS from the French territory of New Caledonia said more research is needed to establish whether mining the seabed below 200 meters (660 feet) is possible without damaging ecosystems and fisheries.
- The moratorium ostensibly thwarts the return of Nautilus Minerals, a Canadian company, to Papua New Guinea and its Solwara 1 project in the Bismarck Sea, where it had hoped to mine gold and copper from sulfide deposits on the seafloor.
- Proponents of deep-sea mining say that minerals found deep beneath the ocean are necessary for the production of batteries used in electric vehicles and thus are critical in the global transition away from fossil fuels.
Big promises to Indigenous groups from new global nature fund — but will it deliver?
- On August 24, 2023, the Global Environment Facility (GEF) ratified and established the new Global Biodiversity Framework Fund to help developing countries meet their targets set up as part of the Global Biodiversity Framework.
- The new fund promises to invest 20% of its resources to directly support initiatives led by Indigenous peoples and local communities to protect and conserve biodiversity.
- While Indigenous communities welcome the move and are hopeful the new allocation will help them achieve their targets, they are skeptical about the barriers to accessing the funds, including delays and lack of knowledge.
- Some Indigenous representatives urge the GEF to rethink documentation requirements, the need for capacity building in the communities, and respect the individual community’s differences while designing the modalities for the GBFF.
New global biodiversity fund to restore nature worldwide by 2030 officially launches
- Representatives of 185 countries officially agreed to launch a new fund to ramp up investment to nations in meeting goals outlined in the Global Biodiversity Framework.
- So far, Canada and the U.K. announced initial contributions to start the fund’s capitalization, contributing $146.8 million (CA$200 million) and $12.58 million (£10 million), respectively.
- Targets include about 20% of funds to support Indigenous and local action to protect and conserve biodiversity and at least 36% of the fund’s resources to support the most vulnerable people, small island developing states, and least developed countries.
- Some human rights and environmental activists are calling for more contributions needed to operationalize the fund and firm commitment to allocate funds to Indigenous groups.
Deep-sea mining project in PNG resurfaces despite community opposition
- An embattled deep-sea mining project appears to be moving ahead in Papua New Guinea, according to officials in the Pacific Island nation, despite more than a decade of opposition from local communities on the grounds that it could harm the fisheries on which they rely as well as the broader ecosystem.
- Backers of deep-sea mining say it could help provide the gold, copper and other minerals necessary for the transition to electric vehicles and away from fossil fuels.
- But deep-sea mining has not yet happened anywhere in the world, and scientists, human rights groups and Indigenous communities highlight the lack of evidence demonstrating its safety.
- The Alliance of Solwara Warriors is a group of Indigenous communities and church organizations that have been fighting the Solwara 1 project in Papua New Guinea, which received the world’s first deep-sea mining license from PNG in 2011.
Deep-sea mining meetings conclude after stalemate on key agenda items
- Negotiations by member states of the International Seabed Authority (ISA), a U.N.-associated regulator, broke down at a crucial meeting in Kingston, Jamaica, before delegates reached a partial compromise in the final hours.
- The point of contention was whether to discuss two proposals at the meeting: one to conduct a review of the ISA itself and the other to discuss the possible consequences to the marine environment from a rule on deep-sea mining.
- The previous week, member states of the ISA council, the organization’s policymaking body, agreed to aim for July 2025 to finalize rules, regulations and procedures to govern deep-sea mining.
- Deep-sea mining has not yet begun anywhere in the world, but the potential impacts of this activity have stirred controversy.
Deep-sea mining rules delayed two more years; mining start remains unclear
- Member states of the International Seabed Authority (ISA) are currently meeting in Kingston, Jamaica, to discuss the future of deep-sea mining in international waters.
- These current meetings were highly anticipated because they coincided with the expiration of a rule that could have enabled deep-sea mining to start in the near future.
- On July 21, nations intensely negotiated an agreement to finalize regulations for deep-sea mining by July 2025, although this timeline is not legally binding.
- While companies can now technically apply for mining licenses, experts say the new agreement may make it more difficult for these to be approved before the mining regulations are finalized.
UN Paris meeting presses ahead with binding plastics treaty — U.S. resists
- At a May-June meeting in Paris, the United Nations Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) agreed to create, and submit by November, a first draft of an international plan to end plastic pollution by 2040.
- The United States declined to join the 58-nation “High Ambition Coalition” to create a legally-binding cradle-to-grave plan to address plastic production and use. The U.S. continues to hold out for a volunteer agreement that would focus on recycling.
- Delaying tactics by Saudi Arabia and other oil and plastics producing nations used up much time at this second international plastics treaty meeting, but these efforts were beaten back at least temporarily. The next international plastics treaty meeting will be in Kenya this November.
- Some activists pointed to the imbalanced representation at the Paris meeting, where about 190 industry lobbyists were allowed to attend, while communities, waste pickers, Indigenous peoples, youth and other members of civil society most impacted by plastic pollution had very limited opportunities to be heard.
U.N. climate chief calls for end to fossil fuels as talks head to Dubai
- International climate talks began in Bonn, Germany, on June 5.
- A key part of the discussion will be the global stocktake, assessing progress toward the emissions cuts pledged by nations as part of the 2015 Paris climate agreement.
- Discussions will work to provide the technical details of the stocktake, but the consensus is that the world is not on track to cut emissions by 50% by 2030, which scientists say is key to keeping the global temperature rise below 1.5°C (2.7°F) over pre-industrial levels.
- The talks are a precursor to COP28, the annual U.N. climate conference, scheduled to begin Nov. 30 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, which is a major oil- and gas-producing nation.
Apache tribe decry loss of sacred site to massive copper mine at both court and the U.N.
- The San Carlos Apache Tribe in Arizona, United States, has taken its legal battle against the U.S. government to the United Nations to save its traditional territory from what could be North America’s largest copper mine.
- The Indigenous tribe say that the mine will permanently alter desert ecosystems and destroy their most sacred site, akin to Jerusalem’s Temple Mount or Mecca’s Kaaba.
- The mine could produce up to 40 billion pounds of copper over 40 years, providing about 1,500 jobs, millions in tax revenue and compensation and minerals for renewable energy development.
- Both sides are awaiting a ruling from the 9th Circuit Court on whether destruction of the site violates the religious rights of the Apache people.
U.N. parties are worlds apart on plastics treaty solutions
- The United Nations Environment Programme will sponsor a Paris meeting in late May and early June in the ongoing effort to create an international treaty to potentially control plastic production and pollution.
- Delegates from 175 nations, along with private stakeholders (including the petrochemical industry and environmental groups), remain far apart on what the treaty should cover: reuse, banning certain chemicals, limiting plastics production, whether to focus on cradle-to-grave supply chain regulation or mostly on ocean pollution, and much more.
- Perhaps most importantly, the world’s countries need to determine how the treaty will be implemented: Should the final agreement require mandatory international compliance, or should individual nations be allowed to act voluntarily to solve the plastics problem?
- China and the United States are taking a far less aggressive position on implementation, recommending a voluntary national approach, while Pacific Island countries and the European Union want to see stricter rules for compliance and more focus on production limits. At this point, no one has any idea what the final treaty document will look like.
At the United Nations, Indigenous Ryukyuans say it’s time for U.S. military to leave Okinawa
- Opponents of the latest U.S. military base in Okinawa, Japan, are calling for urgent intervention by the United Nations to halt the construction of the new base, release military groundwater test data on toxic spills, and close all 32 U.S. military bases.
- The new facility and other military bases have been linked to toxic environmental pollution and construction threatening marine species, along with historical land conflicts between native Okinawans and the mainland Japan and U.S. governments.
- Latest water tests by the Okinawa government reveal PFAS levels up to 42 times higher than Japan’s national water standards with contamination found in drinking and bathing water for roughly 450,000 people.
- Amid rising tensions with China and efforts to counter its influence in the region, Japan and the U.S. cite Okinawa’s proximity to Taiwan and location in the Indo-Pacific as a strategic reason for maintaining bases on the island.
After historic storm in New Zealand, Māori leaders call for disaster relief and rights
- After Cyclone Gabrielle hit New Zealand and mostly impacted Indigenous Māori homes, Māori delegates attending the United Nation’s conference on Indigenous peoples say the government has left them out of recovery services and funding.
- The delegates hope their presence at the United Nations forum will increase pressure on the New Zealand government to include Māori people in disaster recovery plans, provide more support for Indigenous-led climate initiatives, and fully implement the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
- Māori knowledge, known as Mātauranga Māori, has been increasingly included in climate and conservation projects across the country as part of the ‘Vision Mātauranga’ framework, but it has also attracted fierce debate on its status within the scientific community.
Indigenous Maasai ask the United Nations to intervene on reported human rights abuses
- Maasai delegates at the United Nations conference on Indigenous people are calling on the forum to increase pressure on the Tanzanian government to address evictions, forced displacement and thousands of seized cattle in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area and Loliondo.
- Land disputes at both sites have been grinding on for years after the government revealed plans to lease the land to a UAE-based company to create a wildlife corridor for trophy hunting and elite tourism.
- Last year, the dispute reached a boiling point when Tanzanian police officers and authorities shot and beat dozens of Maasai villagers who protested the demarcation of their ancestral land. One Maasai man and one police officer have been killed.
- At the United Nations forum, a Tanzanian government representative rejected accusations brought against it, pointing to a recent court ruling in its favor and a visit by an African human rights commission.
Bankrolling biodiversity: How are private philanthropists investing in nature?
- A Mongabay analysis of the largest-ever private philanthropic campaign for biodiversity conservation has found about a quarter of the pledged $5 billion has already been allocated.
- The Protecting Our Planet (POP) campaign was launched in late 2021 ahead of the COP15 conference in Montreal. The POP group includes foundations representing some of the richest people on Earth.
- Critics of the scheme have called for greater transparency in the use of private funds for protected areas conservation, such as the creation of a charter of principles and commitments, or compliance framework, to mitigate negative impacts.
As U.N. members clinch historic high seas biodiversity treaty, what’s in it?
- On March 4, U.N. member states reached a landmark agreement on a legally binding treaty aimed at protecting the international waters of Earth’s oceans.
- The deal, more than 15 years in the making, was finalized after talks overran their two-week schedule into a final, grueling 36-hour negotiation marathon.
- Delegates reached consensus on multiple thorny matters, including a framework for establishing and maintaining a network of marine protected areas on the high seas and mechanisms to share benefits from high seas resources fairly among nations.
- For the new high seas treaty to be implemented, delegates must officially adopt the treaty text at an unscheduled next meeting, and then a minimum of 60 states must ratify it, a process that could take months or years.
Nations adopt Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
- After multiple delays due to COVID-19, nearly 200 countries at the UN Biodiversity Conference (COP15) in Montreal sealed a landmark deal to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), with four goals and 23 action-oriented targets, comes after two weeks of intense negotiations at COP15, in Montreal, Canada. This agreement replaces the Aichi Biodiversity Targets set in 2010.
- Among the 2030 goals, countries pledged to protect at least 30% of terrestrial and marine areas, while also recognizing Indigenous and traditional territories.
- Concerns have been raised about the ambitions of the framework, with many criticizing the agreement for its corporate influence, vague language and watered-down targets, many of which are not quantitative.
COP15 deal needs a ‘holistic approach to conservation’: Q&A with Joan Carling and Ramiro Batzin
- At the U.N. biodiversity talks, known as COP15, the target to protect 30% of land and ocean by 2030 is seen by many negotiators as the cornerstone of a successful deal to protect nature, and a target that should include Indigenous lands rights.
- But Indigenous leaders at the conference say that several other issues in the deal also concern their communities and should be emphasized for a strong deal, namely direct financing, sustainable agriculture and eliminating subsidies to industries driving biodiversity loss.
- Mongabay speaks with two Indigenous negotiators at COP15, Ramiro Batzin and Joan Carling, to unpack all the issues affecting Indigenous communities in the biodiversity deal and to understand what’s stalling negotiators from agreeing to their proposals.
Amid struggling COP15 talks, Indigenous leaders from Canada offer some solutions
- Talks on a plan to protect land and water globally are underway at the COP15 meeting in Montreal, with the host nation Canada among a legion of countries pushing for a “30×30” deal to protect 30% of the world’s land and ocean by 2030.
- Agreements on the targets, approaches and language in the post-2020 global biodiversity framework have been especially slow, with ministers from around the world set to arrive tomorrow to approve on the text.
- Indigenous delegates and analysts are calling for the integration of Indigenous land rights, knowledge and financing to resolve the 30×30 conservation target, citing Canada’s guardians program as a successful way to meet area-based conservation goals.
- The Canadian government has committed $800 million for Indigenous-run protected areas, with plans to expand them by nearly 1 million square kilometers (247 million acres) over the next seven years.
Scientists plead for protection of peatlands, the world’s carbon capsules
- As the United Nations Biodiversity Conference begins, a group of researchers from more than a dozen countries are calling for worldwide peatland protection and restoration for the protection of species and because of the vast amounts of carbon they contain.
- In a signed statement released Dec. 1, more than 40 scientists note that peatlands contain twice as much carbon as is found in all the world’s forests.
- As long as peatlands remain waterlogged, that carbon will stay in the soil; but if they’re degraded or drained, as around 12% of the world’s peatlands have been, they quickly become a source of atmospheric carbon.
- The scientists are asking for a more prominent role in international negotiations to address climate change and species’ global loss.
U.N. report calls for the ban of mercury trade and its use in gold mining
- Small-scale gold mining is the key driver of global mercury demand, according to a U.N. report on the highly toxic metal, with South America accounting for 39% of this demand.
- Hair samples taken from Indigenous communities in the Bolivian and Brazilian Amazonian regions showed mercury levels in excess of the safe limit prescribed by the World Health Organization.
- In Brazil specifically, mercury use has risen with the boom in illegal mining that has been largely overlooked — and in some cases even encouraged — by the government of President Jair Bolsonaro.
Despite pledges, obstacles stifle community climate and conservation funding
- As science has increasingly shown the importance of conservation led by Indigenous peoples and local communities (IPLCs), donors have begun to steer funding toward supporting the work these groups do.
- In 2021, during last year’s COP26 U.N. climate conference, private and government donors committed $1.7 billion to secure the land rights of Indigenous peoples and local communities.
- But a recent assessment of the first year of the pledge shows that little of the funding goes directly to them, often going first through international NGOs, consultancies, development banks and other intermediaries.
- Most aid intended to support IPLC-led conservation work follows this path. Now, however, donors and IPLC leaders are looking for ways to ease the flow of funding and channel more of it to work that addresses climate change and the global loss of biodiversity.
COP27 boosts carbon trading and ‘non-market’ conservation: But can they save forests?
- For the first time ever at a climate summit, the final text of this month’s COP27 included a “forests” section and a reference to “nature-based solutions,” — recognizing the important role nature can play in curbing human-caused climate change. But it’s too early to declare a victory for forests.
- By referencing REDD+, the text could breathe new life into this UN framework, which has so far failed to be a game-changer in the fight against deforestation as many hoped it would be.
- COP27 also took a step toward implementing Article 6.4 of the Paris agreement, a mechanism that some see as a valid market-based climate solution, though others judge it as just another “bogus” carbon trading scheme.
- Many activists are pinning their hopes instead on Article 6.8, which aims to finance the protection of ecosystems through “non-market approaches” like grants, rather than with carbon credits.
COP27 long on pledges, short on funds for forests — Congo Basin at risk
- The world’s wealthiest nations have made grand statements and offered big monetary pledges to save the world’s tropical rainforests so they can continue sequestering huge amounts of carbon.
- But as COP27 draws to a close, policy experts and activists agree that funding so far is far too little, and too slow coming, with many pledges still unfulfilled. Without major investments that are dozens, or even hundreds, of times bigger, tropical forests will keep disappearing at an alarming rate.
- The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) offers a case study of just how dire the situation is becoming. While some international forest preservation money is promised and available, it is insufficient to stop companies from leasing forestlands to cut timber and to convert to plantations and mines.
- Some experts say that what is urgently needed is the rapid upscaling of carbon markets that offer heftier carbon credits for keeping primary forests growing. Others point to wealthy nations, who while still cutting their own primary forests, encourage poorer tropical nations to conserve theirs without paying enough for protection.
COP27: ‘Brazil is back’ to fight deforestation, Lula says, but hurdles await
- At COP27 this week Brazil president-elect Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva pledged “zero deforestation and degradation of biomes,” a goal to be achieved by 2030.
- Lula also plans to establish a Ministry of Indigenous People, and to end “all the exploration of Indigenous lands by miners, and… to prohibit timber cutters.” Activists said Lula has sent a “strong message” at the COP27 summit, a meeting which has so far seen little climate progress.
- The president-elect has also met with Norway and Germany about restarting the Amazon Fund, which helped finance efforts to keep the rainforest intact until it was frozen in 2019 due to the anti-environmental policies of President Jair Bolsonaro.
- Lula will likely have to pursue stricter forest enforcement through executive action, as he faces a congress with many members hostile to his Amazon protection promises.
Small share of land rights pledge went to Indigenous groups: Progress report
- A report from funders of a $1.7 billion pledge to support Indigenous and community forest tenure made at the 2021 U.N. climate conference found that 19% of the financing has been distributed.
- The findings from 2022 also show that only 7% of the funding went directly to Indigenous and community organizations, despite the protection they provide to forests and other ecosystems. (A subsequent analysis in 2023 revised this figure downward to 2.9%.)
- Both donors and representatives of Indigenous and community groups are calling for more direct funding to these organizations by reducing the barriers they face, improving communication and building capacity.
Humans are decimating wildlife, report warns ahead of U.N. biodiversity talks
- Wildlife populations tracked by scientists shrank by nearly 70%, on average, between 1970 and 2018, a recent assessment has found.
- The “Living Planet Report 2022” doesn’t monitor species loss but how much the size of 31,000 distinct populations have changed over time.
- The steepest declines occurred in Latin America and the Caribbean, where wildlife abundance declined by 94%, with freshwater fish, reptiles and amphibians being the worst affected.
- High-level talks under the U.N. Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) will be held in Canada this December, with representatives from 196 members gathering to decide how to halt biodiversity loss by 2030.
Delegates come close, but fail again to clinch high seas protection treaty
- At the close of two weeks of negotiations on Aug. 26 in New York, delegates from around the world had failed to net consensus on a high-stakes, legally binding treaty to conserve biodiversity on the high seas.
- These areas beyond national jurisdictions comprise two-thirds of the global ocean and are a vast, resource-rich global commons. Yet there is no comprehensive, agreed-upon framework governing resource extraction or conservation there.
- Top sticking points included fair access to marine resources for all and how to establish marine protected areas on the high seas.
- The meeting was the fifth of four planned diplomatic sessions that began in 2017 following more than 10 years of discussion. It ended with a commitment to reconvene before the year is over.
Amid haggling over deep-sea mining rules, chorus of skepticism grows louder
- This week, the International Seabed Authority, the intergovernmental body tasked with overseeing deep-sea mining in international waters, concluded its recent set of meetings, which ran from July 4 to Aug. 4, 2022.
- The purpose of these meetings was to progress with negotiations of mining regulations, with a view that deep-sea mining will start in July 2023 after the Pacific island nation of Nauru triggered a rule that could obligate this to happen.
- While many countries appear to support the rapid development of these regulations, an increasing number of other countries have expressed concern with this deadline, indicating a possible turn of events.
A clean and healthy environment is a human right, U.N. resolution declares
- On July 28, member states of the U.N. General Assembly voted overwhelmingly to adopt a historic resolution that recognizes that a clean, healthy and sustainable environment is a human right.
- While the resolution is not legally binding, experts say it can give rise to constitutional and legal changes that will positively impact the environment and human well-being.
- The resolution comes at a critical moment in human history as we face an accelerating climate crisis, unprecedented biodiversity loss, and the ongoing threat of pollution.
‘The sea means everything’: Q&A with deep-sea mining opponent Debbie Ngarewa-Packer
- New Zealand parliamentarian and Māori activist Debbie Ngarewa-Packer has spent more than two decades serving in leadership roles, using her positions to advance social justice issues and to campaign for the protection of the marine environment.
- A key issue that Ngarewa-Packer is currently working on is a push to ban deep-sea mining in the global ocean, a proposed activity that would extract large amounts of minerals from the seabed.
- Ngarewa-Packer previously worked with other Māori activists, NGOs and community members to block consent for a deep-sea mining operation in her home district of South Taranaki on New Zealand’s North Island.
- In an interview with Mongabay, Ngarewa-Packer talks about why it’s critical to protect the deep sea from mining, what ancestral teachings say about protecting the ocean, and why she feels hopeful about the future.
Disappointment and a few wins, Indigenous leaders react to Nairobi biodiversity talks
- Negotiation talks in Nairobi, Kenya, for the new global agreement to preserve and protect nature ended last week, but parties have not yet come to an agreement over the final draft – including proposals laid out by the International Indigenous Forum on Biodiversity (IIFB).
- Disappointed by the progress made at the latest biodiversity meeting after two years of talks, Indigenous leaders and civil society organizations are urging parties to secure land rights, include monitoring components and strengthen the text’s language around their role in meeting biodiversity goals.
- The inclusion of gender equality and environmental defenders in the text, and their access to justice, is seen as a win for Indigenous people, women and environmental defenders. Some proposals by the IIFB are still held within the draft, though several areas are in square brackets.
- The final agreement is set to be adopted in Montreal in December, but at least one more round of negotiations is expected to take place before then. Dates are yet to be determined.
U.N. Ocean Conference ends with promises. Is a sea change coming?
- The second United Nations Oceans Conference took place from June 27 to July 1 in Lisbon, focusing on the protection of life under water, as dictated by U.N. Sustainable Development Goal No. 14.
- The conference was originally meant to have taken place in 2020, but was delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- While nations, NGOs and other entities made hundreds of conservation commitments, including pledges to expand marine protected areas, end destructive fishing practices, and fund conservation efforts, experts say there is still a lot of work to be done to protect our oceans.
- Coalitions of small-scale fishers and Indigenous peoples also voiced their concerns about being excluded from important conservation dialogues.
Brazil shows no progress in response to U.N. calls on Indigenous rights
- Brazilian civil society groups say the government has failed to implement any of the 34 recommendations on Indigenous rights made by a U.N. council in 2017.
- Those suggestions were part of a larger set of 242 human rights recommendations, of which Brazil has fully implemented just one, according to the civil society coalition.
- Indigenous rights advocates say the fact that the government is highlighting its distribution of food aid to Indigenous communities in its report shows just how little it has done in terms of actual policy.
- A similar analysis by a congressional group also concluded that the government had failed to implement any recommendations on Indigenous rights.
Latest ‘plan for the planet’ calls for protecting 44% of land, home to 1.8b humans
- A new study says 44% of Earth’s terrestrial area needs conservation attention to halt the runaway destruction of the natural world.
- The figure is significantly higher than the goal currently under discussion as part of the global post-2020 agenda, which is to protect 30% of land and ocean by 2030.
- The area identified for protection by the new study is home to 1.8 billion people, almost a quarter of the human population.
- The study authors suggest prioritizing biologically rich regions at the highest risk of being converted for human use by 2030, most notably in Africa.
IPCC report calls for ‘immediate and deep’ carbon cuts to slow climate change
- A new report from the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) finds that the world could face a more than 3° Celsius (5.4° Fahrenheit) increase in the global average temperature over pre-industrial levels based on current carbon emissions.
- However, the authors of the report say investment in renewable energy, green building and responsible land use could lower emissions enough to stay below an increase of 1.5°C (2.7°F), a target identified at the 2015 U.N. climate conference that scientists predict would avoid the worst impacts of global warming.
- Addressing continued global carbon emissions will require trillions, not billions, of dollars in financing from public and private sources to cut emissions, the report finds.
- Its authors also say that including Indigenous and local communities from the beginning in land-use decisions aimed at climate change mitigation is critical.
Chemical recycling: ‘Green’ plastics solution makes more pollution, says report
- The plastics industry claims that ‘chemical recycling’ or ‘advanced recycling’ technologies, which use heat or solvents to convert waste plastic into chemical feedstocks that can potentially be further processed into new plastics, are a green alternative to mechanical recycling.
- But according to a new report, five out of eight U.S. facilities assessed use chemical processes to produce combustible fuel, not new plastics. In addition, facilities are disposing of large amounts of hazardous waste which in some cases includes benzene — a known carcinogen — lead, cadmium and chromium.
- Critics say the chemical recycling industry’s multi-step incineration processes are polluting and generating greenhouse gases without alleviating virgin plastic demand. Environmental permits for six U.S. facilities allow release of hazardous air pollutants that can cause cancer or birth defects.
- A new UN framework to fight global plastic pollution could offer nations flexibility over how they meet recycling targets, potentially allowing the industry to lobby for policy incentives and regulatory exemptions for plastic-to-fuel techniques — policies that may threaten the environment and public health, say experts.
Fourth round of U.N. talks fail to finalize a treaty to manage the high seas
- U.N. member states met this month in New York to hash out a treaty governing the sustainable management of the high seas, resource-rich international waters that span about two-thirds of the ocean.
- Hopes were high that after 10 years of discussion and three previous negotiating sessions, delegates to the meeting would finalize a legally binding treaty.
- Talks ended March 18 with no deal, amid a failure to reach consensus on several key points, including how to establish marine protected areas on the high seas.
- A movement to protect 30% of the ocean by 2030 depends on the swift completion of a high seas treaty, and observers say a deal remains within reach by the end of the year.
NGOs alert U.N. to furtive 2-million-hectare carbon deal in Malaysian Borneo
- Civil society organizations have complained to the United Nations about an opaque “natural capital” agreement in the Malaysian state of Sabah on the island of Borneo.
- The agreement, signed behind closed doors in October 2021, involved representatives from the state government and Hoch Standard Pte. Ltd., a Singaporean firm. But it did not involve substantive input from the state’s numerous Indigenous communities, many of whom live in or near forests.
- The terms ostensibly give Hoch Standard the right to monetize carbon and other natural capital from Sabah’s forests for 100 years.
- Along with the recent letter to the U.N., the state’s attorney general has questioned whether the agreement is enforceable without changes to key provisions. An Indigenous leader is also suing the state over the agreement, and Hoch Standard may be investigated by the Singaporean government after rival political party leaders in Sabah reported the company to Singapore’s ambassador in Malaysia.
‘No planet B’: Groups call for $60bn increase in annual biodiversity funding
- A group of international conservation and environmental organizations is calling on wealthy countries to provide an extra $60 billion in funding a year to protect the planet’s species.
- They argue that the amount compensates for the toll exacted on biodiversity by international trade, which largely benefits rich nations.
- At a March 1 press conference, representatives of the organizations said the inclusion of Indigenous communities, known to be “nature’s best stewards,” would be critical, and they advocated for the bulk of the financing to be in the form of grants to these communities and other “grassroots” organizations.
The world says yes to a cradle to grave plastics treaty: Now the work begins
- 175 countries unanimously agreed last week on a United Nations framework to fight global plastic pollution from cradle to grave. Reluctant nations, including India and Japan, sought a far more limited agreement only dealing with ocean plastic pollution. But they acquiesced in the end.
- A committee will shortly begin work on drafting the treaty, determining global rules, and financing and enforcement mechanisms, with a goal of finishing by the end of 2024.
- While many crucial details remain to be worked out over the next two years, the UN resolution calls for a combination of required and “voluntary actions” to address the cradle to grave plastics crisis. The document even addresses the extraction of chemicals used in production, meaning the final treaty could seriously impact the oil industry.
- Also, wealthier nations may be called on to provide assistance to less developed ones. Environmental groups are pleased with the agreement, though caution that much work lies ahead. The plastics industry had hoped for a far more limited agreement and it is expected to offer input on the final shape of the treaty.
Climate change a threat to human well-being and health of the planet: New IPCC report
- The United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released a report on the impacts of climate change on people, detailing areas of vulnerability and steps for adaptation to the changes brought about by Earth’s warming temperatures.
- The report, the second of three that will be part of the IPCC’s sixth assessment, highlights the importance of Indigenous and local knowledge in grappling with climate change and its effects on weather, water availability and food sources.
- It also notes that some segments of society, especially the most vulnerable, will bear a disproportionate burden as a result of climate change.
- The authors of the report and other climate researchers emphasize that urgent action is needed, both to address the causes of climate change and improve the capability of people to adapt to it.
Malaysian officials dampen prospects for giant, secret carbon deal in Sabah
- The attorney general of the Malaysian state of Sabah has said that a contentious deal for the right to sell credits for carbon and other natural capital will not come into force unless certain provisions are met.
- Mongabay first reported that the 100-year agreement, which involves the protection of some 2 million hectares (4.9 million acres) from activities such as logging, was signed in October 2021 between the state and a Singapore-based firm called Hoch Standard.
- Several leaders in the state, including the attorney general, have called for more due diligence on the companies involved in the transaction.
- Civil society representatives say that a technical review of the agreement is necessary to vet claims about its financial value to the state and its feasibility.
As world drowns in plastic waste, U.N. to hammer out global treaty
- After years of largely neglecting the buildup of plastic waste in Earth’s environment, the U.N. Environment Assembly will meet in February and March in the hopes of drafting the first international treaty controlling global plastics pollution.
- Discarded plastic is currently killing marine life, threatening food security, contributing to climate change, damaging economies, and dissolving into microplastics that contaminate land, water, the atmosphere and even the human bloodstream.
- The U.N. parties will debate how comprehensive the treaty they write will be: Should it, for example, protect just the oceans or the whole planet? Should it focus mainly on reuse/recycling, or control plastics manufacture and every step of the supply chain and waste stream?
- The U.S. has changed its position from opposition to such a treaty under President Donald Trump, to support under President Joe Biden, but has yet to articulate exactly what it wants in an agreement. While environmental NGOs are pushing for a comprehensive treaty, plastics companies, who say they support regulation, likely will want to limit the treaty’s scope.
In the Arctic, Indigenous Sámi keep life centered on reindeer herding
- In Finland’s northern Arctic landscape, the Indigenous Inari Sámi community practice a unique form of reindeer herding and fishing based on traditional knowledge of the region’s climate, winds, ecosystem structure and species behavior.
- The destruction of some of Europe’s last primary forests, along with mining claims and climate change have impacted herding routes, lakes and the availability of important winter foods.
- The community’s food system is also threatened by the loss of language and youth out-migration, disintegrating traditional knowledge of the forests and waters.
- This article is one of an eight-part series showcasing Indigenous food systems covered in the most comprehensive FAO report on the topic to date.
As climate-driven drought slams farms in U.S. West, water solutions loom
- Drought in the U.S. West has been deepening for two decades, with no end in sight. Unfortunately for farmers, water use policies established in the early 20th century (a time of more plentiful rainfall), have left regulators struggling with their hands tied as they confront climate change challenges — especially intensifying drought.
- However, there is hope, as officials, communities and farmers strive to find innovative ways to save and more fairly share water. In Kansas and California, for example, new legislation has been passed to stave off dangerous groundwater declines threatening these states’ vital agricultural economies.
- Experts say that while an overhaul of the water allocation system in the West is needed, along with a coherent national water policy, extreme measures could be disruptive. But there are opportunities to realize incremental solutions now. Key among them is bridging a gap between federal water programs and farmers.
- A major concern is the trend toward single crop industrial agribusiness in semi-arid regions and the growing of water-intensive crops for export, such as corn and rice, which severely depletes groundwater. Ultimately, 20th century U.S. farm policies will need to yield to flexible 21st century policies that deal with unfolding climate change.
Indigenous leader sues over Borneo natural capital deal
- An Indigenous leader in Sabah is suing the Malaysian state on the island of Borneo over an agreement signing away the rights to monetize the natural capital coming from the state’s forests to a foreign company.
- Civil society and Indigenous organizations say local communities were not consulted or asked to provide input prior to the agreement’s signing on Oct. 28.
- Further questions have arisen about whether the company, Hoch Standard, that secured the rights under the agreement has the required experience or expertise necessary to implement the terms of the agreement.
Unique Indigenous Maya food system blends cropping techniques in Guatemala
- Members of the Maya Ch’orti’ Indigenous communities in Guatemala practice a unique agroforestry system and an intercropping technique seen as one of the best methods in the world of maximizing the different intensities of sunlight and complementing soil fertility.
- The communities’ traditional food system also includes home patio gardens, living fences and communal forest areas to cultivate and gather local plant species used in traditional medicine, woven handicrafts and edible food dye production.
- The resilient food system is increasingly affected by climate change, out-migration, extractive industries and COVID-19 economic impacts driving up prices of household goods that families need to purchase.
- This article is one of an eight-part series showcasing Indigenous food systems covered in the most comprehensive FAO report on the topic to date.
For Mekong officials fighting timber traffickers, a chance to level up
- Global wildlife trade authority CITES held a virtual workshop for customs agents and inspections officials in the Lower Mekong region of Southeast Asia on the physical inspection of timber shipments in October.
- The region’s forests are home to around 100 species of trees for which CITES restricts trade to protect their survival.
- But attendees also note that the ability to accurately identify tree species, as well as the knowledge to spot suspicious shipments, is low in the region.
- Improving that capacity will help to address illegal logging in the region, advocates say.
Uganda’s ‘Dr. Gladys’ honored by U.N. for work linking conservation and health
- The United Nations on Dec. 7 recognized Gladys Kalema-Zikusoka as one of its “champions of the Earth” for promoting the One Health approach to conservation in Africa.
- The Ugandan conservationist, a trained wildlife veterinarian, established the NGO Conservation Through Public Health (CTPH) in 2003 to ensure better health care access for communities living around Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and to lower the risk of human pathogens jumping to mountain gorillas.
- UNEP selected Kalema-Zikusoka for its science and innovation category; the other awardees were Barbados Prime Minister Mia Mottley, Kyrgyz youth activist Maria Kolesnikova, and the nonprofit Sea Women of Melanesia.
- “If you make the community feel that you care about them, then there’s less need to fight them,” Kalema-Zikusoka said.
Between land and sea: Agrobiodiversity holds key to health for Melanesian tribes
- Residents of Baniata village on the Solomon Islands’ Western province practice an ancient agroforestry system that intercrops 20 edible species and features the ngali nut, a delicacy sold in domestic and international markets.
- The community’s traditionally self-sufficient and biodiverse diet features 132 species, notably the fe’i banana, a Melanesian specialty that contains 100 times the vitamin A of a typical banana.
- The resilient food system and diet is increasingly affected by climate change, imported crops, processed foods, and the loss of traditional knowledge in younger generations.
- This article is one of an eight-part series showcasing Indigenous food systems covered in the most comprehensive FAO report on the topic to date.
Indigenous groups unveil plan to protect 80% of the Amazon in Peru and Ecuador
- A new plan called the Amazon Sacred Headwaters initiative proposes the protection of 80% of the Amazon in Peru and Ecuador by 2025, consisting of 35 million hectares (86 million acres) of rainforest.
- The Amazonian Indigenous organizations leading the plan aim to center Indigenous-led forest management and land tenure to protect endemic species and prevent approximately 2 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere.
- The proposal has received positive responses from Ecuadoran and Peruvian government officials, but faces a stumbling block in the fact that both countries rely heavily on extractive industries operating within the Amazon to help pay off foreign debt.
The catfight within tiger conservation: Why all stakeholders need to start working together (commentary)
- After 12 years of tiger conservation efforts across borders, the Global Tiger Recovery Program (GTRP) ends in 2022 with most tiger range countries coming in with failed attempts at saving their tigers.
- Tiger conservation can be successful only if the six stakeholder groups involved in it — Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs), governments, NGOs, financiers, forums, and media — came together with shared goals.
- The next Global Tiger Initiative summit at Vladivostok in 2022 will be the ideal moment to repair the flaws of the previous GTI and create true cooperation with all the stakeholders, with full support of all tiger range countries.
- The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
Is colonial history repeating itself with Sabah forest carbon deal? (commentary)
- To the surprise of Indigenous and local communities, a huge forest carbon conservation agreement was recently signed in the Malaysian state of Sabah on the island of Borneo.
- Granting rights to foreign entities on more than two million hectares of the state’s tropical forests for the next 100-200 years, civil society groups have called for more transparency.
- “Is history repeating itself? Are we not yet free or healed from our colonial and wartime histories?” wonders a Sabahan civil society leader who authored this opinion piece calling for more information, more time, and a say.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Allegations of displacement, violence beleaguer Kenyan conservancy NGO
- The California-based Oakland Institute published a report on Nov. 16 alleging that the Kenya-based nonprofit Northern Rangelands Trust (NRT) keeps pastoralists and their herds off of their ancestral grazing areas.
- The institute’s research relied on petitions, court cases and in-person interviews with community members in northern Kenya, with report lead author Anuradha Mittal alleging that NRT’s model of “fortress conservation” exacerbates interethnic tensions and prioritizes the desires of wealthy tourists over the needs of the Indigenous population.
- Tom Lalampaa, NRT’s CEO, denies all allegations that the organization keeps communities from accessing rangeland or that it has played any role in violence in the region.
- Lalampaa said membership with NRT provides innumerable benefits to community-led conservancies, which retain their legal claim to the land and decide on how their rangelands are managed.
Details emerge around closed-door carbon deal in Malaysian Borneo
- Leaders in Sabah have begun to reveal information about a nature conservation agreement signed in the Malaysian state of Sabah on the island of Borneo for the rights to carbon and other natural capital.
- The deal allegedly covers rights to more than 2 million hectares (4.9 million acres) of the state’s tropical forests for the next 100-200 years.
- Indigenous and civil society groups have called for more transparency.
- In response to the public reaction to news of the agreement, its primary proponent, Deputy Chief Minister Jeffrey Kitingan, held a public meeting but has declined to make the agreement public yet.
‘Standing with your feet in the water’: COP26 struggles to succeed
- As at every COP before it, negotiators at COP26 are struggling against time to reach an accord, with negotiators at Glasgow clashing over seemingly irreconcilable differences. With the science of climate change now dire, vulnerable nations are demanding strong specific language, while other nations seek to water it down.
- The group of nations dubbed the “Carbon Club” as long ago as the Kyoto Agreement negotiations in the 1990s, continues to offer the primary stumbling block. Those oil and/or coal producing nations include Russia, Saudi Arabia, China, Australia, Norway, the U.K. and often the U.S.
- The United States, while it has made a major sea change since the denialism of the Trump administration, continues to be cautious about any language that would threaten oil, gas and coal industry subsidies, or antagonize Republican members of Congress or coal company baron and West Virginia Dem. Sen. Joe Manchin.
- As the clock ticks, and the last hours of COP26 slip away, with street protestors increasingly frustrated at the lack of significant movement by the negotiators, the scene remains tense in Glasgow. With the summit now gone into overtime, the outcome of COP26 remains in the balance.
Indigenous leaders share hopes and concerns towards pledges made at COP26
- Mongabay interviewed three Indigenous leaders from the tropics to obtain their views regarding the COP26 climate conference’s growing consensus around pledges towards Indigenous land rights, financial support and stewardship, and on conditions in their nations.
- Valeria Paye, of the Kaxuyana Indigenous group in the Brazilian Amazon, raised the alarm over President Jair Bolsanaro’s 2018 electoral promise to not give any more ancestral land back to Indigenous communities, and over his barring of financial resources destined for Amazon IPLC land rights and Indigenous stewardship of the biodiverse hotspot.
- Joseph Itongwa, a national director of an Indigenous rights group in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, was optimistic about the growing positive consensus at COP regarding Indigenous land rights, which also reflects the increasing momentum within his own country to pass legislation securing Indigenous rights.
- Monica Ndoen, a project manager of AMAN, worries that the Indonesian government’s focus on industrial development and big business to boost the country’s COVID-19 economic recovery will be prioritized over any promises to secure Indigenous land tenure. Indonesia’s leader has already backed away from the Glasgow Forest Declaration.
New global partnership aims to remove barriers to Indigenous climate finance
- At COP26, a new international coalition of organizations and investors, the Peoples Forest Partnership, announced plans to mobilize US $20 billion per year by 2030 directly to Indigenous forest conservation projects.
- The partnership believes this initiative can reduce carbon emissions from deforestation by at least 2 billion tons per year while protecting 500 million hectares of threatened tropical forests and biodiversity.
- While the partnership aims to set a high standard for equitable, accessible and culturally appropriate mechanisms for IPLCs to engage with climate finance, a consultation period is open for interested stakeholders to offer input on criteria and principles.
Bornean communities locked into 2-million-hectare carbon deal they don’t know about
- Leaders in Sabah, a Malaysian state on the island of Borneo, signed a nature conservation agreement on Oct. 28 with a group of foreign companies — apparently without the meaningful participation of Indigenous communities.
- The agreement, with the consultancy Tierra Australia and a private equity-backed funder from Singapore, calls for the marketing of carbon and other ecosystem services to companies looking, for example, to buy credits to offset their emissions.
- The deal involves more than 2 million hectares (4.9 million acres) of forest, which would be restored and protected from mining, logging and industrial agriculture for the next 100-200 years.
- But land rights experts have raised concerns about the lack of consultation with communities living in and around these forests in the negotiations to this point.
Do forest declarations work? How do the Glasgow and New York declarations compare?
- On November 2, 2021 at COP26 in Scotland, 127 countries signed the Glasgow Leaders’ Declaration on Forests and Land Use, which aims to end net forest loss by 2030. Those signatories account for about 90% of global tree cover and about 85% of the world’s primary tropical forests.
- The declaration came seven years after the New York Declaration on Forests, under which 39 countries pledged to halve natural forest loss by 2020 and end it by 2030. Those countries accounted for about 39% of both global tree cover and primary tropical forests.
- While the New York Declaration on Forests catalyzed global awareness for the importance of forests and the need to address deforestation, it missed the mark by a wide margin in terms of achieving its 2020 goal to reduce natural forest loss by 50%.
- The biggest new signatories are Russia (ranked #1 globally in terms of tree cover), Brazil (#2, thanks to the Amazon rainforest), and China (#6) which together account for 1.4 billion hectares of tree cover. Among tropical nations, after Brazil, the biggest new additions are Papua New Guinea (32 million hectares of primary tropical forest), Gabon (23 million hectares), and the Republic of the Congo (21 million hectares).
As fossil fuel use surges, will COP26 protect forests to slow climate change?
- Despite the world’s commitment in Paris in 2015 to hold back the tide of global warming, carbon emissions continue rising, while impacts are rapidly escalating as heat waves, drought and extreme storms stalk the world’s poorest and richest nations — bringing intensified human misery and massive economic impacts.
- Once viewed optimistically, nature-based climate solutions enshrined in Article 5 of the Paris Agreement (calling for protections of carbon-storing forests, peat bogs, wetlands, savannas and other ecosystems) is now threatened by politics as usual, and by the unabated expansion of agribusiness and extraction industries.
- As world leaders gather in Scotland for the COP26 climate summit, scientists and advocates are urging negotiators to at last finalize comprehensive effective rules for Article 5, which will help assure “action to conserve and enhance, as appropriate, sinks and reservoirs of greenhouse gases … including forests.”
- Over the first two weeks in November at COP26, the vision and rules set at Paris are to be settled on and fully implemented; John Kerry, co-architect of the Paris accord and President Joe Biden’s climate envoy, calls this vital COP the world’s “last best chance” to finally move beyond mostly empty political promises into climate action.
A new 100-page report raises alarm over Chevron’s impact on planet
- An independent expert report has determined that of the 70 ongoing cases in 31 countries against Chevron, only 0.006% ($286-million) in fines, court judgements, and settlements have been paid. The company still owes another $50.5-billion in total globally.
- The largest of those payout judgements is for $9.5 billion in environmental damages representing 30,000 plaintiffs in Ecuador where the oil damage is so severe, it’s known as the “Amazon Chernobyl”.
- Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela are amongst a number of countries in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, Latin America and beyond where there are ongoing litigations against Chevron. In the U.S. alone, there are 13 ongoing litigations against Chevron.
- The same day the report was released, international human rights lawyer Steven Donziger, lead attorney on the Chevron Ecuador case, was imprisoned. His incarceration came after nearly two years of house arrest in New York City and an intense legal battle for his freedom.
Domestic bushmeat consumption an “urgent” threat to migratory mammals, U.N. says
- A recent U.N. report has found that many migratory mammals are in grave danger of being hunted for meat for domestic consumption, which in many cases poses a greater risk to population numbers than international trade.
- There is also strong evidence that wild meat taking and consumption is linked to zoonotic diseases.
- The authors say that while wild meat consumption cannot be eliminated because it is an indispensable source of nutrition and income for rural communities, they call for improved national regulations and international cooperation to safeguard threatened species.
Not just sea life: Migratory fish, birds and mammals also fall foul of plastic
- A new report from the U.N. Environment Programme and the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals confirms that plastic pollution poses a major threat to land and freshwater migratory species.
- Mammals, birds and fish are affected through various means, including entanglement, ingestion of plastics, accumulation of microplastics in the food chain, and using plastics in nesting material.
- The report highlights that global capacity to manage plastic pollution is not keeping pace with projected growth in the plastics market.
- The authors call for measures that will ultimately drive change upstream to reduce the volume of plastics entering the marketplace.
Humans’ role in climate warming ‘unequivocal,’ IPCC report shows
- The greenhouse gases humans have released into the atmosphere over the past 100 to 150 years has led to a 1.1°C (2°F) rise in global temperatures, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, or IPCC.
- The authors of the IPCC’s latest report use the strongest language yet to connect human activity to climate change, calling the link “unequivocal.”
- The report draws on the findings of thousands of studies, pointing to the need to cut CO2 emissions immediately while also suggesting that many of the impacts of climate change are irreversible.
- This report focuses on the science behind climate change and will be combined with two subsequent reports on the adaptation and vulnerability to the impacts of climate change and ways to mitigate its effects to produce the IPCC’s sixth assessment, scheduled for publication in September 2022.
Ending Amazon deforestation a top priority on Colombian minister’s D.C. visit
- In an interview with Mongabay, Colombian environment minister Carlos Eduardo Correa provided insights about his recent visit to Washington, D.C., where he held meetings with U.S. government officials and conservation organizations.
- On his first international trip amid the pandemic, the minister reiterated his commitment to protect forests in one of the most biodiverse countries in the world.
- Colombia’s climate goals include reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 51% and achieving zero deforestation by 2030, and achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
Scientists call for solving climate and biodiversity crises together
- A new report from United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) highlights the importance of confronting climate change and biodiversity loss together.
- Global climate change and the unprecedented loss of species currently underway result from a similar suite of human-driven causes, the report’s authors write.
- As a result, solutions that take both issues into account have the best chance of success, they conclude.
U.N. declares decade of ecosystem restoration to ‘make peace with nature’
- The U.N. has declared the coming decade a time for ecosystem restoration, highlighting in a new report the importance of preventing, halting and reversing ecosystem degradation worldwide.
- It calls on the world to restore at least 1 billion hectares (2.5 billion acres) of degraded land in the next decade — an area larger than China — warning that degradation already affects the well-being of 3.2 billion people.
- The report also makes an economic case for restoration, noting that for every dollar that goes into restoration, up to $30 in economic benefits are created.
- A key message of the report is that nature is not something that is “nice to have” — it is essential to our survival, and we are a part of it.
Talks break down over crumbling Yemeni tanker threatening massive oil spill
- The FSO Safer, an oil supertanker anchored for decades off Yemen, risks a catastrophic humanitarian and environmental disaster in the Red Sea.
- The civil war in Yemen has suspended essential maintenance on the increasingly fragile vessel with more than 1 million barrels of oil in its hold and hindered disaster preparedness.
- On June 1, talks appeared to break down between the U.N. and the Houthi administration, which controls the vessel. The two sides had spent months negotiating access for a U.N. team to investigate and stabilize the vessel.
- A spill would jeopardize corals with the best-known chance of surviving predicted global climate change.
Protected areas now cover nearly 17% of Earth’s surface: U.N. report
- A new report from the United Nations Environment Programme and the International Union for Conservation of Nature reveals that countries are closing in on the target set in 2010 of protecting or conserving 17% of the Earth’s surface.
- Since 2010, the area of the marine environment that’s under protection has more than tripled, although global coverage is less than 8%, falling short of the 10% goal set in Aichi Target 11.
- While there has been some success, international leaders agree there should be more focus on quality as well as quantity in designating protected and conservation areas.
- As the U.N. Biodiversity Conference scheduled for October 2021 in Kunming, China, approaches, the report calls for a stronger emphasis on the contributions of Indigenous and local communities, while also ensuring that the world’s poorest don’t shoulder an outsize burden from these efforts.
An engaged society is key for the future of African conservation, says WWF Africa’s Alice Ruhweza
- Protecting Africa’s charismatic megafauna often come first to mind when Westerners think about conservation in Africa, but this is a narrow view that doesn’t capture the range of issues involved in conservation efforts across the continent.
- Alice Ruhweza, the regional director for Africa for WWF, says conservation in Africa is about about ecosystems and people: “As the home of humankind, Africa and its ecosystems have evolved together with people. When we talk about conservation in Africa we are really talking about people and nature.”
- Ruhweza says that growing recognition of this connection is driving “a shift to a more people-centered and rights-based conservation,” including within WWF.
- Ruhweza spoke about these issues and more during a recent interview with Mongabay founder Rhett A. Butler.
As the rest of world tackles plastics disposal, the U.S. resists
- In an expansion of the U.N.’s 1989 Basel Convention, amendments to the international protocol on the shipment of hazardous waste were revised to include plastics in 2021, with nations currently figuring out how to implement the agreement.
- The United States is the only major nation not to have fully implemented the treaty, despite strong support for it among both the Republican and Democratic parties. The Biden administration could soon change that.
- The U.S. remains a major dumper of hazardous waste globally, including large amounts of plastics, despite the attempted limitations imposed by the Basel Convention. The potential impacts of plastics and other “novel entities” on human health and ecosystems are largely unknown.
- Even if the Basel Convention is successful in its mission, it will only solve part of the plastics problem, as it doesn’t address the manufacture of plastics or their domestic disposal. Plastics and a wide variety of human-made materials are included in the “novel entities” planetary boundary — one of nine major threats to life on Earth.
Momentum is building for a ‘robust’ biodiversity framework: Q&A with Elizabeth Mrema
- One of the many impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic has been to rally global ambition for a biodiversity framework that sets the world on a path to a sustainable future, says Elizabeth Maruma Mrema.
- Mrema, executive secretary of the U.N. Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), says there’s growing awareness of the importance of biodiversity for everything from food security to the regulation of water and air quality, to pest and disease regulation.
- “World leaders fully recognize that the continued deterioration and degradation of Earth’s natural ecosystems are having major impacts on the lives and livelihoods of people around the world,” she says.
- In an interview with Mongabay founder Rhett A. Butler, Mrema talks about building a robust post-2020 framework after the Aichi Biodiversity Targets fell short, how the conservation sector has changed over her career, and her hopes for the CBD summit coming up later this year.
Ocean protection scheme can yield ‘triple benefits’ study says
- A new study suggests that carefully planned marine protected areas could yield triple benefits for the ocean, helping to maintain biodiversity, while also increasing fish yields and maximizing the ocean’s ability to sequester carbon in seafloor sediment.
- This study is one of the first to quantify the carbon footprint of ocean trawling, which it equates to the yearly emissions of the global aviation industry.
- The researchers suggest that the planning tools in this study could help inform discussions about how to protect 30% of the oceans by 2030, a goal that is expected to be adopted by the U.N. Convention on Biological Diversity later this year.
- Other proposals for how to achieve 30% protection by 2030 have mostly focused on the high seas, but this plan takes all parts of the ocean into consideration.
Nearly half the Amazon’s intact forest on Indigenous-held lands: Report
- A new report from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and the Fund for the Development of the Indigenous Peoples of Latin America and the Caribbean (FILAC) draws on more than 300 studies from the last two decades to demonstrate the protection that Indigenous societies provide for forests in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- According to the team’s research, about 45% of the intact forests in the Amazon Basin are in Indigenous territories.
- The forests occupied by Indigenous communities in the region hold more carbon than all of the forests in either Indonesia or the Democratic Republic of Congo, home to the next two biggest swaths of tropical forest after Brazil.
- The report’s authors say investing in securing land rights for Indigenous communities is a cheap and effective way to address climate change, while also helping these communities recover from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dutch to limit forest biomass subsidies, possibly signaling EU sea change
- The Dutch Parliament in February voted to disallow the issuing of new subsidies for 50 planned forest biomass-for-heat plants, a small, but potentially key victory for researchers and activists who say that the burning of forests to make energy is not only not carbon neutral, but is dirtier than burning coal and bad climate policy.
- With public opinion opposing forest biomass as a climate solution now growing in the EU, the decision by the Netherlands could be a bellwether. In June, the EU will review its Renewable Energy Directive (RED II), whether to continue allowing biomass subsidies and not counting biomass emissions at the smokestack.
- Currently, forest biomass burning to make energy is ruled as carbon neutral in the EU, even though a growing body of scientific evidence has shown that it takes many decades until forests regrow for carbon neutrality to be achieved.
- The forestry industry, which continues to see increasing demand for wood pellets, argues that biomass burning is environmentally sustainable and a viable carbon cutting solution compared to coal.
U.N. report lays out blueprint to end ‘suicidal war on nature’
- According to a new report from the United Nations Environmental Programme, the world faces three environmental “emergencies”: climate change, biodiversity loss, and air and water pollution.
- U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres said we should view nature as “an ally,” not a foe, in the quest for sustainable human development.
- The report draws on assessments that quantify carbon emissions, species loss and pollutant flows to produce what the authors call concrete actions by governments, private companies and individuals that will help address these issues.
500+ experts call on world’s nations to not burn forests to make energy
- Last week, more than 500 top scientists and economists issued a letter to leaders in the US, EU, Japan, South Korea, and the UK, urging them to stop harvesting and burning forests as a means of making energy in converted coal burning power plants.
- The burning of forest biomass to produce electricity has boomed due to this power source having been tolerated as carbon neutral by the United Nations, which enables nations to burn forest biomass instead of coal and not count the emissions in helping them meet their Paris Climate Agreement carbon reduction targets.
- However, current science says that burning forest biomass is dirtier than burning coal, and that one of the best ways to curb climate change and sequester carbon is to allow forests to keep growing. The EU and UK carbon neutrality designations for forest biomass are erroneous, say the 500 experts who urge a shift in global policy:
- “Governments must end subsidies… for the burning of wood…. The European Union needs to stop treating the burning of biomass as carbon neutral…. Japan needs to stop subsidizing power plants to burn wood. And the United States needs to avoid treating biomass as carbon neutral or low carbon,” says the letter.
Will new US EPA head continue his opposition to burning forests for energy?
- Under President Donald Trump the U.S. made moves toward legally enshrining the burning of forest biomass to make energy on an industrial scale as a national policy. That same policy has been embraced by the United Kingdom and European Union, helping them move toward a target of zero carbon emissions — at least on paper.
- However, the carbon neutrality label given to the burning of woody biomass to make energy, first proclaimed under the Kyoto Protocol, then grandfathered into the Paris Climate Agreement, has been found by science over the last decade to be more accurately characterized as a risky carbon accounting loophole.
- Current science says that carbon neutrality achieved from burning wood pellets would take 50-100 years to achieve, time the world doesn’t have to slash its emissions. Further, burning woody biomass is inefficient, and dirtier than coal.
- Michael S. Regan, President Biden’s choice for EPA head, wrestled with the problem of producing wood pellets for use as energy while leading North Carolina’s environmental agency. Now he’ll be contending with the issue on a national and possibly global scale. His past views on the topic are laid out in this story in detail.
French Guiana soy biofuel power plants risk massive Amazon deforestation
- The French government, with the support of President Emmanuel Macron, appears eager to approve legislation that would bypass French environmental law banning large scale deforestation to build several soy-fired biofuel power plants in French Guiana — a French overseas department on the northeast coast of South America.
- Currently, 98% of this region is still covered in Amazon rainforest and mangrove forest. The largest of the proposed biofuel plants — Larivot in Cayenne, the French Guiana capital — would require between 84,000 and 140,000 metric tons of soy per year to generate enough liquid biofuel to power the 120-megawatt plant.
- Growing that much soy would require a large amount of rainforest clearing, totaling between 536 square miles and 892 square miles (nearly three times larger than the land area of New York City). Environmentalists are very concerned over the loss in forest carbon sequestration and harm to French Guiana’s Amazon biodiversity.
- “The fact that France is pushing for policy deviations in French Guiana from European Union sustainability standards is incredibly alarming.… There will be an impact on forests if they change the laws and it could be pretty massive,” said Almuth Ernsting, a biomass researcher with Biofuelwatch, an environmental NGO.
IPBES report details path to exit current ‘pandemic era’
- A new report from the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) calls for a “transformative change” in addressing the causes of virus outbreaks to prevent future pandemics and their devastating consequences.
- Human-driven climate change, the wildlife trade, and conversion of natural ecosystems all increase the potential for the spillover of viruses that infect animals to people.
- The current COVID-19 pandemic is likely to cost the global economy trillions of dollars, yet preventive measures that include identification of the hundreds of thousands of unknown viruses that are thought to exist would cost only a fraction of that total.
Ambitious and holistic goals key to saving Earth’s biodiversity, study says
- A recently published study in the journal Science gives recommendations for decision-makers preparing to set new biodiversity goals at the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in 2021.
- The researchers urge CBD negotiators and policymakers to consider three critical points as they create the new biodiversity goals: the goals must be multifaceted, developed holistically, and highly ambitious.
- “No net loss” of diversity is an example of a highly ambitious goal. Its targets include increasing natural ecosystem area, saving culturally important species, and conserving 90% of Earth’s genetic diversity.
- To turn the tide, the new biodiversity goals must be both highly ambitious and unified, and address ecosystems, species, genetic diversity, and nature’s contributions to people.
World’s protected areas lack connections, recent study finds
- A recent study, published in the journal Nature Communications, has found that 9.7% of the world’s protected areas are connected by land that’s considered intact.
- The study used the human footprint database, which maps out human impacts, such as roads and farmland, across the planet.
- The research showed that, while some countries have protected 17% of their land — a goal set forth in the U.N. Convention on Biological Diversity’s Aichi targets — others, including repositories of biodiversity such as Vietnam and Madagascar, are lagging with little to no connectivity in their networks of reserves.
- The authors suggest that the research could help guide decisions on which areas of land to protect and how to connect them in a way that gives species the best shot at survival.
World leaders endorse ‘Pledge for Nature’ to address planetary emergency
- In the midst of a planetary emergency, 71 world leaders have endorsed a 10 point pledge to accelerate action to reverse nature loss by 2030 and tackle global warming.
- Justin Trudeau, Jacinda Ardern, Emmanuel Macron, Angela Merkel, Prince Charles and Boris Johnson are among those who signed the Leaders’ Pledge for Nature, stating the world is in a “state of planetary emergency.”
- The pledge addresses sustainable food systems and supply chains, eliminating unregulated fishing, reducing air pollution, integrating a “One-Health” approach, and the participation of Indigenous peoples in decision-making.
- News of the leaders’ participation, announced Sept. 28, comes ahead of the United Nations Summit on Biodiversity this week.
We are failing to save the planet’s species, finds UN report
- In an effort to slow the ongoing sixth mass extinction and safeguard the world’s plants and animals, 20 Aichi Biodiversity Targets were established in 2010. According to a recently released U.N. report, not one goal was met completely.
- Little progress has been made towards eliminating, phasing out or reforming subsidies and other incentives potentially harmful to biodiversity. An estimated $500 billion in government subsidies potentially cause environmental harm, the report states.
- The establishment of the target area of marine and freshwater protected areas has been nearly met. Some extinctions, including up to seven mammal and eighteen bird species, have been prevented by conservation efforts in the past decade.
- Looking to the future, the report outlines eight transitions needed to shift humanity away from “business as usual” toward “a society living in harmony with nature.” However, “action is needed now.”
Global wildlife being decimated by human actions, WWF report warns
- Between 1970 and 2016, wild populations of mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles and fish shrank by 68% on average, according to a new report by WWF and the Zoological Society of London.
- The most catastrophic declines were documented from Latin America and the Caribbean, where populations of monitored species contracted by more than 90% during that 46-year period.
- Among the 3,741 populations of freshwater species they tracked, the researchers found overall declines of more than 80%, underlining the threat from excessive extraction of freshwater, pollution and the destructive impacts of damming waterways.
- The assessment aims to grab the attention of world leaders who will gather virtually for the U.N. General Assembly that kicks off Sept. 15.
Are forests the new coal? Global alarm sounds as biomass burning surges
- As climate change rapidly escalates with worsening impacts, and with standing forests vital to achieving global warming solutions, the forest biomass industry is booming. While the industry does utilize wood scraps, it also frequently cuts standing forests to supply wood pellets to be burned in converted coal power plants.
- Though current science has shown that burning the world’s forests to make electricity is disastrous for biodiversity, generates more emissions than coal, and isn’t carbon neutral, a UN policy established in the 1997 Kyoto Protocol erroneously counts energy produced from forest biomass as carbon neutral.
- As a result, nations pay power companies huge subsidies to burn wood pellets, propelling industry growth. While the industry does utilize tree residue, forests are being cut in the US, Canada, Russia, Eastern Europe and Vietnam to supply pellets to the UK, EU and other nations who can claim the energy creates zero emissions.
- So far, the UN has turned a blind eye to closing the climate destabilizing carbon accounting loophole. The Netherlands, which now gets 61% of its renewable energy from biomass, is being urged to wean itself off biomass for energy and heat. If the Dutch do so, advocates hope it could portend closure of Europe’s carbon loophole.
Expand conserved areas to boost global economy ravaged by COVID-19: Report
- Protecting 30% of the world’s lands and oceans would cost $140 billion annually, with the target reachable by 2030, according to a report by an international team of scientists and economists released this month.
- Dramatically increasing protected areas would provide a buffer between human and wildlife communities, helping prevent pandemics such as COVID-19, while also greatly boosting economic growth and sustainability.
- The benefits of implementing the 30% conservation goal outweigh the costs by a five-to-one ratio, according to this first economic analysis of the U.N. protected areas target.
- Some countries have already met this goal, including Bolivia, Germany, Namibia, Poland, Tanzania, Venezuela and Zambia, but Brazil, home to the world’s largest remaining rainforest, is slipping on its previous conservation commitments.
‘Don’t let your cat outside’: Q&A with author Peter Christie
- Journalist Peter Christie has published a new book about the effects that pets have on wildlife and biodiversity.
- In addition to the billions of birds and small mammals killed by free-roaming pets each year, the wild pet trade, invasive pets, disease spread and the pet food industry are harming biodiversity and contributing to the global crisis.
- Christie calls the book “a call to action,” and he says he hopes that humans’ love for their pets might extend to wild species as well.
New database wrangles data on land rights projects around the globe
- The database was created by the Land Portal Foundation, a nonprofit organization based in the Netherlands.
- Currently, the database includes hundreds of land tenure projects from the Global Map of Donors and the U.S. Agency for International Development.
- Users are also able to add projects to the database, allowing people working on land and property rights projects to share information.
COP25: Self-serving G20 spites youth, humanity, world at climate talks
- With 500,000 mostly young climate activists rallying in Madrid streets, COP25 delegates agreed to disagree on nearly everything, with smaller nations striving to pave the way for implementation of a strong Paris Agreement at COP26 in 2020, while G20 nations dragged their feet, obfuscated, and stopped forward progress.
- The climate conference failed to increase national Paris Agreement carbon reduction pledges, likely dooming the world to catastrophic temperature increases above 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100 unless dramatic advances are implemented next year at COP26 in Glasgow, Scotland.
- The G20 and corporate allies kept the closing of carbon accounting loopholes off the agenda: tree plantations will be counted as forests; the burning of wood pellets (as carbon-polluting as coal) will be counted as carbon neutral; and tropical dams now known to produce major methane releases, will be counted as zero carbon sources.
- The U.S., blocked already promised “loss and damage” financial pledges made to the developing world. Double counting of emissions wasn’t banned. No carbon market mechanism was approved. Paris Agreement language assuring “human rights, the right to health, [and] rights of indigenous peoples” was stripped from COP25 official documents.
COP25: Brazil’s official presence diverges widely from its public persona
- Brazil’s government presence was much shrunken at COP25, as compared to past climate conferences, and its delegation even opted out of hosting a presentation space — this despite the country’s being South America’s biggest economy and among the world’s top ten greenhouse gas emitters.
- The administration of President Jair Bolsonaro is controversial for its anti-environmental and anti-indigenous stance. Its policies have prompted resistance by Amazon indigenous and traditional rural populations.
- Environment Minister Ricardo Salles represented one face of Brazil at COP25, speaking publicly twice at the summit, and focusing mostly on agribusiness and economic development opportunities in Amazonia.
- Indigenous peoples and other activists showed a very different face at COP25, emphasizing government failures to protect the environment as well as indigenous and traditional peoples living in the Amazon.
Indonesian dam raises questions about UN hydropower carbon loophole
- North Samatera Hydro Energy (PT NSHE) wants to build the Batang Toru dam, a 510-megawatt project, in Indonesia. But, the discovery of a new primate species, the Tapanuli orangutan (Pongo tapanuliensis), with under 800 individuals mostly inhabiting the project site, has alarmed activists and put the dam’s funding at risk.
- PT NSHE is at the COP25 climate summit this month extolling the project’s contribution to curbing global warming: company reps say the dam will reduce Indonesia’s carbon emissions by 4 percent. In fact, the nation is already counting the proposed project as part of its 2015 Paris Climate Agreement carbon reduction pledge.
- However, while the United Nations and Paris Agreement count most new hydroelectric dams as carbon neutral, recent science shows that tropical dams can emit high levels of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide; this especially occurs when reservoirs are first filled.
- Dams built over the next decade will be adding their greenhouse gas emission load to the atmosphere when the world can least afford it — as the world rushes to cut emissions to prevent a 2 degree Celsius increase in global temperatures. PT NSHE argues its dam will have a small reservoir, so will not produce significant emissions.
COP25: Laura Vargas inspires with power of faith in defense of forests
- While the Madrid United Nations climate summit (COP25) isn’t expected to yield major strides forward in the effort to curb the climate crisis, that hasn’t stopped hundreds of thousands of environmental activists from being there in the remote hope of influencing negotiators to act decisively.
- One such person is Laura Vargas, born in the Peruvian Andes, who saw her native home polluted and desecrated by the giant La Oroya copper smelting plant. At age 71, the former nun and socioenvironmental activist is in Madrid as part of the Interfaith Rainforest Initiative (IRI).
- The IRI hopes to leverage the voices and votes of millions of people of faith in five tropical nations — Brazil, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Indonesia, Colombia and Peru — in order to slow rapidly spreading deforestation, the destruction of biodiversity, and oppression of indigenous peoples.
- Vargas’ passion and energy is devoted to “caring for God’s creation” which encompasses all of nature, including humanity, and especially children. Her presence in Madrid, and the presence of half a million others like her protesting in the streets, could be the most hopeful news and potent force coming out of the COP25 summit.
Hopes dim as COP25 delegates dicker over Article 6 and world burns: critics
- Even as half a million protesters demonstrate outside, UN climate summit negotiators inside Madrid’s COP25 seem blind to the urgency of the climate crisis. In fact, instead of making effective progress, the rules they’re shaping to carry out the Paris Agreement’s Article 6 could worsen carbon emissions, not staunch them.
- For example, Article 6 doesn’t include rules to protect native forests. Instead it could promote turning forests into monoculture tree plantations — providing minimal carbon sequestration and no ecosystem services, while devastating biodiversity. Some critics think the policy may have been shaped by logging interests.
- The so-called biomass carbon accounting loophole is also not up for discussion. Its continuance will allow the burning of biomass wood pellets at power plants, energy production classified by the UN as carbon neutral. However, establised science has found that industrial biomass burning will add significantly to carbon emissions.
- According to activists at COP25, delegates are working to hide emissions and allow UN carbon accounting loopholes. One key aspect of Article 6 found in the original Paris Agreement which guaranteed “the protection of human rights” was deleted from a revised draft Saturday night, as was verbiage assuring civil society and indigenous consultations.
COP25 may put climate at greater risk by failing to address forests
- COP25, originally slated for Brazil, then Chile, but starting today in Madrid comes as global temperatures, sea level rise, wildfires, coral bleaching, extreme drought and storms break new planetary records.
- But delegates have set a relatively low bar for the summit, with COP25’s primary goal to determine rules under Article 6 of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement for creating carbon markets among nations, cities and corporations as a means of incentivizing emission-reduction strategies.
- Policy experts warn that global forest conservation is not yet being actively incentivized as part of carbon market discussions, a possible lapse apparently backed by Brazil and the government of Jair Bolsonaro which has declared its plan to develop the Amazon basin — the world’s largest remaining rainforest and vital to sequestering carbon to curb climate change.
- COP25 also seems unlikely to address the UN biomass carbon accounting loophole, which allows nations to convert obsolete coal plants to burn wood pellets to produce energy, with the carbon emitted counted as “zero emissions” equivalent to solar and wind. Scientists warn that biomass burning, far from being carbon neutral, is actually worse than burning coal.
Healthy ecosystems, healthy humans: ‘One Health’ broadens its scope
- At an Oct. 25 conference in Berlin, conservation and public health leaders issued 10 principles aimed at encouraging cross-disciplinary research and efforts to address both human health and environmental problems.
- The principles, part of the One Health movement, grew out of the Manhattan Principles introduced in 2004.
- The declaration acknowledges that the world’s poor often suffer the most as a result of environmental degradation.
- However, the conference organizers point out that climate change has global reach and must be addressed from both the environmental and health perspectives.
What’s at stake after Chile cancels its hosting of COP25?
- Massive protests triggered by social unrest over economic, justice and environmental issues have forced Chile to cancel its hosting of this year’s U.N. climate change summit in December.
- As the organizer of the 25th Conference of Parties, Chile was to have led the effort to bolster ambitions in the fight against climate change aimed at ensuring that global temperatures don’t increase by more than 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial levels.
- On Oct. 31, a day after Chile’s president announced the cancellation, Spain offered to hold the conference on the scheduled dates, Dec. 2-13, in Madrid.
Biodiversity ‘not just an environmental issue’: Q&A with IPBES ex-chair Robert Watson
- The World Bank and IMF meetings from Oct. 14-20 will include discussions on protecting biodiversity and the importance of investing in nature.
- A recent U.N. report found that more than 1 million species of plants and animals face extinction.
- In a conversation with Mongabay, Robert Watson, who chaired the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services that produced the report, discusses the economic value of biodiversity.
$65 million deal to protect Congo’s forests raises concerns
- The Central African Forest Initiative negotiated a deal with the Republic of Congo for $65 million in funding.
- The aim of the initiative is to protect forest while encouraging economic development.
- But environmental organizations criticized the timing and the wording of the agreement, which they argue still allows for oil drilling and exploration that could harm peatlands and forest.
- Two companies in the Republic of Congo recently found oil beneath the peatlands that could nearly triple the Central African country’s daily production.
At the UN, losing the race against time to fight climate change
- World leaders gathered on Sept. 23 to address the climate crisis, but activists say they still aren’t doing enough.
- Although nearly 70 countries committed themselves to net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, aside from the European Union most were relatively small and largely incidental to the global economy.
- The urgency of the summit was underscored by leaked details of a U.N. report set to be released this week, which suggests sea ice is melting much faster than expected and that irreversible tipping points have already been reached.
‘From possibility to certainty’: Climate strikers seek action to avert disaster
- Youth activists taking part in the global climate strike have underscored the urgency of taking meaningful action to mitigate the environmental and humanitarian disasters posed by the climate crisis.
- Many low-lying territories in Asia and the Pacific are already struggling with rising sea levels, posing a major challenge for governments dealing with unprecedented levels of internal displacement.
- The activists have also filed a petition with the U.N. Human Rights Commission, seeking to hold polluters accountable for the human rights violations arising from the climate crisis.
- They also want to countries like the Philippines, one of those considered most vulnerable to climate change impacts, to fight harder for justice from richer, more polluting countries.
Youth climate strikes sweep Asia ahead of UN Climate Action Summit
- When Super-Hurricane Haiyan descended on the Philippines in 2013, it not only left behind more than 7,400 casualties and nearly $5 billion in destruction. It also helped birth a strong youth climate justice movement.
- That movement is now surging across Southeast Asia, with major climate strikes by students in the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Myanmar, Thailand and Cambodia on September 20.
- Such acts of defiance are not easy in Asia, where deference and obedience to parents and elders is deeply ingrained. But with the whole world at risk, Asia’s young people are in the streets and determined to save the future for their nations and themselves.
All set to strike: Students, youths and activists clamor for climate justice
- Millions of young people around the world are expected to go on strike to demand immediate and meaningful action by governments and corporations to tackle the climate crisis.
- Youth activists have gathered in New York ahead of the U.N. climate summit there, where they took part in a people’s summit supported by more than 200 environmental and human rights groups.
- A key aspect of the climate injustice being highlighted is the fact that people in poorer countries will be hit hardest by the impacts of a changing climate.
- In the Philippines, one of the countries at greatest risk from those impacts, the government has backed the youth-led climate strike and called on developed countries to step up their climate actions.
As climate change disrupts the annual monsoon, India must prepare (Commentary)
- Over the past few decades, India’s total annual rainfall averages haven’t changed but the intensity of precipitation has increased as extreme weather events (EWEs) become more frequent and widespread. Today, the country witnesses more episodes of extremely heavy rainfall, as compared to the past’s consistent, well spread out seasonal rains.
- The nation’s meteorological department already admits that this is a clear impact of climate change. These intense storms pose a huge danger to India’s agriculture-based economy and to millions of farmers whose livelihoods still largely rely upon a consistent rainfall season. There are also periods of droughts interspersed with floods.
- The good news is that Indian authorities are aware of the change and are trying to tackle the impacts of shifting rainfall patterns and adapt to them.
- These extreme weather events are of global significance since more than 1.8 billion people live on the Indian subcontinent, and the impact in the South Asian region has economic fallout in other parts of the world. This post is a commentary. Views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
UN and policymakers, wake up! Burning trees for energy is not carbon neutral (commentary)
- On September 23, the signatories of the Paris Climate Agreement will gather at the United Nations for a Climate Action Summit to step up their carbon reduction pledges in order to prevent catastrophic climate change, while also kicking off Climate Week events in New York City.
- However, the policymakers, financiers, and big green groups organizing these events will almost certainly turn a blind eye toward renewable energy policies that subsidize forest wood burned for energy as if it is a zero emissions technology like wind or solar.
- Scientists have repeatedly warned that burning forests is not in fact carbon neutral, and that doing so puts the world at risk of overshooting the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C target.
- But that message has fallen on deaf ears, as lucrative renewable energy subsidies have driven exponential growth in use of forest wood as fuel. The world’s nations must stop subsidizing burning forest biomass now to protect forests, the climate, and our future. This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author.
Worldwide deforestation rising despite bold commitments, report finds
- In 2014, the New York Declaration on Forests set out bold commitments to stem deforestation, cutting it in half by 2020 and ending it entirely by 2030, along with global forest restoration targets.
- But a new assessment finds that, globally, the loss of forests is on the rise, at rates that are around 40 percent higher than five years ago when the agreement was signed.
- The report’s authors say that, despite the “sobering” findings, the assessment should serve as a call to action that more needs to be done to address deforestation and forest degradation.
REDD+ more competitive than critics believe, study finds
- Critics have argued that the strategy known as REDD+, or reducing emissions from deforestation and forest degradation, hasn’t adequately slowed emissions from forest loss in developing countries in the way it was intended.
- Introduced in 2007, REDD+ is meant to help individual countries earn money for development when they lower the amount of released carbon from clearing and degrading forests.
- In a recent paper focused on the South American country of Guyana, a team of researchers argues that the problems with REDD+ stem from its implementation at the project level.
- REDD+ implementation across the jurisdiction of an entire country would address nearly all of the problems with individual REDD+ projects, and societies would benefit more financially than they currently do from commercial forest uses such as gold mining and logging, the researchers say.
Carbon to burn: UK net-zero emissions pledge undermined by biomass energy
- The United Kingdom and the European Union are setting goals to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. But that declaration is deeply flawed, analysts say, due to a long-standing United Nations carbon accounting loophole that turns a blind eye toward the conversion of coal burning power plants to burning wood pellets.
- While the cutting of trees to convert them to wood pellets to produce energy is ultimately carbon neutral — if an equal number of new trees are planted — the regrowth process requires 50 to 100 years. That means wood pellets burned today, and in coming decades, will be adding a massive carbon load to the atmosphere.
- That carbon will add significantly to global warming — bringing more sea level rise, extreme weather, and perhaps, climate catastrophe — even as official carbon counting by the UN provides a false sense of security that we are effectively reducing emissions to curb climate change.
- Unless the biomass loophole is dealt with, the risk is very real that the world could easily overshoot its Paris Agreement targets, and see temperatures rise well above the 1.5 degrees Celsius safe limit. At present, there is no official move to address the biomass loophole.
’Livestock revolution’ triggered decline in global pasture: Report
- Since 2000, the area of land dedicated for livestock pasture around the world has declined by 1.4 million square kilometers (540,500 square miles) — an area about the size of Peru.
- A new report attributes the contraction to more productive breeds, better animal health and higher densities of animals on similar amounts of land.
- The report’s authors say that technological solutions could help meet rising demand for meat and milk in developing countries, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, without reversing the downward trend.
Dam in Ethiopia has wiped out indigenous livelihoods, report finds
- A dam in southern Ethiopia built to supply electricity to cities and control the flow of water for irrigating industrial agriculture has led to the displacement and loss of livelihoods of indigenous groups, the Oakland Institute has found.
- On June 10, the policy think tank published a report of its research, demonstrating that the effects of the Gibe III dam on the Lower Omo River continue to ripple through communities, forcing them onto sedentary farms and leading to hunger, conflict and human rights abuses.
- The Oakland Institute applauds the stated desire of the new government, which came to power in April 2018, to look out for indigenous rights.
- But the report’s authors caution that continued development aimed at increasing economic productivity and attracting international investors could further marginalize indigenous communities in Ethiopia.
’Green’ bonds finance industrial tree plantations in Brazil
- The Environmental Paper Network (EPN), a group of some 140 NGOs with the goal of making the pulp and paper industry more sustainable, released a briefing contending that green or climate bonds issued by Fibria, a pulp and paper company, went to maintaining and expanding plantations of eucalyptus trees.
- The report suggests that the Brazilian company inflated the amount of carbon that new planting would store.
- The author of the briefing also questions the environmental benefits of maintaining industrial monocultures of eucalyptus, a tree that requires a lot of water along with herbicides, pesticides and fertilizer that can impact local ecosystems and human communities.
Climate change spurs deadly virus in frogs in the U.K.
- As temperatures climb, ranaviruses cause more frog deaths over a longer part of the year, according to a new study.
- The researchers combined data from outbreaks of disease caused by ranaviruses in common frogs (Rana temporaria) with laboratory investigations.
- They say that shaded areas and deeper ponds could provide refuges for afflicted animals that might slow the spread of the virus, but they also caution that this “short-term solution” is only a stopgap as the warming climate continues to make life difficult for amphibians.
’Unprecedented’ loss of biodiversity threatens humanity, report finds
- The U.N.’s Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services released a summary of far-reaching research on the threats to biodiversity on May 6.
- The findings are dire, indicating that around 1 million species of plants and animals face extinction.
- The full 1,500-page report, to be released later this year, raises concerns about the impacts of collapsing biodiversity on human well-being.
Scientists urge overhaul of the world’s parks to protect biodiversity
- A team of scientists argues that we should evaluate the effectiveness of protected areas based on the outcomes for biodiversity, not simple the area of land or ocean they protect.
- In a paper published April 11 in the journal Science, they outline the weaknesses of Aichi Biodiversity Target 11, which set goals of protecting 17 percent of the earth’s surface and 10 percent of its oceans by 2020.
- They propose monitoring the outcomes of protected areas that measure changes in biodiversity in comparison to agreed-upon “reference” levels and then using those figures to determine how well they are performing.
30 percent by 2030? Study maps out how to protect the world’s oceans
- Scientists have mapped out an enormous network of potential marine protected areas that cover more than one-third of the world’s oceans and represent all marine ecosystem categories.
- The proposed network is part of a wider movement to get countries to commit to protecting 30 percent of the oceans by 2030. Governments are already working toward an international pledge to protect at least 10 percent by 2020.
- The scientists released their report outlining the network on April 4, a day before the conclusion of the second round of negotiations at the United Nations toward a landmark treaty to address the ongoing decline of marine biodiversity on the high seas.
EU sued to stop burning trees for energy; it’s not carbon neutral: plaintiffs
- Plaintiffs in five European nations and the U.S. filed suit Monday, 4 March, in the European General Court in Luxembourg against the European Union. At issue is the EU’s rapid conversion of coal-burning powerplants to burn wood pellets and chips, a process known as bioenergy. Activists see the EUs bioenergy policies as reckless and endangering the climate.
- Bioenergy was classified as carbon neutral under the Kyoto Protocol, meaning that nations don’t need to count wood burning for energy among their Paris Agreement carbon emissions. However, studies over the last 20 years have found that bioenergy, while technically carbon neutral, is not neutral within the urgent timeframe in which the world must cut emissions.
- In essence, it takes many decades for new tree growth to re-absorb the amount of carbon released from burning mature trees in a single day. But the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change last October said that the world has just 12 years – not decades – to drastically cut emissions or face likely disastrous temperature rise and climate impacts.
- The activists filing suit face a difficult fight. Only EU member states and EU institutions are generally given standing to challenge legislative acts. To gain standing, they will have to prove that they are being impacted by the EU’s bioenergy policies. The activists say that ending bioenergy coal plant conversions is vital if the world is to avoid catastrophic climate change.
Our brains can lead us astray when making ‘eco-friendly’ decisions
- Humans rely on a set of cognitive tools, developed to help us sustain interpersonal relationships, to govern our choices that affect the global climate, a pair of psychologists suggests.
- People who purchase food with “eco-friendly” labeling might be apt to buy more of it thinking of it as an offset, when, in reality, all consumption has a climate cost.
- The team suggests that more accurate labeling could help consumers understand which choices are “less bad” rather than “good” for the environment.
Brazil to receive first-ever results-based REDD+ payment, but concerns remain
- The U.N.’s Green Climate Fund (GCF) has approved the first proposal for REDD+ emissions reductions payments, totaling $96 million for around 19 million tons of emissions reductions.
- However, GFC board members and observer NGOs expressed concern over how the emissions reductions are calculated.
- A study published last month sheds light on the difficulty of accurately calculating changes in forest cover and calls for a more standardized approach.
The case for forests’ prominent role in holding off climate change
- The authors of a new report argue that investment in forests as a climate change mitigation strategy is just as important as addressing emissions from the energy sector.
- Despite the recognized potential contributions of forests to slowing the warming of the earth, they aren’t typically seen as a permanent solution to climate change.
- The authors of the report contend that provisions in the Paris rulebook, approved at the UN climate conference in Poland, are designed to hold countries responsible for changes to their forests so that such ‘reversals’ won’t go unaccounted for.
COP24: Summit a step forward, but fails to address climate urgency
- COP24 ran into overtime over the weekend as delegates rushed to approve the Paris rulebook to set up a detailed mechanism for accomplishing and gauging the carbon reduction pledges made by the world’s nations in Paris at the end of 2015.
- But considering the urgency of action needed – with just 12 years left to act decisively to significantly cut emissions, according to an October IPCC science report – the COP24 summit proved to be less successful than many participants had hoped.
- On the negative side: the U.S., Russia and Saudi Arabia tried to undermine the gravity of the IPCC science report. Brazil successfully scuttled plans for an international carbon market. And COP24 failed to address the bioenergy carbon counting loophole, which incentivizes the harvesting and burning of trees to make energy by calling the process carbon neutral.
- On the positive side, “1,000 tiny steps” were made, including an improved transparency framework for reporting emissions; regular assessments called Global Stocktake to gauge emissions-reduction effectiveness at national levels starting in 2023; and an agreement to set new finance goals in 2020 to help vulnerable nations adapt to a warming world.
COP24: Will they stay or will they go? Brazil’s threat to leave Paris
- In October, Brazil elected far-right candidate Jair Bolsonaro to the presidency. During the campaign, he threatened to withdraw from the Paris Climate Agreement, implement extreme environmental deregulation policies, and introduce mining into Amazon indigenous reserves, while also using incendiary language which may be inciting violence in remote rural areas.
- Just days before his election, Bolsonaro contradicted his past utterances, saying he won’t withdraw from the Paris accord. At COP24, the Brazilian delegation has fielded questions from concerned attendees, but it appears that no one there knows with certainty what the volatile leader will do once in office. He begins his presidency on the first of the year.
- Even if Bolsonaro doesn’t pull out of Paris, his plans to develop the Amazon, removing most regulatory impediments to mining and agribusiness, could have huge ramifications for the global climate. The Amazon, the world’s largest rainforest, stores massive amounts of carbon. Deforestation rates are already going up there, and likely to grow under Bolsonaro.
- Some in Brazil hope that environmental and economic realities will prevent Bolsonaro from fully implementing his plans. Escalating deforestation is already reducing Amazon rainfall, putting aquifers and agribusiness at risk. Agricultural producers also fear global consumer perceptions of Brazil as being anti-environmental could lead to a backlash and boycotts.
COP24: Nations complicit in ignoring bioenergy climate bomb, experts say
- Twenty years ago science told policymakers that bioenergy – the burning of woody biomass – was a sustainable form of energy that was carbon neutral. The current United Nations carbon accounting system follows that guidance. However, new science has found the hypothesis to be wrong: bioenergy has been found to add significantly to carbon emissions.
- However, national delegations at the UN climate summit in Poland, COP24, as they wordsmith the Paris Rulebook, are stonewalling on the matter, doing nothing to close the bioenergy carbon accounting loophole. But nature can’t be fooled, which means that the undercounting of emissions could push the world past a climate catastrophe tipping point.
- Still, with the problem unaddressed, developed nations in the European Union and elsewhere continue burning woody biomass as energy, with the U.S., Canada and other nations happy to profit from the accounting error. Tropical nations like Brazil and Peru are eager to jump on the bioenergy bandwagon, a potential disaster for rainforests and biodiversity.
- Meanwhile, NGOs and scientists at COP24 have sought earnestly to alert the media and COP delegations to the bioenergy climate bomb and its looming risks, even going so far as to write language closing the loophole that could be inserted into the Paris Rulebook now being negotiated, but to no avail.
COP24: Trumpers tout clean coal; protesters call it ‘climate suicide’
- As in 2017, the Trump administration delegation was again at COP, seriously praising coal as a climate solution in a public presentation Monday – but behind the scenes the U.S. delegation is reportedly less incendiary and more cooperative. The Polish government is also heavily promoting the dirtiest of fossil fuels at the two-week-long Katowice event.
- But protestors, subnationals and NGOs are having none of it. COP24 participants treated the Trump administration coal public presentation with outrage, as a freakish sideshow and a joke. They used the event to send the message that decarbonization is the only way forward – as a means of curbing climate change, while boosting local economies and creating jobs.
- “It’s ludicrous for Trump officials to claim that they want to clean up fossil fuels, while dismantling standards that would do just that,” said Dan Lashof, director, World Resources Institute US.
- “More and more companies are committing to renewable energy, reducing emissions, and striving for a just [energy] transition that protects the wellbeing of all workers,” said Aron Cramer, CEO of BSR, a sustainability consulting firm in San Francisco.
COP24: US, Russia, Saudis downplay IPCC report in display of disunity
- The U.S., Russia, Saudi Arabia, and Kuwait rejected language strongly affirming the severity of global warming at the COP24 summit in Poland on Saturday night. The United States is in the process of withdrawing from the Paris Climate Agreement, while Russia has failed so far to ratify the accord.
- Some fear this could signal further obstruction this week by major oil producing nations as national leaders arrive at COP24 to wrestle with resolving a host of difficult issues, including an upping of Paris carbon-reduction pledges, completion of the Paris Rulebook measuring energy production, transportation, agriculture, and deforestation to curb climate change.
- Also, to be worked out, transparency rules on emissions, and plans for wealthy nations to help support poor nations adapt to climate damage. This daunting agenda isn’t helped by the leadership void created when the U.S. pulled back from the Paris agreement after Democrat Barack Obama was replaced as president by Republican Donald Trump.
- At COP24, Tom Steyer, a prominent U.S. environmental activist, said that “nothing short of transformational politics” in the United States will get international climate action back on track. He sees U.S. leadership as essential to preventing the worst impacts of global warming. But such a sea change won’t likely come until after the 2020 presidential election.
COP24: World’s nations gather to grapple with looming climate disaster
- Representatives from nearly 200 nations gathered in Katowice, Poland on Sunday for COP24, the annual meeting of the Conference of the Parties, to move forward on climate action. The goal: keep global temperatures from rising less than 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100.
- Unfortunately for the planet, the COP mechanism has stalled since its 2015 triumph in Paris when the world’s nations agreed to work together to cut carbon emissions. To date, just seven nations, most of them tiny, are on track to reduce emissions to meet the 2 degree Celsius goal, while the U.S. is on track to withdraw from the accord by 2020.
- Today, subnationals – cities, states, regions, businesses, faith organizations, indigenous groups, and NGOs – are providing much of the initiative and impetus for cutting emissions. They are working together in a variety of ways, to reduce deforestation and improve agricultural land use, for example. They will have a major presence at COP24.
- But while subnational efforts are commendable and important, they are not near enough, experts say. With the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, and other scientific organizations, publishing increasingly dire forecasts, urgently calling for climate action, it is vital that nations prioritize climate action and move quickly to decarbonize their economies.
Map pinpoints ‘last chance’ locations of endangered species
- A new assessment updates the last known ranges for nearly 1,500 species of animals and plants at 853 locations around the world.
- The three-year effort is aimed at helping scientists, governments and conservationists identify the threats that could lead to the extinction of these species and find ways to address them.
- Governments are already using this information to identify target areas for conservation to protect the last remaining habitats of threatened species.
- Nearly half of the sites identified lack formal protection, despite many of them having been flagged as important more than a decade ago.
Deforested, degraded land restoration a top priority for African leaders
- African leaders met at a summit to discuss land restoration across the continent on Nov. 13, ahead of the U.N. Biodiversity Conference in Sharm-El-Sheikh, Egypt.
- Representatives from several African countries shared their countries’ pledges to restore hundreds of thousands of square kilometers of degraded and deforested land in the coming decades.
- The summit’s leaders said they hoped the deliberations during the day-long summit would help African countries in both their contributions to international targets and to the improvement of their natural ecosystems for the benefit of their citizens.
Honduras aims to save vital wildlife corridor from deforestation
- Honduras has pledged to remove livestock from the Río Plátano Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage site that’s home to jaguars, tapirs and macaws.
- The reserve is found in the Moskitia region’s rainforests, around 30 percent of which have been cleared in the past 15 years, largely due to cattle and livestock ranching.
- Conservation groups hailed the move as one that would benefit both Honduras and the world because of the region’s biodiversity and carbon stocks.
Thousands of radiated tortoises seized from traffickers in Madagascar
- More than 7,000 critically endangered radiated tortoises were confiscated by authorities from suspected wildlife traffickers in Madagascar on Oct. 24.
- The seizure happened in the same area where a similar bust, involving nearly 10,000 tortoises of the same species, took place in April.
- The NGO Turtle Survival Alliance is working with the Madagascar environment ministry to care for the surviving tortoises.
Scientists, conservationists: Give Nobel Peace Prize to Jane Goodall
- Scientists and conservationists argue that primatologist Jane Goodall should receive the Nobel Peace Prize in 2019.
- Goodall’s groundbreaking research uncovered startling revelations, including tool use by chimpanzees, that blurred the lines between humans and animals.
- Goodall, a U.N. Messenger of Peace, now travels around the world to encourage living in harmony with the natural world.
Tracking the shift of tropical forests from carbon sink to source
- Improved maps of carbon stocks, along with a better understanding of how tropical forests respond to climate change, are necessary to meet the challenge of keeping the global temperature below a 2-degree-Celsius (3.6-degree-Fahrenheit) rise, according to scientist Edward Mitchard of the University of Edinburgh.
- Currently, tropical forests take up roughly the same amount of carbon as is released when they’re cleared or degraded.
- But climatic changes, which lead to more droughts and fires resulting in the loss of tropical trees, could shift the balance, making tropical forests a net source of atmospheric carbon.
Global marine wilderness has dwindled to 13 percent, new map reveals
- New research examining the effects of 19 human stressors on the marine environment shows that only 13 percent of oceans can still be considered wilderness.
- Of the remaining wilderness, much of which is located in the high seas and at the poles, less than 5 percent falls under protection, and climate change and advances in technology could threaten it.
- The authors of the study call for international cooperation to protect the ocean’s wilderness areas, including a “Paris Agreement for the Ocean,” which they hope will be signed in 2020.
To protect the Congolese peatlands, protect local land rights (commentary)
- In 2017, researchers reported the existence of the largest tropical peatland complex in the world in the Congo Basin.
- In early 2018, a team of scientists, including the author, traveled to the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to probe deeper into the peatlands, which cover an area about the size of England and hold some 30 billion tons of carbon.
- Around the same time, the DRC government has awarded logging concessions that overlap with the peatlands, in violation of a 16-year-old moratorium on logging.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
Religious leaders mobilize to protect indigenous people and forests
- Religious leaders joined forces with indigenous peoples from Brazil, Colombia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Indonesia, Meso-America and Peru at the Nobel Peace Center in Oslo in 2017 to launch the Interfaith Rainforest Initiative (IRI).
- The IRI plans to mobilize high profile religious leaders to intervene in policy forums and advocate for forests and indigenous people with support from UN Environment.
- It has been estimated that one third of climate change mitigation is from tropical rainforests and securing land rights for indigenous peoples is an effective and low-cost method of reducing carbon emissions.
Suspected poisoning takes down 11 lions in Uganda park
- Eight cubs and three female lions have been found dead, apparently from eating poisoned meat in Queen Elizabeth National Park.
- Lions, along with other predators, have been in decline across Uganda since the 1970s.
- Recent studies indicate that the country’s growing human population has driven lions out of their former habitats and that the big cats are killed to defend the livestock of local communities.
AI can ‘help us move mountains’ for people and planet, Watson developer says
- IBM Master Developer Neil Sahota believes artificial intelligence (AI) can help humanity ‘move mountains’ in terms of improving lives and the environment.
- Sahota helped develop Watson, the supercomputer which is now being used in a variety of useful ways, like predicting crop yields for farmers in Africa.
- In this interview with Mongabay, he shares multiple examples of AI being used by actors ranging from the UN to NASA and NGOs, for good.
Sarawak’s Penan now have detailed maps of their ancestral homeland
- Some 63 Penan communities came together to create 23 maps of their territory in central Borneo over the past 15 years.
- For three days in late November 2017, the Penan of the region celebrated the completion of the maps.
- The Penan now believe they are armed with the information that will help them hold on to their land in the face of pressure from outside timber and industrial agriculture interests.
Jaguar numbers rising at field sites, WCS says
- WCS reports that jaguar numbers have risen by almost 8 percent a year between 2002 and 2016 at study sites in Central and South America.
- The sites cover around 400,000 square kilometers (154,440 square miles) of jaguar habitat.
- Despite the promising findings, WCS scientists caution that habitat destruction, hunting in response to livestock killings, and poaching for their body parts remain critical threats to jaguars.
Carbon pricing could save millions of hectares of tropical forest: new study
- Recently published research in the journal Environmental Research Letters found that setting a price of $20 per metric ton (about $18/short ton) of carbon dioxide could diminish deforestation by nearly 16 percent and the amount of carbon released into the atmosphere by nearly 25 percent.
- The pair of economists calculated that, as things currently stand, the world stands to lose an India-size chunk of tropical forest by 2050.
- In addition to carbon pricing, stricter policies to halt deforestation, such as those that helped Brazil cut its deforestation rate by 80 percent in the early 2000s, could save nearly 1 million square kilometers (386,000 square miles).
Maps tease apart complex relationship between agriculture and deforestation in DRC
- A team from the University of Maryland’s GLAD laboratory has analyzed satellite images of the Democratic Republic of Congo to identify different elements of the “rural complex” — where many of the DRC’s subsistence farmers live.
- Their new maps and visualizations allow scientists and land-use planners to pinpoint areas where the cycle of shifting cultivation is contained, and where it is causing new deforestation.
- The team and many experts believe that enhanced understanding of the rural complex could help establish baselines that further inform multi-pronged approaches to forest conservation and development, such as REDD+.
Roads, dams and railways: Ten infrastructure stories from Southeast Asia in 2017
- Southeast Asia is one of the epicenters of a global “tsunami” of infrastructure development.
- As the countries in the region work to elevate their economic standing, concerns from scientists and NGOs highlight the potential pitfalls in the form of environmental degradation and destruction that roads, dams and other infrastructure can bring in tow.
- Mongabay had reporters covering the region in 2017. Here are 10 of their stories.
UN General Assembly adopts resolution to move forward with high seas treaty negotiations
- The General Assembly of the United Nations adopted a resolution on Sunday to convene negotiations for an international treaty to protect the marine environments of the high seas.
- Earth’s high seas represent about two-thirds of the oceans, but are not governed by any one international body or agency and there is currently no comprehensive management structure in place to protect the marine life that relies on them.
- According to the Pew Charitable Trusts, the treaty would be the first international agreement to address the impacts of human activities like fishing and shipping on the high seas.
Temer uses controversial deforestation data in speech to UN
- In his speech to the 72nd General Assembly of the United Nations in New York on Monday, Brazil’s president Michel Temer referred to preliminary data showing reduced deforestation that critics say may not be accurate.
- Critics also refute other aspects of his speech, including his touting of Brazil’s renewable energy movement. Hydropower is the country’s largest source of renewable energy, which scientists say can have a huge carbon footprint.
- A protest comprised of representatives from more than 150 organizations gathered in Brasilia on Tuesday in reaction to Temer’s speech.
Pursuing a decent life for all on a sustainable planet (commentary)
- Mounting evidence reminds us how human actions have begun changing the climate and forced an awareness of global warming’s impact on the quality of human life. That awareness will be top of mind for participants in the 72nd Regular Session of the UN General Assembly taking place in New York City this week.
- General Debate in the assembly this year considers the theme of “Focusing on People: Striving for Peace and a Decent Life for All on a Sustainable Planet.”
- That topic deliberately invites discussion about the inter-connectedness of all the world’s people and our dependence on a shared planet if we are to thrive and prosper.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors.
Central Africa’s ivory trade shifts underground, according to new report
- A series of undercover investigations by the NGO TRAFFIC over several years in five Central African countries has revealed a shift in the region from local markets for ivory to an ‘underground’ international trade.
- The resulting report, published Sept. 7, finds that organized crime outfits, aided by high-level corruption, are moving ivory out of Central African to markets abroad, especially in China and other parts of Asia.
- A 2013 study found that elephant numbers in Central Africa’s forests dropped by 62 percent between 2002 and 2011.
Religious leaders: Rainforest protection a ‘moral imperative’
- The three-day event, held in Oslo, Norway, includes discussions between NGOs, government agencies, universities, indigenous groups and major religions.
- The event marks the launch of the Interfaith Rainforest Initiative, which seeks to build on the moral case for rainforest protection with tangible metrics and goals.
- Indigenous and religious leaders from 21 countries attended the event, organized by the UN Development Programme, Rainforest Foundation Norway and Norway’s International Climate and Forest Initiative.
Gabon pledges ‘massive’ protected network for oceans
- The network of marine protected areas covers some 53,000 square kilometers (20,463 square miles) of ocean, an area larger than Costa Rica.
- The marine parks and reserves could also draw tourists eager to catch a glimpse of the humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae), olive ridley sea turtles (Lepidochelys olivacea) and leatherback sea turtles (Dermochelys coriacea) that all shuttle through Gabonese waters.
- Government officials are in the process of overhauling how they manage fisheries, and they hope the move to protect Gabon’s territorial waters will improve the country’s food security and give its citizens a better chance to earn a living from fishing.
Trump failure to lead on climate doesn’t faze UN policymakers in Bonn
- Policymakers from nearly 200 countries are gathering in Bonn this week for climate change talks aimed at fulfilling the promise of the Paris Agreement. U.S. negotiators will be there too, despite President Trump’s denial of climate change and his signaled alliance with the fossil fuel industry.
- Under President Obama, the U.S. played a key leadership role in climate negotiations, bringing China fully on board, and helping broker the landmark 2015 Paris Agreement. President Trump has threatened to withdraw from the pact — a four-year process — and claims he will make a final decision this month. It seems likely China would step into the leadership gap left by the U.S.
- Bonn negotiators remain unfazed by Trump’s climate change denialism or his threat to withdraw from Paris. Every signatory nation is going forward with meeting voluntary carbon reduction pledges. Some policymakers do worry how the parties to the Paris Agreement will make up the loss of billions of dollars in U.S. climate aid promised under Obama, but now denied by Trump.
- The feeling among Bonn participants is that the rest of the world will go forward briskly and effectively in combatting climate change by embracing alternative energy solutions that will bring jobs and prosperity to their countries, while the U.S. will play the role of a rogue nation that will share no part in the resulting economic boon.
Successful forest protection in DRC hinges on community participation
- Forest covers at least 112 million hectares of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Studies from 2013 show that subsistence agriculture and the need for firewood threaten DRC’s forests, and new investments in the countries forests by industrial outfits could contribute to the problem.
- DRC’s leaders have signed on to international agreements and have begun to receive millions of dollars to finance projects aimed at keeping DRC’s forests standing, protecting global climate and reducing poverty.
Science needed for more transparency in Paris climate projections
- According to a new study, forest-rich nations could play a huge role in keeping the temperature rise under 2 degrees Celsius compared to pre-industrial levels, the key metric agreed to at the 2015 UN climate talks in Paris.
- Forests could account for a quarter of emissions reductions to meet targets in the Paris Agreement.
- However, the ways that countries measure emissions differ, making it difficult to track progress.
Is Brazil green washing hydropower? The case of the Teles Pires dam
- The Teles Pires Hydroelectric Company (builder and operator of Brazil’s Teles Pires dam in the Amazon Basin) was awarded a Green Certificate in the “Responsible Social and Environmental Management” category of the Chico Mendes Award, a prize named after the murdered Brazilian eco-hero.
- The company has won other green awards for its construction projects (including Amazon dams), and been awarded carbon credits by the United Nations.
- But critics ask how green the company that built the Tele Pires dam can be when their project wrecked indigenous and traditional communities, led to the dynamiting of an indigenous sacred site, did harm to biodiversity and fisheries, while also likely producing significant carbon emissions.
- The company claims it is not to blame, because it complied with all government regulations during the dam’s construction, and even went further to make the project sustainable. The Teles Pires dam raises key questions about “sustainability,” and who has the right to define it.
Indonesia shifts emissions-reduction burden from energy to forestry sector
- Ahead of the UN climate summit in Paris last year, Indonesia pledged to reduce its emissions growth by 29 percent over business-as-usual levels by 2030, or by 41 percent with adequate international aid.
- Previously, the government had announced that the lion’s share for meeting the commitment would fall on the coal-dependent energy sector.
- Ahead of the latest climate summit in Morocco, however, Indonesia announced a shift in the breakdown that would see the forestry sector carry the heaviest load.
Myanmar’s forests face myriad problems as logging ban continues
- Between 1990 and 2015 Myanmar lost nearly 15 million hectares of forest and other wooded land.
- Approximately 527 mainly UN-led forest user groups manage around 40,000 hectares of in-country forest.
- Illicit cross-border trade of illegal timber continues despite the logging ban set to expire in April 2017.
International treaty targeting illegal fishing takes effect
- Illegal fishing puts the world’s already-strained fish stocks at risk, capturing as much as 26 million metric tons of fish valued at up to $23 billion each year.
- The treaty, known officially as the Agreement on Port State Measures to Prevent, Deter, and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated Fishing, will enter into force this Sunday, June 5.
- It represents an international effort to shore up the global seafood supply by preventing vessels from landing illegal catches.
Climate negotiators focus on carbon credits, underplay human rights
- The climate talks in Bonn Germany this month are looking at reinvigorating the UN’s Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) that provides carbon credits to industrialized nations that invest in clean energy or efficient energy projects in developing countries.
- Over 7,000 CDM-financed projects in more than 100 nations were done since 2006. Critics say some large-scale industrial CDM projects, including dams and more efficient coal burning power plants, have violated the human rights of local and indigenous people.
- Those critics have recommended that the revitalized CDM include protections for local populations, but most UN negotiators in Bonn have showed little interest in including such safeguards, asserting that the great majority of CDM projects don’t violate human rights.
- CDM detractors also question the wisdom of a UN mechanism that allows construction of new coal-fired power plants, which will add to fossil fuel emissions for decades to come. No final decisions will be made in Bonn; that must wait until the COP22 meeting in November.
First round of UN negotiations to regulate high seas fishing concludes
- About 40 percent of commercial fish species spend time on the high seas, where they are caught with few limitations. Experts fear they are being severely depleted.
- Today countries conclude the first round of negotiations at the United Nations in New York City toward a new treaty aimed at conserve biodiversity on the high seas.
- The treaty is expected to be finalized by 2019, at the earliest.
Indigenous Brazilians under threat from killings and resource projects: UN Rapporteur
- United Nations Special Rapporteur on the rights of indigenous peoples Victoria Tauli-Corpuz visited Brazil in March.
- In an end-of-mission statement released on March 17, she concluded that indigenous peoples in Brazil are at risk from an alarming uptick in violence as well as from natural-resource development projects that threaten their existence.
- For instance, in 2014, the Catholic Church-affiliated Indigenist Missionary Council documented the killings of 138 indigenous leaders in Brazil, compared to 92 in 2007, according to Tauli-Corpuz. Gunmen opened fire on one indigenous village just hours after Tauli-Corpuz departed.
- Noting the government’s failure to uphold legal protections enshrined in the Brazilian constitution as well as other factors, such as attempts in Congress to weaken legal protections for indigenous rights and the environment, Tauli-Corpuz warned that “The risk of ethnocidal effects in such contexts cannot be overlooked nor underestimated.”
Indigenous forest activist released from prison amid Cambodian crackdown
- Ven Vorn, imprisoned since October, was convicted of harvesting forest products without authorization and sentenced to one year in prison. However, the judge suspended the remaining seven months of his sentence, allowing his release.
- Vorn was arrested after leading a successful campaign to halt construction of a hydropower dam in the Chong indigenous people’s homeland in Cambodia’s Cardamom Mountains.
- His release occurred even as other environmental activists from the region remain in prison or in exile, part of a wider crackdown by the Cambodian government against its opponents.
Want to end illegal fishing? Make all ships trackable, say researchers
- Some ships already carry automatic identification systems (AIS) — devices that transmit publicly available data about the vessel’s identity, position, and course. But commercial fishing vessels are exempt in many jurisdictions.
- A group of researchers argues that new policies, including mandating that commercial fishing vessels carry AIS devices, are needed to curb illegal fishing, especially over vast stretches of ocean.
- Making vessels trackable will also help prevent collisions with whales and enable officials to monitor undersea mining, among other benefits, the researchers argue.
Norway extends forest conservation initiative
- At the Paris climate convention on Friday, Norwegian Minister of Environment and Climate Tine Sundtoft said the country would extend its International Climate and Forest Initiative through 2030.
- Norway has already put 17 billion krone ($2.5 billion) into supporting forest conservation initiatives.
- Norway said most of its spending will be targeted “towards paying for verified emissions reductions, in line with relevant UNFCCC decisions”. Norway already has performance-based agreements for reducing deforestation with Brazil, Colombia, Ethiopia, Guyana, Indonesia, Liberia, and Ethiopia.
Sneak Peek into Paris: new climate change draft treaty revealed
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors.
- Following the recent flood of national climate change commitments, or Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs), the United Nations uploaded the newest draft of the upcoming Paris Agreement.
- Unlike past installments, the new document resembles a proper draft treaty, rather than a tornado-wrecked brainstorming session. A far cry from the incremental, inch-worm-pace that critics feared, the new draft agreement shows that the Co-Chairs have been listening attentively, and have tried to accelerate negotiations by presenting something more streamlined.
A pre-game analysis of what to expect, and not expect, at COP 21
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors.
- The upcoming COP21 in Paris is expected to be the most important meeting for a very long time for both forests and climate.
- Here Patrick Cage, a Research Fellow at the Carbon Institute, and John-O Niles, the Director of the Carbon Institute, write about the negotiations leading up to the conference.
2015 Equator Prize winners span 19 countries
- The United Nations today announced 21 winners of the 2015 Equator Prize, a prestigious award that recognizes community-led environmental initiatives.
- The winners, selected from a pool of 1,461 nominations across 126 countries, include a wide range of groups from around the world.
- The winners were announced during a ceremony hosted by actor Alec Baldwin
UN resolves to negotiate treaty governing the high seas
The high seas are often called the Wild West of the ocean. These vast oceanic tracts begin 200 miles from shore and fall under no nation’s jurisdiction. And while there are various agreements governing human activities there, there is no comprehensive management framework coordinating them all. That is now likely to change. The United Nations […]
Climate negotiators make key breakthrough on forest protection deal ahead of Paris talks
 A rainforest in Borneo. Photo credit: Rhett Butler. Negotiators at U.N. climate talks in Bonn, Germany, have produced a draft agreement on the technical provisions of a plan to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Known as REDD+, the forest conservation plan is now far more likely to be included in a climate deal […]
A rainforest in Borneo. Photo credit: Rhett Butler. Negotiators at U.N. climate talks in Bonn, Germany, have produced a draft agreement on the technical provisions of a plan to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Known as REDD+, the forest conservation plan is now far more likely to be included in a climate deal […]
Indonesia’s public water movement consolidates after two of its biggest wins
 Water filter chamber at a Palyja treatment plant in Jakarta. Photo: ANTARA/Dhoni Setiawan With the tide of privatized water in Indonesia as close to turning since the dictator Suharto was president, an entire spectrum of stakeholders is scrambling to chart a path forward on the heels of two landmark – and unexpected – court decisions. […]
Water filter chamber at a Palyja treatment plant in Jakarta. Photo: ANTARA/Dhoni Setiawan With the tide of privatized water in Indonesia as close to turning since the dictator Suharto was president, an entire spectrum of stakeholders is scrambling to chart a path forward on the heels of two landmark – and unexpected – court decisions. […]
Seeing the trees but not the forest (commentary)
 Kenneth MacDicken and Francesco Tubiello work at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The views expressed in this commentary are their own. Old-growth rainforest in Malaysian Borneo. Photos by Rhett A. Butler Understanding forest dynamics is necessary for the sound management of forests, for both production and conservation. This includes an […]
Kenneth MacDicken and Francesco Tubiello work at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The views expressed in this commentary are their own. Old-growth rainforest in Malaysian Borneo. Photos by Rhett A. Butler Understanding forest dynamics is necessary for the sound management of forests, for both production and conservation. This includes an […]
An end to unjust conservation? (commentary)
- The views expressed in this commentary are those of the authors.
UN to promote RSPO-certified palm oil as conservation solution
 Oil palm plantation and natural forest in Costa Rica. All photos by Rhett Butler. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has signed an agreement with the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to promote eco-certified palm oil as part of the broader effort to conserve biodiversity. The move, announced Thursday, commits UNEP and RSPO to […]
Oil palm plantation and natural forest in Costa Rica. All photos by Rhett Butler. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has signed an agreement with the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to promote eco-certified palm oil as part of the broader effort to conserve biodiversity. The move, announced Thursday, commits UNEP and RSPO to […]
Behind on biodiversity targets, govts pledge to increase funding for conservation
 Coquerel’s Sifaka (Propithecus coquereli) in Madagascar. Photos by Rhett Butler. On the heels of a report showing that the world is far behind on targets to halve habitat loss, cut pollution, and reduce overfishing, delegates meeting at a United Nations conference in Pyeongchang, South Korea have agreed to increase step up efforts to conserve biodiversity […]
Coquerel’s Sifaka (Propithecus coquereli) in Madagascar. Photos by Rhett Butler. On the heels of a report showing that the world is far behind on targets to halve habitat loss, cut pollution, and reduce overfishing, delegates meeting at a United Nations conference in Pyeongchang, South Korea have agreed to increase step up efforts to conserve biodiversity […]
Researchers create global map of world’s forests circa 1990
 Global distribution of forest cover, circa-1990. Click image to enlarge Researchers have created a global map of the world’s forests in the year 1990, enabling accurate comparisons between past and current deforestation rates. The GIS data underpinning the map is available at LandCover.org. The research, published by University of Maryland scientists in the journal Remote […]
Global distribution of forest cover, circa-1990. Click image to enlarge Researchers have created a global map of the world’s forests in the year 1990, enabling accurate comparisons between past and current deforestation rates. The GIS data underpinning the map is available at LandCover.org. The research, published by University of Maryland scientists in the journal Remote […]
Leaders pledge to end deforestation by 2030
 Cleared timber plantation and peat forest in Indonesia. Photos by Rhett A. Butler. Dozens of companies, non-profit organizations, and governments pledged to work together to halve forest loss by 2020 and end it altogether by 2030. If implemented, the commitment could reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 4.5-8.8 billion tons annually, equivalent to removing a […]
Cleared timber plantation and peat forest in Indonesia. Photos by Rhett A. Butler. Dozens of companies, non-profit organizations, and governments pledged to work together to halve forest loss by 2020 and end it altogether by 2030. If implemented, the commitment could reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 4.5-8.8 billion tons annually, equivalent to removing a […]
Leonard DiCaprio to UN Climate Summit: ‘You can make history or you will be vilified by it’
 DiCaprio: not enough for individuals to make changes, governments and industry must do so as well Actor, environmental activist, and recently named UN Messenger of Peace, Leonardo DiCaprio, spoke today to a UN Climate Summit. The summit, which is hosting the largest gathering of world leaders to address the crisis in five years, is meant […]
DiCaprio: not enough for individuals to make changes, governments and industry must do so as well Actor, environmental activist, and recently named UN Messenger of Peace, Leonardo DiCaprio, spoke today to a UN Climate Summit. The summit, which is hosting the largest gathering of world leaders to address the crisis in five years, is meant […]
The cheap option on climate change: recognize indigenous rights to forests
 Indigenous boy paddles in the Colombian Amazon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Since 2008, governments have invested $1.64 billion in funds to kick-start REDD+, or Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation, the global effort to conserve the world’s forests in order to better mitigate climate change. However, a new report by the Rights and Resources […]
Indigenous boy paddles in the Colombian Amazon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Since 2008, governments have invested $1.64 billion in funds to kick-start REDD+, or Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation, the global effort to conserve the world’s forests in order to better mitigate climate change. However, a new report by the Rights and Resources […]
How do we save the world’s vanishing old-growth forests?
 Scientists say both rich and developing countries must recognize primary forests as a conservation priority. Primary rainforest in Imbak Canyon in the state of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. The forest is home to pygmy elephants, clouded leopard, orangutans, banteng, and proboscis monkeys among thousands of other species. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. There’s nothing in the […]
Scientists say both rich and developing countries must recognize primary forests as a conservation priority. Primary rainforest in Imbak Canyon in the state of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. The forest is home to pygmy elephants, clouded leopard, orangutans, banteng, and proboscis monkeys among thousands of other species. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. There’s nothing in the […]
Norway puts $1.6B into rainforest conservation
 Tropical rainforest. Photos by Rhett Butler. Since 2008 Norway has been the single largest foreign donor to tropical forest conservation, putting more than 10 billion Norwegian Krone, or $1.6 billion, toward programs in several countries under its International Climate and Forest Initiative (NICFI). But how effective have those funds been in actually protecting forests? A […]
Tropical rainforest. Photos by Rhett Butler. Since 2008 Norway has been the single largest foreign donor to tropical forest conservation, putting more than 10 billion Norwegian Krone, or $1.6 billion, toward programs in several countries under its International Climate and Forest Initiative (NICFI). But how effective have those funds been in actually protecting forests? A […]
Trawling: destructive fishing method is turning seafloors to ‘deserts’
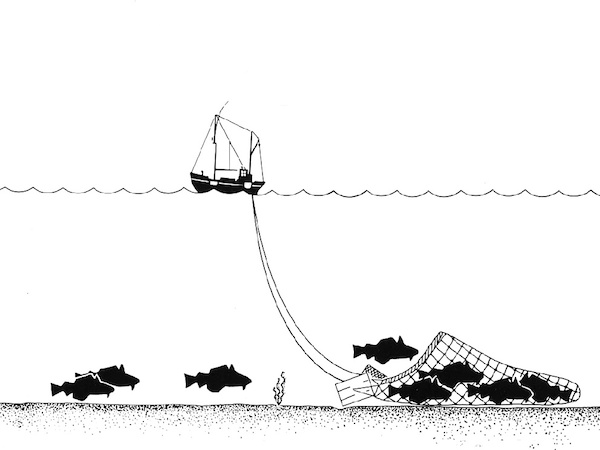 Bottom trawling is a practice used by commercial fisheries around the world in which a large, heavy net is dragged along the ocean floor to scoop up everything in its path. Previous research has linked trawling to significant environmental impacts, such as the harvest of large numbers of non-target species, collectively termed “bycatch,” as well […]
Bottom trawling is a practice used by commercial fisheries around the world in which a large, heavy net is dragged along the ocean floor to scoop up everything in its path. Previous research has linked trawling to significant environmental impacts, such as the harvest of large numbers of non-target species, collectively termed “bycatch,” as well […]
Extreme cold and drought in U.S. linked to climate change
 The U.S. Midwest and Northeast experienced one of the coldest, snowiest winters on record this past season. This might seem contrary to warming trends forecast by climate scientists, but a new analysis released this week in Science points out that climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions may actually have contributed to the well-below average […]
The U.S. Midwest and Northeast experienced one of the coldest, snowiest winters on record this past season. This might seem contrary to warming trends forecast by climate scientists, but a new analysis released this week in Science points out that climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions may actually have contributed to the well-below average […]
Climate change solution? UN touts ambitious (but cheap) investment in renewable energy
 The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
Is 20 millions tons enough? Scientists recommend plastic crackdown as oceans choke
 Every year, 20 million tons of plastic enters the world’s oceans. In 2012, the Rio +20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development dubbed marine plastic litter “a major environmental issue that the world must address,” and asked for management action by 2025. One group of researchers started early and was among the first to take […]
Every year, 20 million tons of plastic enters the world’s oceans. In 2012, the Rio +20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development dubbed marine plastic litter “a major environmental issue that the world must address,” and asked for management action by 2025. One group of researchers started early and was among the first to take […]
U.N.: We can save world’s forests at a fraction of cost of fossil fuels subsidies
 Cumulative deforestation and population growth. Courtesy of UNREDD Investing $30 billion a year in forest conservation — less than seven percent of the $480 billion spent annually on fossil fuels subsidies — could help stop deforestation while accelerating a transition toward a greener global economy, asserts a new report published by the International Resource Panel […]
Cumulative deforestation and population growth. Courtesy of UNREDD Investing $30 billion a year in forest conservation — less than seven percent of the $480 billion spent annually on fossil fuels subsidies — could help stop deforestation while accelerating a transition toward a greener global economy, asserts a new report published by the International Resource Panel […]
REDD+ program to cut deforestation gets final approval in Warsaw
 Rainforest in Sabah. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Negotiators in Warsaw have reached formal agreement on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), a program that aims to compensate tropical countries for protecting their forests. After seven years of discussions, countries approved the final REDD+ text on Friday. The document includes provisions on safeguards; addressing […]
Rainforest in Sabah. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Negotiators in Warsaw have reached formal agreement on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), a program that aims to compensate tropical countries for protecting their forests. After seven years of discussions, countries approved the final REDD+ text on Friday. The document includes provisions on safeguards; addressing […]
Citizen groups walk out of UN Climate Summit to protest lack of ambition
 Australia, Japan and Poland blamed for sabotaging UN Climate Summit talks. Thirteen citizen groups—including Oxfam, Greenpeace, and WWF—have walked out of ongoing climate talks in Warsaw to protest what they view as a lack of ambition and long-stalled progress on combating global climate change. Nearly 200 governments are currently meeting in Warsaw, Poland at the […]
Australia, Japan and Poland blamed for sabotaging UN Climate Summit talks. Thirteen citizen groups—including Oxfam, Greenpeace, and WWF—have walked out of ongoing climate talks in Warsaw to protest what they view as a lack of ambition and long-stalled progress on combating global climate change. Nearly 200 governments are currently meeting in Warsaw, Poland at the […]
UN talks tough to global coal industry
 Yesterday, at the International Coal and Climate Summit—just a couple miles from the ongoing UN Climate Summit—Christiana Figueres delivered a speech unlike anything ever heard at a coal industry meeting before. Figueres, the Executive Director of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), took time off from wrangling world leaders and officials toward a […]
Yesterday, at the International Coal and Climate Summit—just a couple miles from the ongoing UN Climate Summit—Christiana Figueres delivered a speech unlike anything ever heard at a coal industry meeting before. Figueres, the Executive Director of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), took time off from wrangling world leaders and officials toward a […]
Carbon emissions set to hit new record high in 2013
 The amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere in 2013 is expected to hit a new high of 36 billion tonnes, according to a Carbon Budget released today by the Global Carbon Project (GCP). This is a 2.1 percent rise from 2012 based on data from the same group. “We have exhausted about 70 […]
The amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere in 2013 is expected to hit a new high of 36 billion tonnes, according to a Carbon Budget released today by the Global Carbon Project (GCP). This is a 2.1 percent rise from 2012 based on data from the same group. “We have exhausted about 70 […]
60,000 protest in Australia to keep carbon price
 Around 60,000 Australians marched yesterday across the country calling on their government not to go backwards on climate action, according to organizers. Australia has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy with the election of Prime Minister Tony Abbott in September, including legislation to end its carbon pricing, cutting funding to renewable energies, and obstructing […]
Around 60,000 Australians marched yesterday across the country calling on their government not to go backwards on climate action, according to organizers. Australia has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy with the election of Prime Minister Tony Abbott in September, including legislation to end its carbon pricing, cutting funding to renewable energies, and obstructing […]
Japan pledges to raise carbon emissions, instead of cutting them
 Japan’s decision to weaken carbon emissions target a ‘slap in the face’ to poor countries. In 2009, Japan pledged to cut its carbon emissions by 25 percent based on 1990 levels within 11 years. Four years later—including a nuclear meltdown at Fukushima—and Japan has reset its goal with a new target to cut emissions by […]
Japan’s decision to weaken carbon emissions target a ‘slap in the face’ to poor countries. In 2009, Japan pledged to cut its carbon emissions by 25 percent based on 1990 levels within 11 years. Four years later—including a nuclear meltdown at Fukushima—and Japan has reset its goal with a new target to cut emissions by […]
World’s most vulnerable nation to climate change turns to coal power
 Bangladesh’s rush to coal could increase emissions by 160 percent. In October, a global risks analysis company, Maplecroft, named Bangladesh the world’s most vulnerable nation to climate change by 2050. The designation came as little surprise, since Bangladesh’s government and experts have been warning for years of climatic impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather, […]
Bangladesh’s rush to coal could increase emissions by 160 percent. In October, a global risks analysis company, Maplecroft, named Bangladesh the world’s most vulnerable nation to climate change by 2050. The designation came as little surprise, since Bangladesh’s government and experts have been warning for years of climatic impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather, […]
Zero net deforestation is the wrong target, warn experts
 Environmental initiatives that target zero net deforestation may miss their mark when it comes to slowing climate change and protecting biodiversity, warns a commentary published in this week’s issue of the journal Science. While zero net deforestation may seem like a worthy target in efforts to curb forest loss, Sandra Brown and Daniel Zarin argue […]
Environmental initiatives that target zero net deforestation may miss their mark when it comes to slowing climate change and protecting biodiversity, warns a commentary published in this week’s issue of the journal Science. While zero net deforestation may seem like a worthy target in efforts to curb forest loss, Sandra Brown and Daniel Zarin argue […]
Is Australia becoming the new Canada in terms of climate inaction?
 For many concerned about climate change, Australia has suddenly become the new Canada. With the election of Tony Abbott as Prime Minister in September, the land down under has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy, including pushing to end its fledgling carbon emissions program which was only implemented in 2012 and cutting funding for […]
For many concerned about climate change, Australia has suddenly become the new Canada. With the election of Tony Abbott as Prime Minister in September, the land down under has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy, including pushing to end its fledgling carbon emissions program which was only implemented in 2012 and cutting funding for […]
Redeeming REDD: a conversation with Michael Brown
 In Redeeming REDD: Policies, Incentives and Social Feasibility for Avoided Deforestation, anthropologist Michael Brown relays a constructive critique of the contemporary aims, standards and modalities for mitigating climate change by reducing emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD). Brown advocates for REDD as a viable mechanism for the long-term pro-poor conservation and restoration of tropical forests […]
In Redeeming REDD: Policies, Incentives and Social Feasibility for Avoided Deforestation, anthropologist Michael Brown relays a constructive critique of the contemporary aims, standards and modalities for mitigating climate change by reducing emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD). Brown advocates for REDD as a viable mechanism for the long-term pro-poor conservation and restoration of tropical forests […]
Delegate for the Philippines vows to stop eating at climate summit
 Following the devastation wrought by Typhoon Haiyan—which is arguably the strongest typhoon to ever make landfall—Filipino delegate, Naderev ‘Yeb’ Saño, has vowed to go on a fast at the UN Climate Summit that opened today in Warsaw, Poland. Saño made the vow during a powerful speech in which he said he would fast, “until we […]
Following the devastation wrought by Typhoon Haiyan—which is arguably the strongest typhoon to ever make landfall—Filipino delegate, Naderev ‘Yeb’ Saño, has vowed to go on a fast at the UN Climate Summit that opened today in Warsaw, Poland. Saño made the vow during a powerful speech in which he said he would fast, “until we […]
America’s growing inequality helped scuttle the global climate change initiative
 The link between good economic policy and climate change mitigation is instigated by policies such as the triple-bottom line, carbon limitations, and pro-environmental legislation. However, economic inequality is a little explored piece of the successful fight against climate change. For climate change mitigation and good economic policy to work, economic growth must be broad-based. Indeed, […]
The link between good economic policy and climate change mitigation is instigated by policies such as the triple-bottom line, carbon limitations, and pro-environmental legislation. However, economic inequality is a little explored piece of the successful fight against climate change. For climate change mitigation and good economic policy to work, economic growth must be broad-based. Indeed, […]
‘Yet another wakeup call’: global warming is here, it’s manmade, and we’re not doing enough to stop it
 Human actions are responsible for warming the Earth, reconfirms the landmark Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released today, the first mammoth report on the physical science of climate change issued in seven years. Scientists now say they are 95-100 percent certain that human actions—such as burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests—are behind […]
Human actions are responsible for warming the Earth, reconfirms the landmark Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released today, the first mammoth report on the physical science of climate change issued in seven years. Scientists now say they are 95-100 percent certain that human actions—such as burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests—are behind […]
A year after devastating attack, security returns to the Okapi Wildlife Reserve (photos)
 John Lukas will be speaking at the Wildlife Conservation Network Expo in San Francisco on October 12th, 2013. On June 24th of last year, MaiMai Simba rebels, led by an elephant poacher known as Morgan, launched a devastating attack on the headquarters of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve in Epulu, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The […]
John Lukas will be speaking at the Wildlife Conservation Network Expo in San Francisco on October 12th, 2013. On June 24th of last year, MaiMai Simba rebels, led by an elephant poacher known as Morgan, launched a devastating attack on the headquarters of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve in Epulu, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The […]
Why Panama’s indigenous pulled out of the UN’s REDD program
 An Interview with Cacique Betanio Chiquidama, National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples of Panama This week in Lombok, Indonesia, the Policy Board of the United Nations climate change program known as UNREDD is addressing the first major test of the 2007 UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples of the United Nations (UN DRIP), which […]
An Interview with Cacique Betanio Chiquidama, National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples of Panama This week in Lombok, Indonesia, the Policy Board of the United Nations climate change program known as UNREDD is addressing the first major test of the 2007 UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples of the United Nations (UN DRIP), which […]
Logging endangers UNESCO World Heritage Site in Solomon Islands
A world heritage site in the Solomon Islands is “in danger” due to logging, warns the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The East Rennell area of the Solomon Islands was inscribed on the list of world heritage sites in 1998 for its forests and coral reefs. East Rennell is the world’s largest […]
Fertility in Africa could push world population over 11 billion
 The global population could grow by another 4 billion people by the end of the century if fertility rates in Africa don’t decline, according to a new report by the United Nations. Currently around 1.1 billion people live on the continent, but that number could skyrocket to 4.2 billion (a 380 percent increase) by 2100, […]
The global population could grow by another 4 billion people by the end of the century if fertility rates in Africa don’t decline, according to a new report by the United Nations. Currently around 1.1 billion people live on the continent, but that number could skyrocket to 4.2 billion (a 380 percent increase) by 2100, […]
Water and biodiversity pictures for the UN International Day for Biological Diversity
 Today is the United Nations’ International Day for Biological Diversity, an initiative that aims to raise understanding and awareness of biodiversity issues. This year marks the 12th International Day for Biological Diversity. The theme is “Water and Biodiversity”. “Water is central to the well being of people and the planet,” U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said […]
Today is the United Nations’ International Day for Biological Diversity, an initiative that aims to raise understanding and awareness of biodiversity issues. This year marks the 12th International Day for Biological Diversity. The theme is “Water and Biodiversity”. “Water is central to the well being of people and the planet,” U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said […]
Mining companies must turn to recycling as demand for metals grows
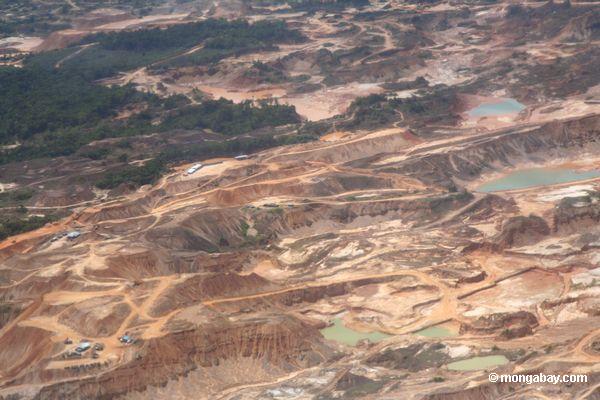 Demand for metals is likely to increase tenfold as developing economies surge ahead, putting severe stress on the natural environment, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (Unep) has warned. The organization has suggested a novel response: bring in the mining companies—often seen as the environmental villains—to sort out the recycling. At present, […]
Demand for metals is likely to increase tenfold as developing economies surge ahead, putting severe stress on the natural environment, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (Unep) has warned. The organization has suggested a novel response: bring in the mining companies—often seen as the environmental villains—to sort out the recycling. At present, […]
China ‘looting’ Africa of its fish
 Just 9% of the millions of tonnes of fish caught by China’s giant fishing fleet in African and other international waters is officially reported to the UN, say researchers using a new way to estimate the size and value of catches. Fisheries experts have long considered that the catches reported by China to the UN’s […]
Just 9% of the millions of tonnes of fish caught by China’s giant fishing fleet in African and other international waters is officially reported to the UN, say researchers using a new way to estimate the size and value of catches. Fisheries experts have long considered that the catches reported by China to the UN’s […]
Madagascar swamped by locust invasion
 More than 60 percent of Madagascar is suffering from a massive locust infestation that is threatening crops and livestock, potentially increasing risks to native wildlife and forests from hungry farmers, warns the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). According to a report issued Monday, the locust plague is especially severe in the central and southern […]
More than 60 percent of Madagascar is suffering from a massive locust infestation that is threatening crops and livestock, potentially increasing risks to native wildlife and forests from hungry farmers, warns the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). According to a report issued Monday, the locust plague is especially severe in the central and southern […]
Indigenous protester killed by masked assailants in Panama over UN-condemned dam
 Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam under construction. Photo courtesy of Robin Oisín Llewellyn. A Ngäbe indigenous Panamanian, Onesimo Rodriguez, opposing the Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam project was killed last Friday evening by four masked men. His body was then thrown into a nearby stream where it was discovered the following day. Onesimo Rodriguez was attacked with […]
Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam under construction. Photo courtesy of Robin Oisín Llewellyn. A Ngäbe indigenous Panamanian, Onesimo Rodriguez, opposing the Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam project was killed last Friday evening by four masked men. His body was then thrown into a nearby stream where it was discovered the following day. Onesimo Rodriguez was attacked with […]
Panama’s indigenous people drop REDD+
 Giant kapok (‘Big Tree’) in Panama’s rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP) has announced it is withdrawing from the United Nation’s REDD+ program following a series of disagreements. The exit of COONAPIP from the negotiating table with UN officials and the Panamanian government will likely be […]
Giant kapok (‘Big Tree’) in Panama’s rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP) has announced it is withdrawing from the United Nation’s REDD+ program following a series of disagreements. The exit of COONAPIP from the negotiating table with UN officials and the Panamanian government will likely be […]
Deforestation, wetlands loss in Brazil and Indonesia generated 45b tons of CO2 in 20 years
 Annual deforestation emissions estimates released by the FAO Deforestation in Borneo. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched a global set of statistics on carbon emissions from deforestation, agriculture and other forms of land use for the 1990-2010 period. The dataset, which is part of the FAO’s […]
Annual deforestation emissions estimates released by the FAO Deforestation in Borneo. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched a global set of statistics on carbon emissions from deforestation, agriculture and other forms of land use for the 1990-2010 period. The dataset, which is part of the FAO’s […]
REDD+ should pave way for more research into genetic studies of tropical species
 Rainforest beetle in Malaysian Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), the UN program to conserve tropical forests by paying developing nations to keep them standing, should go hand-in-hand with increased genetic studies of imperiled tropical biodiversity, according to a new opinion article in mongabay.com’s open access journal Tropical […]
Rainforest beetle in Malaysian Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), the UN program to conserve tropical forests by paying developing nations to keep them standing, should go hand-in-hand with increased genetic studies of imperiled tropical biodiversity, according to a new opinion article in mongabay.com’s open access journal Tropical […]
Climate Summit in Doha characterized by lack of ambition
 Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. Ahead of the 18th United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Doha, Qatar a variety of reports warned that the world was running out of time to avoid dangerous climate change, and that there was a widening gap between what nations have […]
Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. Ahead of the 18th United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Doha, Qatar a variety of reports warned that the world was running out of time to avoid dangerous climate change, and that there was a widening gap between what nations have […]
Wealthy nations’ fossil fuel subsidies dwarf climate financing
 Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. A new analysis finds that 21 wealthy countries spent five-times more on subsidizing fossil fuels in 2011 than they have on providing funds for poor nations to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change. The analysis, by Oil Change […]
Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. A new analysis finds that 21 wealthy countries spent five-times more on subsidizing fossil fuels in 2011 than they have on providing funds for poor nations to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change. The analysis, by Oil Change […]
‘No-one is listening to the entire scientific community’: global carbon emissions set to hit new high
 Coal truck in western China. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial sources are set to hit a new record high this year according to a new analysis by Global Carbon Project. The analysis in Nature Climate Changes predicts that CO2 emissions will rise another 2.6 percent, hitting 35.6 billion […]
Coal truck in western China. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial sources are set to hit a new record high this year according to a new analysis by Global Carbon Project. The analysis in Nature Climate Changes predicts that CO2 emissions will rise another 2.6 percent, hitting 35.6 billion […]
Unique program to leave oil beneath Amazonian paradise raises $300 million
 Black caiman (Melanosuchus niger) with fly near its eye in an ox-bow lake in Yasuni National Park. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. The Yasuni-ITT Initiative has been called many things: controversial, ecological blackmail, revolutionary, pioneering, and the best chance to keep oil companies out of Ecuador’s Yasuni National Park. But now, after a number of ups […]
Black caiman (Melanosuchus niger) with fly near its eye in an ox-bow lake in Yasuni National Park. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. The Yasuni-ITT Initiative has been called many things: controversial, ecological blackmail, revolutionary, pioneering, and the best chance to keep oil companies out of Ecuador’s Yasuni National Park. But now, after a number of ups […]
As Doha Climate Summit kicks off, more ambitious cuts to greenhouse gas emissions needed
 Bangui Windfarm in the Philippines. Photo by: John Ryan Cordova. As the 18th meeting of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) kicks off this morning in oil and gas rich Qatar, the world body warns that much more ambitious greenhouse gas cuts are needed to keep catastrophic climate change at bay. A new […]
Bangui Windfarm in the Philippines. Photo by: John Ryan Cordova. As the 18th meeting of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) kicks off this morning in oil and gas rich Qatar, the world body warns that much more ambitious greenhouse gas cuts are needed to keep catastrophic climate change at bay. A new […]
One in eight people suffer from malnutrition worldwide
 Girl in village in Madagascar. One of the world’s poorest countries, it has been estimated that about 70 percent of Malagasy people suffer from malnutrition. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In a world where technology has advanced to a point where I can instantly have a face-to-face conversation via online video with a friend in […]
Girl in village in Madagascar. One of the world’s poorest countries, it has been estimated that about 70 percent of Malagasy people suffer from malnutrition. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In a world where technology has advanced to a point where I can instantly have a face-to-face conversation via online video with a friend in […]
UNESCO disturbed by gas plans for Peru’s Manu National Park
 Rio Pini Pini flowing out of Manu National Park. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Major concerns about the danger posed by gas exploration in a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Amazon rainforest has prompted UNESCO to promise to lobby the Peruvian government. Manu National Park’s biological diversity exceeds “that of any other place on […]
Rio Pini Pini flowing out of Manu National Park. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Major concerns about the danger posed by gas exploration in a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Amazon rainforest has prompted UNESCO to promise to lobby the Peruvian government. Manu National Park’s biological diversity exceeds “that of any other place on […]
Saving the world’s species from oblivion will cost around $80 billion a year, but still a good deal
 The mongoose lemur (Eulemur mongoz) is listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. If the world is to conserve its wealth of life—species great and small, beautiful and terrible, beloved and unknown—it will cost from $3.41-4.76 billion annually in targeted conservation funds, according to a new study in Science. […]
The mongoose lemur (Eulemur mongoz) is listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. If the world is to conserve its wealth of life—species great and small, beautiful and terrible, beloved and unknown—it will cost from $3.41-4.76 billion annually in targeted conservation funds, according to a new study in Science. […]
First REDD Textbook – Forest and Climate Change: The Social Dimensions of REDD in Latin America – Book Review
 Rainforest in Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Thank you Professor Anthony Hall. After many years, we finally have a REDD textbook that can be used in the undergraduate and graduate classroom. Professor Hall has produced an excellent contribution to the growing Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) literature. He has written both […]
Rainforest in Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Thank you Professor Anthony Hall. After many years, we finally have a REDD textbook that can be used in the undergraduate and graduate classroom. Professor Hall has produced an excellent contribution to the growing Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) literature. He has written both […]
Food prices rise as food aid needed in Middle East and Africa
 A mother with her severely malnourished child in the Sahel region. Photo: UNICEF/Chad/2012/C Tidey. Food prices increased in September on the FAO Food Price Index after two months of stability, while food aid has been urgently called for in Yemen and Syria, and concerns lingered in parts of Africa. Food prices globally rose 3 points […]
A mother with her severely malnourished child in the Sahel region. Photo: UNICEF/Chad/2012/C Tidey. Food prices increased in September on the FAO Food Price Index after two months of stability, while food aid has been urgently called for in Yemen and Syria, and concerns lingered in parts of Africa. Food prices globally rose 3 points […]
Indigenous groups in Panama wait for UN REDD to meet promises
 Giant ceiba tree in Panamanian rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A dispute over the implementation of REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation) in Panama has pitted the United Nations (UN) against the nation’s diverse and large indigenous groups. Represented by the National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP), indigenous groups charge that […]
Giant ceiba tree in Panamanian rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A dispute over the implementation of REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation) in Panama has pitted the United Nations (UN) against the nation’s diverse and large indigenous groups. Represented by the National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP), indigenous groups charge that […]
India’s Western Ghats rainforest declared UNESCO World Heritage Site
 View from Varandha Pass in the Western Ghats. India’s Western Ghats, considered one of the richest biodiversity hotspots in the world, has been dubbed a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In total, 39 different sites in the tropical rainforest—home to Asian elephants, Bengal tigers, lion-tailed macaques, and thousands of other species—have made it under the listing. […]
View from Varandha Pass in the Western Ghats. India’s Western Ghats, considered one of the richest biodiversity hotspots in the world, has been dubbed a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In total, 39 different sites in the tropical rainforest—home to Asian elephants, Bengal tigers, lion-tailed macaques, and thousands of other species—have made it under the listing. […]
10,000 sq mi of Congo rainforest declared World Heritage site
 Infant lowland gorilla in the Congo basin rainforest. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Central Africa has the newest World Heritage site. On Tuesday, the United Nations Education, Science, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the Sangha Tri-National Protected Area complex (TNS) as a World Heritage Site for its density and diversity of rainforest wildlife. Formed by […]
Infant lowland gorilla in the Congo basin rainforest. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Central Africa has the newest World Heritage site. On Tuesday, the United Nations Education, Science, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the Sangha Tri-National Protected Area complex (TNS) as a World Heritage Site for its density and diversity of rainforest wildlife. Formed by […]
Cowards at Rio?: organizations decry ‘pathetic’ agreement
 A Malagasy girl. While Madagascar faces widespread deforestation and erosion, it is estimated that 70 percent of its people suffer from malnutrition. The Rio+20 Summit is attempting to tackle both environmental degradation and poverty, but civil groups say the agreement falls far short of what is needed. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders […]
A Malagasy girl. While Madagascar faces widespread deforestation and erosion, it is estimated that 70 percent of its people suffer from malnutrition. The Rio+20 Summit is attempting to tackle both environmental degradation and poverty, but civil groups say the agreement falls far short of what is needed. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders […]
Scientists give world leaders ‘Fs’ on climate change, biodiversity, and desertification
 Aerial view of Egypt’s drylands. Desertification is a global problem, but a UN treaty on the issue has largely been ignored. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. It seems world leaders may need to retake environmental studies. As the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development opens, the scientific journal, Nature, has evaluated the progress made on three […]
Aerial view of Egypt’s drylands. Desertification is a global problem, but a UN treaty on the issue has largely been ignored. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. It seems world leaders may need to retake environmental studies. As the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development opens, the scientific journal, Nature, has evaluated the progress made on three […]
WWF: biggest villain at Rio+20 is Canada
 U.S. President Barack Obama (left) meets with Canadian Prime Minister (right) Stephen Harper in 2009. WWF criticizes both nations for watering down negotiations at the Rio+20 Summit. Photo by: Pete Souza. Having sent a delegation to the United Nation’s Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the world’s biggest conservation […]
U.S. President Barack Obama (left) meets with Canadian Prime Minister (right) Stephen Harper in 2009. WWF criticizes both nations for watering down negotiations at the Rio+20 Summit. Photo by: Pete Souza. Having sent a delegation to the United Nation’s Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the world’s biggest conservation […]
Experts: ignoring climate change at Rio+20 makes other goals “meaningless”
 Turkana children from northern Kenya, a region which suffers prolonged and extreme droughts. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The Climate Change Task Force (CCTF)—made up of 30 climate scientists, other experts and world leaders—warned today that sidelining climate change at the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development threatened progress on the conference’s other goals, which includes […]
Turkana children from northern Kenya, a region which suffers prolonged and extreme droughts. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The Climate Change Task Force (CCTF)—made up of 30 climate scientists, other experts and world leaders—warned today that sidelining climate change at the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development threatened progress on the conference’s other goals, which includes […]
World failing to meet promises on the oceans
 Industrial tuna fishing has pushed some species to the edge of extinction. Photo by: Alex Hoffard/Greenpeace. Despite a slew of past pledges and agreements, the world’s governments have made little to no progress on improving management and conservation in the oceans, according to a new paper in Science. The paper is released just as the […]
Industrial tuna fishing has pushed some species to the edge of extinction. Photo by: Alex Hoffard/Greenpeace. Despite a slew of past pledges and agreements, the world’s governments have made little to no progress on improving management and conservation in the oceans, according to a new paper in Science. The paper is released just as the […]
Featured video: the Rio speech heard round the world
 Cattle ranches carve into the Amazon rainforest in Brazil. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders, officials, NGOs, businesses, and experts gather in Rio de Janeiro for the UN Summit on Sustainable Development, or more well known as Rio+20, it might be useful to look at the landmark Rio Earth Summit in 1992, which […]
Cattle ranches carve into the Amazon rainforest in Brazil. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders, officials, NGOs, businesses, and experts gather in Rio de Janeiro for the UN Summit on Sustainable Development, or more well known as Rio+20, it might be useful to look at the landmark Rio Earth Summit in 1992, which […]
Should we devote 2014 to wilderness?
 Meandering river in the lowlands of Gabon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. American writer and philosopher, Henry David Thoreau once said, “In wilderness is the preservation of the world.” Anyone who has spent time in vast untouched wild space likely understands Thoreau’s comment. Yet wilderness everywhere—already vanishing—remains imperiled by a variety of threats. To draw […]
Meandering river in the lowlands of Gabon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. American writer and philosopher, Henry David Thoreau once said, “In wilderness is the preservation of the world.” Anyone who has spent time in vast untouched wild space likely understands Thoreau’s comment. Yet wilderness everywhere—already vanishing—remains imperiled by a variety of threats. To draw […]
Scientists: if we don’t act now we’re screwed
 Aerial view of the infamous Río Huaypetue gold mine in the Peruvian Amazon. This remote but massive gold mine is known for the destruction of primary rainforest, widespread mercury pollution, and child and slave labor. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Scientists warn that the Earth may be reaching a planetary tipping point due to a […]
Aerial view of the infamous Río Huaypetue gold mine in the Peruvian Amazon. This remote but massive gold mine is known for the destruction of primary rainforest, widespread mercury pollution, and child and slave labor. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Scientists warn that the Earth may be reaching a planetary tipping point due to a […]
Want to stop climate change: buy fossil fuel deposits
 Coal truck in western China. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Governments, NGOs, and others fighting climate change should consider buying coal and oil deposits—not to exploit them, but to keep them from being exploited, according to a bold new policy paper in the Journal of Political Economy. Economist Bard Harstad with the Kellogg School of […]
Coal truck in western China. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Governments, NGOs, and others fighting climate change should consider buying coal and oil deposits—not to exploit them, but to keep them from being exploited, according to a bold new policy paper in the Journal of Political Economy. Economist Bard Harstad with the Kellogg School of […]
Scientists to Rio+20: save biodiversity to save ourselves
 An as yet unidentified species of gecko on the island of Java, Indonesia. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. World leaders need to do much more to protect the Earth’s millions of species for the services they provide, according to a new scientific consensus statement in Nature based on over 1,000 research papers. Written by 17 […]
An as yet unidentified species of gecko on the island of Java, Indonesia. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. World leaders need to do much more to protect the Earth’s millions of species for the services they provide, according to a new scientific consensus statement in Nature based on over 1,000 research papers. Written by 17 […]
Indigenous rights rising in tropical forests, but big gaps remain
 Children in Dani village in West Papua, Indonesia. The Indonesian constitution gives the government ownership over all land and natural resources. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In the last twenty years, rights for indigenous forest dwellers have expanded significantly, according to a new report by the Rights and Resources Initiative (RRI). Covering nearly thirty tropical […]
Children in Dani village in West Papua, Indonesia. The Indonesian constitution gives the government ownership over all land and natural resources. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In the last twenty years, rights for indigenous forest dwellers have expanded significantly, according to a new report by the Rights and Resources Initiative (RRI). Covering nearly thirty tropical […]
Groups urge President Obama to attend Rio+20 Sustainability Summit
 Deforestation in the Amazon for cattle pasture. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Twenty-two conservation, indigenous, health and science groups have called on U.S. President Barack Obama to attend the up-coming Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development. “Your presence at this Summit would signal its critical importance to all Americans, demonstrate our country’s deep concern over urgent […]
Deforestation in the Amazon for cattle pasture. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Twenty-two conservation, indigenous, health and science groups have called on U.S. President Barack Obama to attend the up-coming Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development. “Your presence at this Summit would signal its critical importance to all Americans, demonstrate our country’s deep concern over urgent […]
Consumption, population, and declining Earth: wake-up call for Rio+20
 Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Featured video: the oceans and Rio+20
A new video by Pew Environment Group and the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) hopes to convince policy-makers attending the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development this summer that urgent action is needed to save the ocean’s from an environmental crisis. The video highlights what an ocean in 2050 might look like if world governments courageously […]
‘The real Hunger Games’: a million children at risk as Sahel region suffers punishing drought
 Livestock lay dead during the East Africa famine last year. Photo by: Oxfam East Africa. The UN warns that a million children in Africa’s Sahel region face malnutrition due to drought in region. In all 15 million people face food insecurity in eight nations across the Sahel, a region that is still recovering from drought […]
Livestock lay dead during the East Africa famine last year. Photo by: Oxfam East Africa. The UN warns that a million children in Africa’s Sahel region face malnutrition due to drought in region. In all 15 million people face food insecurity in eight nations across the Sahel, a region that is still recovering from drought […]
For Earth Day, 17 celebrated scientists on how to make a better world
 Observations of planet Earth from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on July 11, 2005. Photo by: NASA. Seventeen top scientists and four acclaimed conservation organizations have called for radical action to create a better world for this and future generations. Compiled by 21 past winners of the prestigious Blue Planet Prize, a new paper […]
Observations of planet Earth from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on July 11, 2005. Photo by: NASA. Seventeen top scientists and four acclaimed conservation organizations have called for radical action to create a better world for this and future generations. Compiled by 21 past winners of the prestigious Blue Planet Prize, a new paper […]
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
 A rainforest in Borneo. Photo credit: Rhett Butler. Negotiators at U.N. climate talks in Bonn, Germany, have produced a draft agreement on the technical provisions of a plan to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Known as REDD+, the forest conservation plan is now far more likely to be included in a climate deal […]
A rainforest in Borneo. Photo credit: Rhett Butler. Negotiators at U.N. climate talks in Bonn, Germany, have produced a draft agreement on the technical provisions of a plan to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Known as REDD+, the forest conservation plan is now far more likely to be included in a climate deal […] Water filter chamber at a Palyja treatment plant in Jakarta. Photo: ANTARA/Dhoni Setiawan With the tide of privatized water in Indonesia as close to turning since the dictator Suharto was president, an entire spectrum of stakeholders is scrambling to chart a path forward on the heels of two landmark – and unexpected – court decisions. […]
Water filter chamber at a Palyja treatment plant in Jakarta. Photo: ANTARA/Dhoni Setiawan With the tide of privatized water in Indonesia as close to turning since the dictator Suharto was president, an entire spectrum of stakeholders is scrambling to chart a path forward on the heels of two landmark – and unexpected – court decisions. […] Kenneth MacDicken and Francesco Tubiello work at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The views expressed in this commentary are their own. Old-growth rainforest in Malaysian Borneo. Photos by Rhett A. Butler Understanding forest dynamics is necessary for the sound management of forests, for both production and conservation. This includes an […]
Kenneth MacDicken and Francesco Tubiello work at the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The views expressed in this commentary are their own. Old-growth rainforest in Malaysian Borneo. Photos by Rhett A. Butler Understanding forest dynamics is necessary for the sound management of forests, for both production and conservation. This includes an […] Oil palm plantation and natural forest in Costa Rica. All photos by Rhett Butler. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has signed an agreement with the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to promote eco-certified palm oil as part of the broader effort to conserve biodiversity. The move, announced Thursday, commits UNEP and RSPO to […]
Oil palm plantation and natural forest in Costa Rica. All photos by Rhett Butler. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has signed an agreement with the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) to promote eco-certified palm oil as part of the broader effort to conserve biodiversity. The move, announced Thursday, commits UNEP and RSPO to […] Coquerel’s Sifaka (Propithecus coquereli) in Madagascar. Photos by Rhett Butler. On the heels of a report showing that the world is far behind on targets to halve habitat loss, cut pollution, and reduce overfishing, delegates meeting at a United Nations conference in Pyeongchang, South Korea have agreed to increase step up efforts to conserve biodiversity […]
Coquerel’s Sifaka (Propithecus coquereli) in Madagascar. Photos by Rhett Butler. On the heels of a report showing that the world is far behind on targets to halve habitat loss, cut pollution, and reduce overfishing, delegates meeting at a United Nations conference in Pyeongchang, South Korea have agreed to increase step up efforts to conserve biodiversity […] Global distribution of forest cover, circa-1990. Click image to enlarge Researchers have created a global map of the world’s forests in the year 1990, enabling accurate comparisons between past and current deforestation rates. The GIS data underpinning the map is available at LandCover.org. The research, published by University of Maryland scientists in the journal Remote […]
Global distribution of forest cover, circa-1990. Click image to enlarge Researchers have created a global map of the world’s forests in the year 1990, enabling accurate comparisons between past and current deforestation rates. The GIS data underpinning the map is available at LandCover.org. The research, published by University of Maryland scientists in the journal Remote […] Cleared timber plantation and peat forest in Indonesia. Photos by Rhett A. Butler. Dozens of companies, non-profit organizations, and governments pledged to work together to halve forest loss by 2020 and end it altogether by 2030. If implemented, the commitment could reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 4.5-8.8 billion tons annually, equivalent to removing a […]
Cleared timber plantation and peat forest in Indonesia. Photos by Rhett A. Butler. Dozens of companies, non-profit organizations, and governments pledged to work together to halve forest loss by 2020 and end it altogether by 2030. If implemented, the commitment could reduce annual carbon dioxide emissions by 4.5-8.8 billion tons annually, equivalent to removing a […] DiCaprio: not enough for individuals to make changes, governments and industry must do so as well Actor, environmental activist, and recently named UN Messenger of Peace, Leonardo DiCaprio, spoke today to a UN Climate Summit. The summit, which is hosting the largest gathering of world leaders to address the crisis in five years, is meant […]
DiCaprio: not enough for individuals to make changes, governments and industry must do so as well Actor, environmental activist, and recently named UN Messenger of Peace, Leonardo DiCaprio, spoke today to a UN Climate Summit. The summit, which is hosting the largest gathering of world leaders to address the crisis in five years, is meant […] Indigenous boy paddles in the Colombian Amazon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Since 2008, governments have invested $1.64 billion in funds to kick-start REDD+, or Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation, the global effort to conserve the world’s forests in order to better mitigate climate change. However, a new report by the Rights and Resources […]
Indigenous boy paddles in the Colombian Amazon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Since 2008, governments have invested $1.64 billion in funds to kick-start REDD+, or Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation, the global effort to conserve the world’s forests in order to better mitigate climate change. However, a new report by the Rights and Resources […] Scientists say both rich and developing countries must recognize primary forests as a conservation priority. Primary rainforest in Imbak Canyon in the state of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. The forest is home to pygmy elephants, clouded leopard, orangutans, banteng, and proboscis monkeys among thousands of other species. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. There’s nothing in the […]
Scientists say both rich and developing countries must recognize primary forests as a conservation priority. Primary rainforest in Imbak Canyon in the state of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. The forest is home to pygmy elephants, clouded leopard, orangutans, banteng, and proboscis monkeys among thousands of other species. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. There’s nothing in the […] Tropical rainforest. Photos by Rhett Butler. Since 2008 Norway has been the single largest foreign donor to tropical forest conservation, putting more than 10 billion Norwegian Krone, or $1.6 billion, toward programs in several countries under its International Climate and Forest Initiative (NICFI). But how effective have those funds been in actually protecting forests? A […]
Tropical rainforest. Photos by Rhett Butler. Since 2008 Norway has been the single largest foreign donor to tropical forest conservation, putting more than 10 billion Norwegian Krone, or $1.6 billion, toward programs in several countries under its International Climate and Forest Initiative (NICFI). But how effective have those funds been in actually protecting forests? A […] Bottom trawling is a practice used by commercial fisheries around the world in which a large, heavy net is dragged along the ocean floor to scoop up everything in its path. Previous research has linked trawling to significant environmental impacts, such as the harvest of large numbers of non-target species, collectively termed “bycatch,” as well […]
Bottom trawling is a practice used by commercial fisheries around the world in which a large, heavy net is dragged along the ocean floor to scoop up everything in its path. Previous research has linked trawling to significant environmental impacts, such as the harvest of large numbers of non-target species, collectively termed “bycatch,” as well […] The U.S. Midwest and Northeast experienced one of the coldest, snowiest winters on record this past season. This might seem contrary to warming trends forecast by climate scientists, but a new analysis released this week in Science points out that climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions may actually have contributed to the well-below average […]
The U.S. Midwest and Northeast experienced one of the coldest, snowiest winters on record this past season. This might seem contrary to warming trends forecast by climate scientists, but a new analysis released this week in Science points out that climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions may actually have contributed to the well-below average […] The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […] Every year, 20 million tons of plastic enters the world’s oceans. In 2012, the Rio +20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development dubbed marine plastic litter “a major environmental issue that the world must address,” and asked for management action by 2025. One group of researchers started early and was among the first to take […]
Every year, 20 million tons of plastic enters the world’s oceans. In 2012, the Rio +20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development dubbed marine plastic litter “a major environmental issue that the world must address,” and asked for management action by 2025. One group of researchers started early and was among the first to take […] Cumulative deforestation and population growth. Courtesy of UNREDD Investing $30 billion a year in forest conservation — less than seven percent of the $480 billion spent annually on fossil fuels subsidies — could help stop deforestation while accelerating a transition toward a greener global economy, asserts a new report published by the International Resource Panel […]
Cumulative deforestation and population growth. Courtesy of UNREDD Investing $30 billion a year in forest conservation — less than seven percent of the $480 billion spent annually on fossil fuels subsidies — could help stop deforestation while accelerating a transition toward a greener global economy, asserts a new report published by the International Resource Panel […] Rainforest in Sabah. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Negotiators in Warsaw have reached formal agreement on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), a program that aims to compensate tropical countries for protecting their forests. After seven years of discussions, countries approved the final REDD+ text on Friday. The document includes provisions on safeguards; addressing […]
Rainforest in Sabah. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Negotiators in Warsaw have reached formal agreement on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), a program that aims to compensate tropical countries for protecting their forests. After seven years of discussions, countries approved the final REDD+ text on Friday. The document includes provisions on safeguards; addressing […] Australia, Japan and Poland blamed for sabotaging UN Climate Summit talks. Thirteen citizen groups—including Oxfam, Greenpeace, and WWF—have walked out of ongoing climate talks in Warsaw to protest what they view as a lack of ambition and long-stalled progress on combating global climate change. Nearly 200 governments are currently meeting in Warsaw, Poland at the […]
Australia, Japan and Poland blamed for sabotaging UN Climate Summit talks. Thirteen citizen groups—including Oxfam, Greenpeace, and WWF—have walked out of ongoing climate talks in Warsaw to protest what they view as a lack of ambition and long-stalled progress on combating global climate change. Nearly 200 governments are currently meeting in Warsaw, Poland at the […] Yesterday, at the International Coal and Climate Summit—just a couple miles from the ongoing UN Climate Summit—Christiana Figueres delivered a speech unlike anything ever heard at a coal industry meeting before. Figueres, the Executive Director of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), took time off from wrangling world leaders and officials toward a […]
Yesterday, at the International Coal and Climate Summit—just a couple miles from the ongoing UN Climate Summit—Christiana Figueres delivered a speech unlike anything ever heard at a coal industry meeting before. Figueres, the Executive Director of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), took time off from wrangling world leaders and officials toward a […] The amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere in 2013 is expected to hit a new high of 36 billion tonnes, according to a Carbon Budget released today by the Global Carbon Project (GCP). This is a 2.1 percent rise from 2012 based on data from the same group. “We have exhausted about 70 […]
The amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere in 2013 is expected to hit a new high of 36 billion tonnes, according to a Carbon Budget released today by the Global Carbon Project (GCP). This is a 2.1 percent rise from 2012 based on data from the same group. “We have exhausted about 70 […] Around 60,000 Australians marched yesterday across the country calling on their government not to go backwards on climate action, according to organizers. Australia has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy with the election of Prime Minister Tony Abbott in September, including legislation to end its carbon pricing, cutting funding to renewable energies, and obstructing […]
Around 60,000 Australians marched yesterday across the country calling on their government not to go backwards on climate action, according to organizers. Australia has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy with the election of Prime Minister Tony Abbott in September, including legislation to end its carbon pricing, cutting funding to renewable energies, and obstructing […] Japan’s decision to weaken carbon emissions target a ‘slap in the face’ to poor countries. In 2009, Japan pledged to cut its carbon emissions by 25 percent based on 1990 levels within 11 years. Four years later—including a nuclear meltdown at Fukushima—and Japan has reset its goal with a new target to cut emissions by […]
Japan’s decision to weaken carbon emissions target a ‘slap in the face’ to poor countries. In 2009, Japan pledged to cut its carbon emissions by 25 percent based on 1990 levels within 11 years. Four years later—including a nuclear meltdown at Fukushima—and Japan has reset its goal with a new target to cut emissions by […] Bangladesh’s rush to coal could increase emissions by 160 percent. In October, a global risks analysis company, Maplecroft, named Bangladesh the world’s most vulnerable nation to climate change by 2050. The designation came as little surprise, since Bangladesh’s government and experts have been warning for years of climatic impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather, […]
Bangladesh’s rush to coal could increase emissions by 160 percent. In October, a global risks analysis company, Maplecroft, named Bangladesh the world’s most vulnerable nation to climate change by 2050. The designation came as little surprise, since Bangladesh’s government and experts have been warning for years of climatic impacts, including rising sea levels, extreme weather, […] Environmental initiatives that target zero net deforestation may miss their mark when it comes to slowing climate change and protecting biodiversity, warns a commentary published in this week’s issue of the journal Science. While zero net deforestation may seem like a worthy target in efforts to curb forest loss, Sandra Brown and Daniel Zarin argue […]
Environmental initiatives that target zero net deforestation may miss their mark when it comes to slowing climate change and protecting biodiversity, warns a commentary published in this week’s issue of the journal Science. While zero net deforestation may seem like a worthy target in efforts to curb forest loss, Sandra Brown and Daniel Zarin argue […] For many concerned about climate change, Australia has suddenly become the new Canada. With the election of Tony Abbott as Prime Minister in September, the land down under has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy, including pushing to end its fledgling carbon emissions program which was only implemented in 2012 and cutting funding for […]
For many concerned about climate change, Australia has suddenly become the new Canada. With the election of Tony Abbott as Prime Minister in September, the land down under has taken a sudden U-turn on climate policy, including pushing to end its fledgling carbon emissions program which was only implemented in 2012 and cutting funding for […] In Redeeming REDD: Policies, Incentives and Social Feasibility for Avoided Deforestation, anthropologist Michael Brown relays a constructive critique of the contemporary aims, standards and modalities for mitigating climate change by reducing emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD). Brown advocates for REDD as a viable mechanism for the long-term pro-poor conservation and restoration of tropical forests […]
In Redeeming REDD: Policies, Incentives and Social Feasibility for Avoided Deforestation, anthropologist Michael Brown relays a constructive critique of the contemporary aims, standards and modalities for mitigating climate change by reducing emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD). Brown advocates for REDD as a viable mechanism for the long-term pro-poor conservation and restoration of tropical forests […] Following the devastation wrought by Typhoon Haiyan—which is arguably the strongest typhoon to ever make landfall—Filipino delegate, Naderev ‘Yeb’ Saño, has vowed to go on a fast at the UN Climate Summit that opened today in Warsaw, Poland. Saño made the vow during a powerful speech in which he said he would fast, “until we […]
Following the devastation wrought by Typhoon Haiyan—which is arguably the strongest typhoon to ever make landfall—Filipino delegate, Naderev ‘Yeb’ Saño, has vowed to go on a fast at the UN Climate Summit that opened today in Warsaw, Poland. Saño made the vow during a powerful speech in which he said he would fast, “until we […] The link between good economic policy and climate change mitigation is instigated by policies such as the triple-bottom line, carbon limitations, and pro-environmental legislation. However, economic inequality is a little explored piece of the successful fight against climate change. For climate change mitigation and good economic policy to work, economic growth must be broad-based. Indeed, […]
The link between good economic policy and climate change mitigation is instigated by policies such as the triple-bottom line, carbon limitations, and pro-environmental legislation. However, economic inequality is a little explored piece of the successful fight against climate change. For climate change mitigation and good economic policy to work, economic growth must be broad-based. Indeed, […] Human actions are responsible for warming the Earth, reconfirms the landmark Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released today, the first mammoth report on the physical science of climate change issued in seven years. Scientists now say they are 95-100 percent certain that human actions—such as burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests—are behind […]
Human actions are responsible for warming the Earth, reconfirms the landmark Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report released today, the first mammoth report on the physical science of climate change issued in seven years. Scientists now say they are 95-100 percent certain that human actions—such as burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests—are behind […] John Lukas will be speaking at the Wildlife Conservation Network Expo in San Francisco on October 12th, 2013. On June 24th of last year, MaiMai Simba rebels, led by an elephant poacher known as Morgan, launched a devastating attack on the headquarters of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve in Epulu, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The […]
John Lukas will be speaking at the Wildlife Conservation Network Expo in San Francisco on October 12th, 2013. On June 24th of last year, MaiMai Simba rebels, led by an elephant poacher known as Morgan, launched a devastating attack on the headquarters of the Okapi Wildlife Reserve in Epulu, Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The […] An Interview with Cacique Betanio Chiquidama, National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples of Panama This week in Lombok, Indonesia, the Policy Board of the United Nations climate change program known as UNREDD is addressing the first major test of the 2007 UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples of the United Nations (UN DRIP), which […]
An Interview with Cacique Betanio Chiquidama, National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples of Panama This week in Lombok, Indonesia, the Policy Board of the United Nations climate change program known as UNREDD is addressing the first major test of the 2007 UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples of the United Nations (UN DRIP), which […] The global population could grow by another 4 billion people by the end of the century if fertility rates in Africa don’t decline, according to a new report by the United Nations. Currently around 1.1 billion people live on the continent, but that number could skyrocket to 4.2 billion (a 380 percent increase) by 2100, […]
The global population could grow by another 4 billion people by the end of the century if fertility rates in Africa don’t decline, according to a new report by the United Nations. Currently around 1.1 billion people live on the continent, but that number could skyrocket to 4.2 billion (a 380 percent increase) by 2100, […] Today is the United Nations’ International Day for Biological Diversity, an initiative that aims to raise understanding and awareness of biodiversity issues. This year marks the 12th International Day for Biological Diversity. The theme is “Water and Biodiversity”. “Water is central to the well being of people and the planet,” U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said […]
Today is the United Nations’ International Day for Biological Diversity, an initiative that aims to raise understanding and awareness of biodiversity issues. This year marks the 12th International Day for Biological Diversity. The theme is “Water and Biodiversity”. “Water is central to the well being of people and the planet,” U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said […] Demand for metals is likely to increase tenfold as developing economies surge ahead, putting severe stress on the natural environment, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (Unep) has warned. The organization has suggested a novel response: bring in the mining companies—often seen as the environmental villains—to sort out the recycling. At present, […]
Demand for metals is likely to increase tenfold as developing economies surge ahead, putting severe stress on the natural environment, a new report from the United Nations Environment Program (Unep) has warned. The organization has suggested a novel response: bring in the mining companies—often seen as the environmental villains—to sort out the recycling. At present, […] Just 9% of the millions of tonnes of fish caught by China’s giant fishing fleet in African and other international waters is officially reported to the UN, say researchers using a new way to estimate the size and value of catches. Fisheries experts have long considered that the catches reported by China to the UN’s […]
Just 9% of the millions of tonnes of fish caught by China’s giant fishing fleet in African and other international waters is officially reported to the UN, say researchers using a new way to estimate the size and value of catches. Fisheries experts have long considered that the catches reported by China to the UN’s […] More than 60 percent of Madagascar is suffering from a massive locust infestation that is threatening crops and livestock, potentially increasing risks to native wildlife and forests from hungry farmers, warns the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). According to a report issued Monday, the locust plague is especially severe in the central and southern […]
More than 60 percent of Madagascar is suffering from a massive locust infestation that is threatening crops and livestock, potentially increasing risks to native wildlife and forests from hungry farmers, warns the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). According to a report issued Monday, the locust plague is especially severe in the central and southern […] Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam under construction. Photo courtesy of Robin Oisín Llewellyn. A Ngäbe indigenous Panamanian, Onesimo Rodriguez, opposing the Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam project was killed last Friday evening by four masked men. His body was then thrown into a nearby stream where it was discovered the following day. Onesimo Rodriguez was attacked with […]
Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam under construction. Photo courtesy of Robin Oisín Llewellyn. A Ngäbe indigenous Panamanian, Onesimo Rodriguez, opposing the Barro Blanco hydroelectric dam project was killed last Friday evening by four masked men. His body was then thrown into a nearby stream where it was discovered the following day. Onesimo Rodriguez was attacked with […] Giant kapok (‘Big Tree’) in Panama’s rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP) has announced it is withdrawing from the United Nation’s REDD+ program following a series of disagreements. The exit of COONAPIP from the negotiating table with UN officials and the Panamanian government will likely be […]
Giant kapok (‘Big Tree’) in Panama’s rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP) has announced it is withdrawing from the United Nation’s REDD+ program following a series of disagreements. The exit of COONAPIP from the negotiating table with UN officials and the Panamanian government will likely be […] Annual deforestation emissions estimates released by the FAO Deforestation in Borneo. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched a global set of statistics on carbon emissions from deforestation, agriculture and other forms of land use for the 1990-2010 period. The dataset, which is part of the FAO’s […]
Annual deforestation emissions estimates released by the FAO Deforestation in Borneo. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has launched a global set of statistics on carbon emissions from deforestation, agriculture and other forms of land use for the 1990-2010 period. The dataset, which is part of the FAO’s […] Rainforest beetle in Malaysian Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), the UN program to conserve tropical forests by paying developing nations to keep them standing, should go hand-in-hand with increased genetic studies of imperiled tropical biodiversity, according to a new opinion article in mongabay.com’s open access journal Tropical […]
Rainforest beetle in Malaysian Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+), the UN program to conserve tropical forests by paying developing nations to keep them standing, should go hand-in-hand with increased genetic studies of imperiled tropical biodiversity, according to a new opinion article in mongabay.com’s open access journal Tropical […] Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. Ahead of the 18th United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Doha, Qatar a variety of reports warned that the world was running out of time to avoid dangerous climate change, and that there was a widening gap between what nations have […]
Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. Ahead of the 18th United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Doha, Qatar a variety of reports warned that the world was running out of time to avoid dangerous climate change, and that there was a widening gap between what nations have […] Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. A new analysis finds that 21 wealthy countries spent five-times more on subsidizing fossil fuels in 2011 than they have on providing funds for poor nations to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change. The analysis, by Oil Change […]
Coal-powered Castle Gate Power Plant in Ohio. Photo by: David Jolley. A new analysis finds that 21 wealthy countries spent five-times more on subsidizing fossil fuels in 2011 than they have on providing funds for poor nations to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change. The analysis, by Oil Change […] Black caiman (Melanosuchus niger) with fly near its eye in an ox-bow lake in Yasuni National Park. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. The Yasuni-ITT Initiative has been called many things: controversial, ecological blackmail, revolutionary, pioneering, and the best chance to keep oil companies out of Ecuador’s Yasuni National Park. But now, after a number of ups […]
Black caiman (Melanosuchus niger) with fly near its eye in an ox-bow lake in Yasuni National Park. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. The Yasuni-ITT Initiative has been called many things: controversial, ecological blackmail, revolutionary, pioneering, and the best chance to keep oil companies out of Ecuador’s Yasuni National Park. But now, after a number of ups […] Bangui Windfarm in the Philippines. Photo by: John Ryan Cordova. As the 18th meeting of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) kicks off this morning in oil and gas rich Qatar, the world body warns that much more ambitious greenhouse gas cuts are needed to keep catastrophic climate change at bay. A new […]
Bangui Windfarm in the Philippines. Photo by: John Ryan Cordova. As the 18th meeting of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) kicks off this morning in oil and gas rich Qatar, the world body warns that much more ambitious greenhouse gas cuts are needed to keep catastrophic climate change at bay. A new […] Girl in village in Madagascar. One of the world’s poorest countries, it has been estimated that about 70 percent of Malagasy people suffer from malnutrition. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In a world where technology has advanced to a point where I can instantly have a face-to-face conversation via online video with a friend in […]
Girl in village in Madagascar. One of the world’s poorest countries, it has been estimated that about 70 percent of Malagasy people suffer from malnutrition. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In a world where technology has advanced to a point where I can instantly have a face-to-face conversation via online video with a friend in […] Rio Pini Pini flowing out of Manu National Park. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Major concerns about the danger posed by gas exploration in a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Amazon rainforest has prompted UNESCO to promise to lobby the Peruvian government. Manu National Park’s biological diversity exceeds “that of any other place on […]
Rio Pini Pini flowing out of Manu National Park. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Major concerns about the danger posed by gas exploration in a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Amazon rainforest has prompted UNESCO to promise to lobby the Peruvian government. Manu National Park’s biological diversity exceeds “that of any other place on […] The mongoose lemur (Eulemur mongoz) is listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. If the world is to conserve its wealth of life—species great and small, beautiful and terrible, beloved and unknown—it will cost from $3.41-4.76 billion annually in targeted conservation funds, according to a new study in Science. […]
The mongoose lemur (Eulemur mongoz) is listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. If the world is to conserve its wealth of life—species great and small, beautiful and terrible, beloved and unknown—it will cost from $3.41-4.76 billion annually in targeted conservation funds, according to a new study in Science. […] Rainforest in Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Thank you Professor Anthony Hall. After many years, we finally have a REDD textbook that can be used in the undergraduate and graduate classroom. Professor Hall has produced an excellent contribution to the growing Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) literature. He has written both […]
Rainforest in Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Thank you Professor Anthony Hall. After many years, we finally have a REDD textbook that can be used in the undergraduate and graduate classroom. Professor Hall has produced an excellent contribution to the growing Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) literature. He has written both […] A mother with her severely malnourished child in the Sahel region. Photo: UNICEF/Chad/2012/C Tidey. Food prices increased in September on the FAO Food Price Index after two months of stability, while food aid has been urgently called for in Yemen and Syria, and concerns lingered in parts of Africa. Food prices globally rose 3 points […]
A mother with her severely malnourished child in the Sahel region. Photo: UNICEF/Chad/2012/C Tidey. Food prices increased in September on the FAO Food Price Index after two months of stability, while food aid has been urgently called for in Yemen and Syria, and concerns lingered in parts of Africa. Food prices globally rose 3 points […] Giant ceiba tree in Panamanian rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A dispute over the implementation of REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation) in Panama has pitted the United Nations (UN) against the nation’s diverse and large indigenous groups. Represented by the National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP), indigenous groups charge that […]
Giant ceiba tree in Panamanian rainforest. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A dispute over the implementation of REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation) in Panama has pitted the United Nations (UN) against the nation’s diverse and large indigenous groups. Represented by the National Coordinator of Indigenous Peoples in Panama (COONAPIP), indigenous groups charge that […] View from Varandha Pass in the Western Ghats. India’s Western Ghats, considered one of the richest biodiversity hotspots in the world, has been dubbed a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In total, 39 different sites in the tropical rainforest—home to Asian elephants, Bengal tigers, lion-tailed macaques, and thousands of other species—have made it under the listing. […]
View from Varandha Pass in the Western Ghats. India’s Western Ghats, considered one of the richest biodiversity hotspots in the world, has been dubbed a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In total, 39 different sites in the tropical rainforest—home to Asian elephants, Bengal tigers, lion-tailed macaques, and thousands of other species—have made it under the listing. […] Infant lowland gorilla in the Congo basin rainforest. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Central Africa has the newest World Heritage site. On Tuesday, the United Nations Education, Science, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the Sangha Tri-National Protected Area complex (TNS) as a World Heritage Site for its density and diversity of rainforest wildlife. Formed by […]
Infant lowland gorilla in the Congo basin rainforest. Photo by Rhett A. Butler. Central Africa has the newest World Heritage site. On Tuesday, the United Nations Education, Science, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) declared the Sangha Tri-National Protected Area complex (TNS) as a World Heritage Site for its density and diversity of rainforest wildlife. Formed by […] A Malagasy girl. While Madagascar faces widespread deforestation and erosion, it is estimated that 70 percent of its people suffer from malnutrition. The Rio+20 Summit is attempting to tackle both environmental degradation and poverty, but civil groups say the agreement falls far short of what is needed. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders […]
A Malagasy girl. While Madagascar faces widespread deforestation and erosion, it is estimated that 70 percent of its people suffer from malnutrition. The Rio+20 Summit is attempting to tackle both environmental degradation and poverty, but civil groups say the agreement falls far short of what is needed. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders […] Aerial view of Egypt’s drylands. Desertification is a global problem, but a UN treaty on the issue has largely been ignored. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. It seems world leaders may need to retake environmental studies. As the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development opens, the scientific journal, Nature, has evaluated the progress made on three […]
Aerial view of Egypt’s drylands. Desertification is a global problem, but a UN treaty on the issue has largely been ignored. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. It seems world leaders may need to retake environmental studies. As the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development opens, the scientific journal, Nature, has evaluated the progress made on three […] U.S. President Barack Obama (left) meets with Canadian Prime Minister (right) Stephen Harper in 2009. WWF criticizes both nations for watering down negotiations at the Rio+20 Summit. Photo by: Pete Souza. Having sent a delegation to the United Nation’s Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the world’s biggest conservation […]
U.S. President Barack Obama (left) meets with Canadian Prime Minister (right) Stephen Harper in 2009. WWF criticizes both nations for watering down negotiations at the Rio+20 Summit. Photo by: Pete Souza. Having sent a delegation to the United Nation’s Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development, the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the world’s biggest conservation […] Turkana children from northern Kenya, a region which suffers prolonged and extreme droughts. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The Climate Change Task Force (CCTF)—made up of 30 climate scientists, other experts and world leaders—warned today that sidelining climate change at the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development threatened progress on the conference’s other goals, which includes […]
Turkana children from northern Kenya, a region which suffers prolonged and extreme droughts. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. The Climate Change Task Force (CCTF)—made up of 30 climate scientists, other experts and world leaders—warned today that sidelining climate change at the Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development threatened progress on the conference’s other goals, which includes […] Industrial tuna fishing has pushed some species to the edge of extinction. Photo by: Alex Hoffard/Greenpeace. Despite a slew of past pledges and agreements, the world’s governments have made little to no progress on improving management and conservation in the oceans, according to a new paper in Science. The paper is released just as the […]
Industrial tuna fishing has pushed some species to the edge of extinction. Photo by: Alex Hoffard/Greenpeace. Despite a slew of past pledges and agreements, the world’s governments have made little to no progress on improving management and conservation in the oceans, according to a new paper in Science. The paper is released just as the […] Cattle ranches carve into the Amazon rainforest in Brazil. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders, officials, NGOs, businesses, and experts gather in Rio de Janeiro for the UN Summit on Sustainable Development, or more well known as Rio+20, it might be useful to look at the landmark Rio Earth Summit in 1992, which […]
Cattle ranches carve into the Amazon rainforest in Brazil. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. As world leaders, officials, NGOs, businesses, and experts gather in Rio de Janeiro for the UN Summit on Sustainable Development, or more well known as Rio+20, it might be useful to look at the landmark Rio Earth Summit in 1992, which […] Meandering river in the lowlands of Gabon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. American writer and philosopher, Henry David Thoreau once said, “In wilderness is the preservation of the world.” Anyone who has spent time in vast untouched wild space likely understands Thoreau’s comment. Yet wilderness everywhere—already vanishing—remains imperiled by a variety of threats. To draw […]
Meandering river in the lowlands of Gabon. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. American writer and philosopher, Henry David Thoreau once said, “In wilderness is the preservation of the world.” Anyone who has spent time in vast untouched wild space likely understands Thoreau’s comment. Yet wilderness everywhere—already vanishing—remains imperiled by a variety of threats. To draw […] Aerial view of the infamous Río Huaypetue gold mine in the Peruvian Amazon. This remote but massive gold mine is known for the destruction of primary rainforest, widespread mercury pollution, and child and slave labor. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Scientists warn that the Earth may be reaching a planetary tipping point due to a […]
Aerial view of the infamous Río Huaypetue gold mine in the Peruvian Amazon. This remote but massive gold mine is known for the destruction of primary rainforest, widespread mercury pollution, and child and slave labor. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Scientists warn that the Earth may be reaching a planetary tipping point due to a […] An as yet unidentified species of gecko on the island of Java, Indonesia. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. World leaders need to do much more to protect the Earth’s millions of species for the services they provide, according to a new scientific consensus statement in Nature based on over 1,000 research papers. Written by 17 […]
An as yet unidentified species of gecko on the island of Java, Indonesia. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. World leaders need to do much more to protect the Earth’s millions of species for the services they provide, according to a new scientific consensus statement in Nature based on over 1,000 research papers. Written by 17 […] Children in Dani village in West Papua, Indonesia. The Indonesian constitution gives the government ownership over all land and natural resources. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In the last twenty years, rights for indigenous forest dwellers have expanded significantly, according to a new report by the Rights and Resources Initiative (RRI). Covering nearly thirty tropical […]
Children in Dani village in West Papua, Indonesia. The Indonesian constitution gives the government ownership over all land and natural resources. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. In the last twenty years, rights for indigenous forest dwellers have expanded significantly, according to a new report by the Rights and Resources Initiative (RRI). Covering nearly thirty tropical […] Deforestation in the Amazon for cattle pasture. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Twenty-two conservation, indigenous, health and science groups have called on U.S. President Barack Obama to attend the up-coming Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development. “Your presence at this Summit would signal its critical importance to all Americans, demonstrate our country’s deep concern over urgent […]
Deforestation in the Amazon for cattle pasture. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Twenty-two conservation, indigenous, health and science groups have called on U.S. President Barack Obama to attend the up-coming Rio+20 Summit on Sustainable Development. “Your presence at this Summit would signal its critical importance to all Americans, demonstrate our country’s deep concern over urgent […] Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […] Livestock lay dead during the East Africa famine last year. Photo by: Oxfam East Africa. The UN warns that a million children in Africa’s Sahel region face malnutrition due to drought in region. In all 15 million people face food insecurity in eight nations across the Sahel, a region that is still recovering from drought […]
Livestock lay dead during the East Africa famine last year. Photo by: Oxfam East Africa. The UN warns that a million children in Africa’s Sahel region face malnutrition due to drought in region. In all 15 million people face food insecurity in eight nations across the Sahel, a region that is still recovering from drought […] Observations of planet Earth from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on July 11, 2005. Photo by: NASA. Seventeen top scientists and four acclaimed conservation organizations have called for radical action to create a better world for this and future generations. Compiled by 21 past winners of the prestigious Blue Planet Prize, a new paper […]
Observations of planet Earth from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on July 11, 2005. Photo by: NASA. Seventeen top scientists and four acclaimed conservation organizations have called for radical action to create a better world for this and future generations. Compiled by 21 past winners of the prestigious Blue Planet Prize, a new paper […]