Sites: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
topic: Iucn
Social media activity version | Lean version
Bangladesh survey records invasive alien plants threatening protected forests
- According to a survey, 44 exotic invasive plant species were recorded in five protected forests in Bangladesh. Of them, seven species were found to be harmful, with significant environmental impacts on protected forest areas.
- As a signatory of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), the country is committed to protecting ecosystems and biodiversity of flora and fauna.
- To check the number and reduce the negative impacts of the identified alien invasive plant species on ecology and environment, the government has taken five strategic management plans.
Study: More than 900 at-risk species lack international trade protections
- A recent study reveals concerning gaps in trade protections for the most at-risk animal and plant species.
- To identify potential gaps, researchers compared species on the IUCN Red List with those covered by the CITES, the global wildlife trade convention.
- Two-fifths of the species considered at risk due to international wildlife trade, 904 species, aren’t covered by CITES, the study found.
- The researchers suggest steps that the CITES committees can take to incorporate these findings, including both strengthening protections for overlooked species and relaxing trade controls for species that have shown improvement in their conservation status.
Bangladesh’s new red list of plants shows country has already lost seven species
- Bangladesh’s first-ever red list of plant species shows the country has lost seven species in the last century and now risks losing at least another five.
- Researchers involved in the assessments of the conservation status of 1,000 species cited climate change, pollution, deforestation, and poor management of protected areas as major drivers behind the ecological damage.
- The Bangladesh Forest Department is working to protect native plant species through large-scale planting efforts across the country.
Bearded pigs a ‘cultural keystone species’ for Borneo’s Indigenous groups: Study
- A recent study examined the impacts of ecological and sociocultural influences on bearded pig populations in Malaysian Borneo.
- The researchers found that the presence of pigs is “compatible” with Indigenous hunting in certain areas.
- The team’s findings point to the importance of a nuanced understanding of nearby human cultural values and local ecology in determining policies toward hunting.
More than half of palm species may be threatened with extinction, study finds
- Using novel machine-learning techniques, researchers found that of the 1,889 species of palms with enough data to investigate, more than half (56%) may be threatened with extinction.
- Researchers hope that the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning, paired with data from the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, can speed up preliminary evaluations of a species’ conservation status, reduce costs, and avoid bias toward vertebrate animals.
- The study found that nearly half of the functionally distinct species were threatened, as well as nearly one-third of species used by humans (at least 185 palm species). The study also identified high-priority regions for palm conservation including Borneo, Hawai‘i, Jamaica, Madagascar, New Caledonia, New Guinea, the Philippines, Sulawesi, Vanuatu, and Vietnam.
- Like many other threatened plant and animal species, the greatest risk to palms is habitat destruction from agricultural and urban expansion.
‘A bigger deal than it sounds’: Coconut crabs are vanishing, island by island
- Despite being widespread across the Pacific and Indian oceans, coconut crabs are disappearing across their range, according to a new conservation assessment that warns they’re vulnerable to extinction.
- The species, the largest land crab in the world, is threatened by habitat destruction for coastal development and agriculture, as well as by harvesting for the seafood trade.
- The harvesting is also impacting reproductive outcomes for the crabs, given the preference among both consumers and female crabs for bigger male crabs.
- Some conservation groups are already working on the ground in places like Indonesia’s West Papua province to educate community members, tourism operators, guides, and tourists about the importance of coconut crabs.
Deforestation threatens tree kangaroo habitat in Papua New Guinea
- A proposed conservation area in northwestern Papua New Guinea has experienced a substantial surge in deforestation-related alerts, according to satellite data from the University of Maryland.
- The still-unofficial Torricelli Mountain Range Conservation Area is home to critically endangered tree kangaroo species, along with a host of other biodiversity.
- In May 2021, communities voiced concern about road construction that was approaching the boundaries of the proposed conservation area and that the intended target may have been high-value timber species found within the region’s forests.
- Investment in local communities and the protection of the forests that these communities provide have led to an apparent rise in tree kangaroo populations, but logging and other potentially destructive land uses such as conversion to large-scale agriculture remain threats in the Torricellis and throughout Papua New Guinea.
OECM concept may bring more inclusive approach to conserving biodiversity
- Devised under the U.N. Convention on Biological Diversity, “other effective area based conservation measures” (OECM) are an alternative to traditional protected areas, in that they can include any geographically defined area that has a management structure and can show a long-term positive impact on biodiversity.
- OECM supporters say they are potentially a more equitable form of conservation that can work for groups previously disenfranchised or sometimes at odds with traditional conservation, such as some Indigenous groups and local communities as well as sustainable agriculture, fisheries and forestry sectors.
- A key aspect of the OECM definition is that these areas must effectively contribute toward biodiversity, something currently not required of a protected area; but how that is defined and measured in practice will take time to establish.
Deep-sea mining gets a resounding rejection from conservation authorities
- Members of the IUCN World Conservation Congress have voted overwhelmingly in support of a moratorium on deep-sea mining, an activity that conservationists say could cause irreversible damage to the ocean.
- The South Pacific nation of Nauru recently triggered a two-year rule, which would require the International Seabed Authority (ISA) to grant it a license to begin mining under whatever regulations are in place by then.
- Conservationists say there is currently little to no understanding of how deep-sea mining could negatively affect the deep-sea environment.
‘Global Indigenous Agenda’ for land rights, conservation launched at IUCN congress
- In 2016, members of the IUCN, the global conservation authority, voted to change its membership structure and include Indigenous peoples’ organizations as a new constituency.
- The agenda was released following a summit for Indigenous participants at the IUCN World Conservation Congress, and calls for greater recognition of the link between nature conservation and Indigenous land rights.
- Other key issues covered in the agenda include respect for human rights in protected areas, guidelines on access to Indigenous lands for bioprospecting, and support for land defenders.
- The IUCN’s director-general welcomed the agenda, but Indigenous representatives say that policymakers now need to take action in support of it.
One in three tree species is in the red, new global assessment says
- Of the 60,000 known species of trees, 440 are critically endangered, an assessment spearheaded by Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) has found.
- There are more threatened tree species in the world today than there are threatened mammal, reptile, bird and amphibian species combined.
- Among tree biodiversity hotspots, which boast a large number of indigenous trees, Brazil, Indonesia and Malaysia fare poorly.
- Lack of in-country expertise is holding back such initiatives, Frank Mbago, a Tanzanian botanist, told Mongabay.
Conservation needs more women, says Razan Khalifa Al Mubarak
- Razan Khalifa Al Mubarak is in the running to become the first woman from the Arab world to head the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Ms. Al Mubarak is up against two other candidates in the election, which will take place during IUCN’s World Conservation Congress, which starts this week.
- Having served as the managing director of three prominent institutions — the Environment Agency Abu Dhabi (EAD), a government agency; the Mohamed bin Zayed Species Conservation Fund, the philanthropy funded by the crown prince of Abu Dhabi; and Emirates Nature, an NGO affiliated with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) — Ms. Al Mubarak would bring distinct experience to the helm 73-year-old conservation organization.
- In these roles Ms. Al Mubarak has been an advocate for improving inclusivity in conservation, providing resources to communities that have often been marginalized in the sector, including Indigenous peoples and women.
- “It is critical that women have an equal voice in decision-making when it comes to the sustainable use of land, water, and other natural resources,” she told Mongabay founder Rhett A. Butler during a recent interview. “Women are not just lacking an equal seat at the table at a grassroots level. Like many fields dominated by men such as science, engineering, and government, women are also underrepresented in the conservation world.”
For species in the red, IUCN’s new Green Status signals conservation wins
- The IUCN will soon be launching the IUCN Green Status of Species, a new assessment tool that will illuminate the ecological functionality of species within their ranges, and also show how much a species has recovered due to conservation efforts.
- The new framework will classify species into nine recovery categories, and measure the impact of past and present conservation efforts and recovery potential in the short term and long term.
- A team of more than 200 international researchers presented preliminary Green Status assessments for 181 species in a new paper.
- The IUCN Green Status for Species will officially launch online at the start of the IUCN World Conservation Congress in September.
Road construction imperils tree kangaroo recovery in PNG
- The Torricelli Mountains of northwestern Papua New Guinea are home to a wide variety of wildlife, including three species of tree kangaroos.
- Recently, construction of a road that could potentially be used by loggers has pushed closer to the border of a proposed conservation area that, if gazetted, would be the country’s second-largest.
- The Tenkile Conservation Alliance, a Papua New Guinean NGO, has worked with communities for around two decades in the Torricellis with the goal of improving the lives of humans and wildlife living in the mountains.
- Now, the group’s leaders fear that the road could jeopardize a tenuous recovery by several of the area’s threatened tree kangaroo species.
Protected areas now cover nearly 17% of Earth’s surface: U.N. report
- A new report from the United Nations Environment Programme and the International Union for Conservation of Nature reveals that countries are closing in on the target set in 2010 of protecting or conserving 17% of the Earth’s surface.
- Since 2010, the area of the marine environment that’s under protection has more than tripled, although global coverage is less than 8%, falling short of the 10% goal set in Aichi Target 11.
- While there has been some success, international leaders agree there should be more focus on quality as well as quantity in designating protected and conservation areas.
- As the U.N. Biodiversity Conference scheduled for October 2021 in Kunming, China, approaches, the report calls for a stronger emphasis on the contributions of Indigenous and local communities, while also ensuring that the world’s poorest don’t shoulder an outsize burden from these efforts.
Skin in the game? Reptile leather trade embroils conservation authority
- The reptile skin trade is a controversial issue, with some experts saying that harvesting programs help conserve species and provide livelihood benefits, while others say that the trade is fraught with issues and animal welfare concerns.
- From a conservation standpoint, there is evidence that the reptile skin trade is sustainable for some species and in some contexts, but other research suggests that the trade could be decimating wild populations and doing more harm than good.
- Exotic leather is falling out of favor in the fashion industry: Numerous companies and brands have banned products made from reptile skin as well as fur, replacing them with products made from materials such as apple, grape or mushroom leather.
- Experts connected with the IUCN have written open letters and op-eds to lament the decisions of companies to ban exotic leather, arguing that these bans have damaged conservation efforts, but other experts question the IUCN’s unfailing support of an imperfect trade.
Flamingos form lasting friendships, a new study finds
- Flamingos, like humans, form social bonds that can last for years and appear to be important for survival in the wild, a new study shows.
- Researchers studying the bird’s social interactions at a captive center in the U.K. found they tended to make long-standing friendships rather than loose, random connections.
- In addition to the friends they tend to “hang out” with, flamingos also actively avoid some individuals.
- The findings could prove useful in managed breeding programs, to ensure that bonded flamingos aren’t separated from each other.
COVID-19 disrupts a major year for biodiversity policy and planning
- The COVID-19 pandemic has scrambled this year’s packed schedule of international meetings and negotiations to hash out what the future will hold for Earth’s ecosystems and wildlife.
- Amid a string of delayed meetings, today, the IUCN announced that its World Conservation Congress, scheduled for June in Marseille, France, has been postponed to January, 2021.
- Experts worry the world will lose critical time to turn around alarming trends in biodiversity loss and climate change, and that the resources allocated to fight COVID-19 might mean fewer resources for biodiversity initiatives later on.
- Given the new coronavirus’s likely origins in an animal, however, some experts hope the pandemic will motivate efforts to address the relationship between drivers of biodiversity loss and human health, in particular the way land-use change, ecosystem degradation and other drivers are believed to increase the risk of new zoonotic diseases spilling over into humans.
Science-backed policy boosts critically endangered Nassau grouper
- A study, published Jan. 6, has found that the population of Nassau grouper (Epinephelus striatus) around Little Cayman Island more than tripled between 2003 and 2015.
- The researchers attribute the rebound to a scientific monitoring effort by NGOs and universities as well as the Cayman Islands government response to the data.
- The government has closed the fishery and instituted size and catch limits to protect the critically endangered species.
Deforestation for potential rubber plantation raises concerns in Papua New Guinea
- The project, ostensibly for a 125-square-kilometer (48-square-mile) rubber plantation, began in mid-2018.
- Satellite imagery shows that Maxland, working with a local landowner company, has built logging roads and deforested patches of the Great Central Forest on Manus Island.
- Like Papua New Guinea as a whole, Manus is home to a wide variety of unique wildlife — just one aspect of the forest on which human communities have depended for thousands of years.
- Government forestry and environment officials were aware of the importance of the forest and a local forest management committee protested the project before it began, but it’s been allowed to continue anyway.
Finding hope in ‘extreme conservation’ (Insider)
- A Mongabay staff writer shares an account of his trek to see mountain gorillas in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- From a low of 250 individuals in the 1980s, the mountain gorilla subspecies now numbers more than 1,000, making it the only great ape whose population is growing.
- Those gains have come thanks to the “extreme conservation” practiced by a dedicated group of people who have worked to ensure the survival of one of our closest relatives in the animal kingdom.
- This post is insider content, which is available to paying subscribers.
Study tracks first incursion of poachers into ‘pristine’ African forest
- Researchers logged the first evidence of elephant poaching in a remote, pristine section of Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park in the northern Republic of Congo.
- The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Forests and Global Change, also revealed unique behavior changes between gorillas and chimpanzees as a result of selective logging.
- The research highlights the need to incorporate the results of biodiversity surveys into plotting out the locations of areas set aside for conservation.
From over 100,000 species assessments in IUCN update, zero improvements
- The latest IUCN Red List update, which includes assessments of 105,732 species, lists more than 28,000 species as threatened with extinction.
- The declines of many of these species can be attributed to human overexploitation, according to the IUCN. The red-capped mangabey (Cercocebus torquatus), for example, has moved from vulnerable to endangered in 2019, largely because of threats from illegal hunting for bushmeat and conversion of much of the monkey’s Atlantic coast forest habitat in West Africa to agriculture.
- More than 5,000 trees from 180 countries, and 500 deep-sea bony fish species like the bioluminescent lanternfishes, were also added to the Red List this year.
- No species was assessed as having genuinely improved in status enough to earn it a place in a lower threat category, according to the IUCN.
After a lengthy delay, still no green light for Sri Lanka’s red list
- The rediscovery in recent years of species long thought to be extinct has sparked calls by scientists for an update of Sri Lanka’s red list of threatened species.
- The current list is based on assessments from 2012, and a scheduled update in 2017 was missed because of procedural delays and resource constraints.
- Conservationists have also called for the red-listing criteria used in Sri Lanka to be consistent with the global guidelines set out by the IUCN, in order to ensure consistency in conservation efforts.
- They also want more species recovery initiatives based on the national red list, to make better use of the data to optimize conservation efforts.
Altered fish communities persist long after reefs bleach, study finds
- In a new study, bleached reefs in the Indian Ocean archipelago of Seychelles had fewer predators like snappers and groupers and more plant-eating fish such as parrotfish and rabbitfish.
- The researchers found that this change in the composition of fish species persisted for more than a decade and a half after bleaching occurred in 1998.
- Scientists expect bleaching events to occur more frequently as a result of climate change, making it likely that these shifts in fish communities will become permanent.
Logging road construction has surged in the Congo Basin since 2003
- Logging road networks have expanded widely in the Congo Basin since 2003, according to a new study.
- The authors calculated that the length of logging roads doubled within concessions and rose by 40 percent outside of concessions in that time period, growing by 87,000 kilometers (54,000 miles).
- Combined with rising deforestation in the region since 2000, the increase in roads is concerning because road building is often followed by a pulse of settlement leading to deforestation, hunting and mining in forest ecosystems.
Primates lose ground to surging commodity production in their habitats
- “Forest risk” commodities, such as beef, palm oil, and fossil fuels, led to a significant proportion of the 1.8 million square kilometers (695,000 square miles) of forest that was cleared between 2001 and 2017 — an area almost the size of Mexico.
- A previous study found that 60 percent of primates face extinction and 75 percent of species’ numbers are declining.
- The authors say that addressing the loss of primate habitat due to the production of commodities is possible, though it will require a global effort to “green” the international trade in these commodities.
Leopards get a $20m boost from Panthera pact with Saudi prince
- Big-cat conservation group Panthera has signed an agreement with Saudi prince and culture minister Bader bin Abdullah bin Mohammad bin Farhan Al Saud in which the latter’s royal commission has pledged $20 million to the protection of leopards around the world, including the Arabian leopard, over the next decade.
- The funds will support a survey of the animals in Saudi Arabia and a captive-breeding program.
- The coalition also hopes to reintroduce the Arabian leopard into the governorate of Al-Ula, which Bader heads and which the kingdom’s leaders believe could jump-start the local tourism sector.
Out on a limb: Unlikely collaboration boosts orangutans in Borneo
- Logging and hunting have decimated a population of Bornean orangutans in Bukit Baka Bukit Raya National Park in Indonesia.
- Help has recently come from a pair of unlikely allies: an animal welfare group and a human health care nonprofit.
- Cross-disciplinary collaboration to meet the needs of ecosystems and humans is becoming an important tool for overcoming seemingly intractable obstacles in conservation.
Altered forests threaten sustainability of subsistence hunting
- In a commentary, two conservation scientists say that changes to the forests of Central and South America may mean that subsistence hunting there is no longer sustainable.
- Habitat loss and commercial hunting have put increasing pressure on species, leading to the loss of both biodiversity and a critical source of protein for these communities.
- The authors suggest that allowing the hunting of only certain species, strengthening parks and reserves, and helping communities find alternative livelihoods and sources of food could help address the problem, though they acknowledge the difficult nature of these solutions.
Conservation groups concerned as WHO recognizes traditional Chinese medicine
- The World Health Organization (WHO) will include traditional Chinese medicine in the revision of its influential International Classification of Diseases for the first time.
- The move concerns wildlife scientists and conservationists who say the WHO’s formal backing of traditional Chinese medicine could legitimize the hunting of wild animals for their parts, which are used in some remedies and treatments.
- The WHO has responded by saying that the inclusion of the practice in the volume doesn’t imply that the organization condones the contravention of international law aimed at protecting species like rhinos and tigers.
The health of penguin chicks points scientists to changes in the ocean
- A recent closure of commercial fishing around South Africa’s Robben Island gave scientists the chance to understand how fluctuations in prey fish populations affect endangered African penguins (Spheniscus demersus) absent pressure from humans.
- The researchers found that the more fish were available, the better the condition of the penguin chicks that rely on their parents for food.
- This link between prey abundance in the sea and the condition of penguin chicks on land could serve as an indicator of changes in the ecosystem.
Social media enables the illegal wildlife pet trade in Malaysia
- Conservationists say that prosecuting wildlife traffickers in Malaysia for trading in protected species isn’t easy, as traders have several loopholes to aid their efforts.
- One wildlife trafficker known as Kejora Pets has been operating in Peninsular Malaysia for years, selling “cute” pets to individuals through social media.
- Malaysia’s wildlife act doesn’t address the posting of protected animals for sale on social media, and operators like Kejora Pets appear to avoid ever being in possession of protected animals, allowing them to skirt statutes aimed at catching illicit traders.
- Proposed changes to Malaysia’s wildlife act could offer some relief to besieged populations of protected species by making it easier to prosecute online trafficking of protected animals.
’Unprecedented’ loss of biodiversity threatens humanity, report finds
- The U.N.’s Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services released a summary of far-reaching research on the threats to biodiversity on May 6.
- The findings are dire, indicating that around 1 million species of plants and animals face extinction.
- The full 1,500-page report, to be released later this year, raises concerns about the impacts of collapsing biodiversity on human well-being.
Mobile app encourages Indian fishers to free entangled whale sharks
- When whale sharks in waters off the Indian state of Gujarat get trapped in fishing nets, a new mobile app lets fishers easily document their release.
- Conservationists and fishers alike hope the app will speed up the compensation fishers receive for damaged nets.
- However, fishers say the compensation, a maximum of 25,000 rupees ($360), should be increased to reflect the true loss of their revenue during their downtime without nets.
Bird flu in Namibia’s penguins wanes, after killing nearly 500
- More than 450 African penguins, an IUCN-listed endangered animal, have died in an outbreak of bird flu on three islands off the coast of Namibia.
- The virus, H5N8, is thought to have been introduced to the colonies, which hold 96 percent of Namibia’s penguins, by another bird traveling from South Africa, where a similar outbreak occurred in 2018.
- The disease appears to be abating, and researchers are hopeful that the country’s penguins will recover.
- However, they continue to face threats from food shortages caused by overfishing and climate change.
Scientists urge overhaul of the world’s parks to protect biodiversity
- A team of scientists argues that we should evaluate the effectiveness of protected areas based on the outcomes for biodiversity, not simple the area of land or ocean they protect.
- In a paper published April 11 in the journal Science, they outline the weaknesses of Aichi Biodiversity Target 11, which set goals of protecting 17 percent of the earth’s surface and 10 percent of its oceans by 2020.
- They propose monitoring the outcomes of protected areas that measure changes in biodiversity in comparison to agreed-upon “reference” levels and then using those figures to determine how well they are performing.
To stop extinctions, start with these 169 islands, new study finds
- New research shows that culling invasive, non-native animals on just 169 islands around the world over roughly the next decade could help save almost 10 percent of island-dwelling animals at risk of extinction.
- A team of scientists surveyed nearly 1,300 islands where 1,184 threatened native animals have collided with 184 invasive mammals.
- Their analyses gave them a list of 107 islands where conservationists could start eradication projects by 2020, potentially keeping 80 threatened species from sliding closer to extinction.
New research teases apart complex effects of naval sonar on whales
- A pair of recent studies shows the unique responses of different whales to sonar, typically used by navies to detect submarines.
- Sonar sounds have been linked to hearing loss, deadly mass strandings and interference with whales’ communication with each other.
- One of the studies found that the distance the whales were from sonar sounds didn’t matter — they generally fled whether they were close to or far from it.
- Another study showed that sonar affected the feeding patterns of deep-diving blue whales, but not those that were feasting on krill at the surface.
Malaysian state chief: Highway construction must not destroy forest
- The chief minister of Sabah, one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo, said that the Pan Borneo Highway project should expand existing roads where possible to minimize environmental impact.
- A coalition of local NGOs and scientific organizations applauded the announcement, saying that it could usher in a new era of collaboration between the government and civil society to look out for Sabah’s people and forests.
- These groups have raised concerns about the impacts on wildlife and communities of the proposed path of the highway, which will cover some 5,300 kilometers (3,300 miles) in the states of Sabah and Sarawak.
Tapirs could be key in helping degraded rainforests bounce back
- A new study has found that lowland tapirs spend more time in degraded forests than in pristine Amazon rainforest.
- They also defecate and deposit three times more seeds in these degraded areas.
- The results indicate that tapirs may help human-affected forests recover and grow back.
Possible vaquita death accompanies announcement that only 10 are left
- The environmental organization Sea Shepherd said it found a dead vaquita in a gillnet on March 12.
- One day later, scientists from the group CIRVA announced that around 10 — as many as 22 or as few as six — vaquitas survive in the Gulf of California.
- Despite a ban on gillnets used catch totoaba, a fish prized for its swim bladders used in traditional Chinese medicine, vaquita numbers have continued to decline.
New maps show where humans are pushing species closer to extinction
- A new study maps out how disruptive human changes to the environment affect the individual ranges of more than 5,400 mammal, bird and amphibian species around the world.
- Almost a quarter of the species are threatened by human impacts in more than 90 percent of their range, and at least one human impact occurred in an average of 38 percent of the range of a given species.
- The study also identified “cool” spots, where concentrations of species aren’t negatively impacted by humans.
- The researchers say these “refugia” are good targets for conservation efforts.
Proximity to towns stretches giraffe home ranges
- A recent study found that female giraffes that live close to towns have larger home ranges than those living further afield.
- The study’s authors believe that large human settlements reduce giraffes’ access to food and water.
- The team cites the importance of understanding the size of the area that giraffe populations need to survive to address the precipitous decline in the animal’s numbers across Africa in the past 30 years.
You’re gonna need a smaller boat: Media obscures shrinking ‘newsworthy’ fish
- The sizes of certain species of fish that qualify as “newsworthy” have diminished over time, a new study has found.
- The authors scoured English-language newspapers going back to 1869, searching for terms like “massive” and “giant” in mentions of noteworthy fish landings, and compared the reported lengths with the largest specimens on record for that species.
- They found that for some “charismatic megafish,” such as whale sharks and manta rays, the size that qualified as large has declined over time.
- That shifting baseline could pose a problem for conservation efforts because it gives the impression that “there are still a lot of very large fish in the sea,” marine ecologist Isabelle Côté said.
Corruption-riddled caviar trade pushes fish closer to extinction
- TRAFFIC, WWF and several other organizations and institutions have published a report demonstrating that corruption drives the illegal trade of caviar around the world.
- Many of the species of fish, including those that produce the highest-priced caviar, are critically endangered.
- The report’s authors surfaced evidence of bribery, conflicts of interest, poaching and improper labeling in the industry, all of which are putting further pressure on the resource.
Massive pangolin seizure in Borneo smuggling operation bust
- A team of police and wildlife officials in the Malaysian state of Sabah seized nearly 30 metric tons (33 tons) of pangolins on Feb. 7.
- The raids on a factory in the state capital, Kota Kinabalu, and a warehouse in a village outside the city revealed a “smuggling syndicate,” which police believe has been operating for seven years.
- Sabah has become a waypoint for the trafficking of scales from pangolins in Africa to Asia.
- In this case, however, a man arrested in the raid told police that he had purchased the pangolins from local hunters in Malaysian Borneo.
Sumatran tiger killed at London Zoo by potential mate
- Melati, a 10-year-old female Sumatran tiger (Panthera tigris sumatrae), was killed Feb. 8 at ZSL London Zoo when she was introduced to a 7-year-old male called Asim.
- Asim had been transferred from Denmark as part of the European Endangered Species Programme, a captive-breeding program.
- The two tigers had been kept in separate but adjacent paddocks for 10 days before zookeepers opened the door between them on the morning of Feb. 8.
- Scientists believe that fewer than 400 Sumatran tigers live on their namesake Indonesian island.
Urbanization in Asia provides a window of hope for tigers, study finds
- The transition to cities by Asia’s human population is likely to affect the continent’s remaining tiger populations, according to a new study.
- Depending on policy decisions around migration, urbanization, education and economics, the trend toward urbanization could provide more space for tiger numbers to rebound.
- A team of researchers modeled five different “socioeconomic pathways” for the continent, showing that a focus on sustainable living could result in fewer than 40 million people living within the tiger’s range by the end of the century.
- But that number could also balloon to more than 106 million people if countries veer away from international cooperation and poor management of urbanization.
Wildlife rangers in DRC park report waning motivation, job satisfaction
- Surveys of more than 60 rangers in Kahuzi-Biega National Park in eastern Democratic Republic of Congo cite poor salaries, few chances for advancement, and security concerns as reasons for their low satisfaction with their jobs.
- The authors of the study, published in the journal Oryx, believe that the rangers’ discontentment leads to waning motivation in protecting the park and its wildlife, which includes the critically endangered Grauer’s gorilla.
- Improved conditions, in the form of better salaries, opportunities for promotion, and better support from the judicial and legal authorities, could translate into improved protections for the park, the researchers write.
Bans on the bird trade in South America yield mixed results
- After decades of rampant exports, several South American countries banned the international trade of wild-caught birds.
- In some cases, in concert with conservation, the bans have helped bird populations recover, leading several countries to invest in birdwatching tourism.
- However, the bans have also led to a significant illegal trade on the continent and a shift of the economic benefits from the wild bird trade to other countries.
Dam drove ‘collapse’ of rainforest bird populations in Thailand
- A 165-square-kilometer (64-square-mile) reservoir in the lowland rainforest of Thailand has led to the “collapse” of the region’s bird populations, according to recent research.
- Built in 1986, the Ratchaprapha dam altered the habitat and led to deforestation, resulting in the decline of many species and the local extinction of perhaps five.
- The authors of the study say their findings highlight concerns about whether hydroelectric dams “are worth the environmental costs.”
Culls push endangered fruit bat closer to extinction in Mauritius
- The government of Mauritius plans to cull 20 percent of the population of Mauritian flying foxes (Pteropus niger) in 2018 to protect farmers’ fruit trees.
- Culls in prior years led to the extermination of tens of thousands of the bats, and the IUCN now lists the species, which lives only in Mauritius and perhaps a few nearby islands, as endangered.
- A recent study found that, while bats (along with birds) do take a toll on farmers’ orchards, nets over the trees when the fruit ripens can dramatically diminish the damage they do.
Map pinpoints ‘last chance’ locations of endangered species
- A new assessment updates the last known ranges for nearly 1,500 species of animals and plants at 853 locations around the world.
- The three-year effort is aimed at helping scientists, governments and conservationists identify the threats that could lead to the extinction of these species and find ways to address them.
- Governments are already using this information to identify target areas for conservation to protect the last remaining habitats of threatened species.
- Nearly half of the sites identified lack formal protection, despite many of them having been flagged as important more than a decade ago.
‘Not all hope is lost’ as outlook for mountain gorillas brightens
- The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) changed the status of mountain gorillas from Critically Endangered to Endangered today.
- The new assessment cites the subspecies’ growing numbers, now at around 1,000 individuals, and the conservation efforts on its behalf.
- Scientists say that, while this is an important milestone, mountain gorillas’ survival depends on continued conservation.
Absent for decades, zebras reintroduced to park in southern Tanzania
- Staff from the Wildlife Conservation Society and its partners in Tanzania released 24 zebras into Kitulo National Park on Oct. 12 and 13.
- The Kitulo Plateau in Tanzania’s southern highlands includes high-elevation grasslands, a unique habitat that requires fire and grazing animals to maintain its plant diversity.
- The reintroduction, with plains zebras from Mikumi National Park, is part of a broader effort to “rewild” the southern highlands after decades of wildlife hunting and livestock grazing.
Conservation groups herald protection of tiger habitat in Malaysia
- The state government of Terengganu has set aside more than 100 square kilometers (39 square miles) for critically endangered Malayan tigers and other wildlife in Peninsular Malaysia.
- The state’s chief minister said the newly created Lawit-Cenana State Park’s high density of threatened species made the area a priority for protection.
- The park is home to 291 species of birds and 18 species of mammals, including elephants, tapirs and pangolins.
‘Biological passports’ show whale sharks travel less than we thought
- A study looking at chemical signatures in whale shark tissue and using photographic identification has revealed that young sharks in three countries along the western rim of the Indian Ocean don’t typically stray more than a few hundred kilometers from their feeding sites.
- Of the more than 1,200 sharks photographed, only two traveled between different feeding sites — in this case, about 2,000 kilometers (1,240 miles) between Mozambique and Tanzania.
- The authors of the study say their findings demonstrate that local conservation of these populations is important because if whale sharks are wiped out in an area, they’re unlikely to repopulate it later on.
Millipedes might soothe itchy lemurs, research finds
- Scientists have observed red-fronted lemurs in Madagascar biting millipedes and then rubbing themselves with the secretions.
- A team of researchers published their observations in the journal Primates, along with their hypothesis that the lemurs were using the millipede secretions to treat worm infections.
- The study’s lead author also observed lemurs eating the millipedes, which may slow the growth of parasites living in the primates’ intestines.
Cross-border camera trap research puts wild Amur leopard number at 84
- Scientists working in Russia and China have used camera traps to estimate that 84 Amur leopards remain in the wild.
- Previous studies tracked the cats using their footprints in snow, but the camera trap photographs allowed the researchers to identify individual animals by their unique spot patterns.
- The team found that 20 percent of the Amur leopards appeared on both sides of the border between China and Russia, highlighting the importance of cross-border collaboration.
Fingerprinting technology gives investigators an edge against pangolin traffickers
- Researchers in the U.K. have modified the gelatin lifters used in criminal forensic investigations so they can pick up clues from pangolin scales and other illegally traded wildlife body parts.
- Wildlife guards in Kenya and Cameroon are using packs of the gelatin lifters in the field to gather evidence.
- The researchers say this new technology allows wildlife conservation officials to collect this evidence more quickly in remote areas, which in turn helps to ensure their safety.
One tortoise at a time: Q&A with zoo veterinarian Justin Rosenberg
- In April, authorities discovered around 10,000 radiated tortoises, believed to be destined for the Asian pet trade, in an abandoned house in southwestern Madagascar.
- The Turtle Survival Alliance (TSA) took the animals to its rescue center in Ifaty, and soon, veterinarians and keepers from around the world began traveling to Madagascar to help the animals.
- Currently, between 9,000 and 10,000 tortoises are alive, with around 100 still in need of critical care.
- Mongabay spoke with a veterinarian who spent several weeks at TSA’s facility about the ongoing efforts.
Hunters are wiping out hornbills in Ghana’s forests
- According to a new study, Ghana is losing hornbill species to “uncontrolled” hunting, mostly for meat, from its forested parks and reserves.
- The researchers found that the five largest species of hornbills in the Bia Biosphere Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, have disappeared in recent decades.
- The authors of the paper suggest that increased enforcement will help protect threatened hornbills, as well as other wildlife species, in areas under intense pressure from humans.
Fishing gear poses the greatest danger to young great whites off the West Coast of the U.S.
- Fishing lines and nets pose the most significant threat to the survival of young white sharks in the waters off Mexico and southern California, according to a new study.
- A team of scientists used a relatively “untapped” but ubiquitous storehouse of data to develop a statistical model for the survival rates of juvenile white sharks.
- The researchers calculated that 63 percent of young white sharks living in this part of the Pacific survive annually, but that nearly half probably come in contact with gillnets set by commercial fishers.
- The findings point to best practices, such as barring gillnets from inshore “nurseries” and asking fishers to check their nets for trapped sharks more regularly, that could help protect great whites.
Longest recorded whale shark migration eclipses 20,000 kilometers
- Scientists followed the movements of a whale shark for nearly two and a half years as she swam more than 20,000 kilometers (over 12,000 miles) from the coast of Central America to the Marianas Trench near Asia.
- Whale sharks, whose numbers have dropped by more than half in the past 75 years according to the IUCN, are taken by fishing boats for their fins, cartilage, meat and teeth, and studies have shown that boats bringing tourists to swim with the largest fish in the ocean change the species’ behavior.
- Given these threats, scientists hope studies such as this one will help guide conservation policy aimed at protecting these animals throughout their migrations.
Black rhinos return to Zakouma National Park in Chad
- The NGO African Parks and its partners in South Africa and Chad reintroduced six black rhinos to Zakouma National Park on May 4.
- Chad’s oldest national park had not had rhinos since the early 1970s, when they were wiped out by hunting.
- After a brief acclimation period in transitional bomas, or enclosures, the rhinos will be released into a protected sanctuary in the park.
- Around 5,000 black rhinos remain on the African continent, and poaching for their horns, used in traditional Asian medicine, continues to be a threat to their survival as a species.
More than 800 totoaba swim bladders confiscated by Mexican authorities in smuggling busts
- In two separate arrests of Chinese nationals, Mexican police confiscated more than 800 swim bladders from a large fish called the totoaba.
- Totoaba swim bladders are used in traditional medicine and can fetch thousands of dollars per kilogram in Chinese markets.
- Fishing for totoaba has also pushed a small porpoise called the vaquita close to extinction. One recent estimate puts the number of animals left in the wild at 12.
More gorillas and chimpanzees living in Central Africa’s forests than thought
- A study led by WCS researchers pulled together wildlife survey data collected between 2003 and 2013 at 59 sites in five countries across western Central Africa.
- They then developed mathematical models to understand where the highest densities of gorillas and chimpanzees are and why, as well as broader trends in the populations.
- They found that more than 361,000 western lowland gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) and almost 129,000 central chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) inhabit these forests — about 30 percent more gorillas and 10 percent more chimpanzees than previously estimated.
- The team’s analyses also demonstrate that western lowland gorilla numbers are slipping by 2.7 percent a year.
‘Monumental’ bust in Madagascar triggers effort to save thousands of endangered tortoises
- Authorities discovered 9,888 starving and dehydrated radiated tortoises in a vacant house in southwestern Madagascar on April 10.
- Since then, a team of organizations led by the Turtle Survival Alliance has been working to provide care for the critically endangered tortoises, 574 of which died during the first week.
- The tortoises, endemic to Madagascar, have lost around 40 percent of their habitat to deforestation, and poachers commonly capture them for the pet trade in Asia and the United States.
Suspected poisoning takes down 11 lions in Uganda park
- Eight cubs and three female lions have been found dead, apparently from eating poisoned meat in Queen Elizabeth National Park.
- Lions, along with other predators, have been in decline across Uganda since the 1970s.
- Recent studies indicate that the country’s growing human population has driven lions out of their former habitats and that the big cats are killed to defend the livestock of local communities.
‘IUCN Green List of species’: A new way to measure conservation success
- Scientists have proposed a framework for a new “Green List of species” that outlines a standard way of measuring species recovery and conservation success.
- The framework starts by defining what a “fully recovered species” looks like, then lays down four metrics that quantify the importance of conservation efforts for a species’ recovery.
- The Green List will eventually become a part of the IUCN Red List, the scientists say, with the final species assessment including both the extinction risk categories as well as the four conservation metrics to help judge whether conservation actions are helping a species recover.
More than 40 percent of Madagascar’s freshwater life sliding toward extinction, IUCN finds
- In an assessment of 653 freshwater plant and animal species living on Madagascar and nearby islands, biologists found that 43 percent are threatened with extinction or there isn’t enough information to assess how well they’re doing.
- Nearly 80 percent of endemic plants examined in the study face extinction.
- The team lists unsustainable farming practices, deforestation, dam construction, mining and the overuse of natural resources, such as overfishing, as causes for the widespread declines.
Conservationists rush to save Bolivian turtles threatened by egg trafficking
- The large-scale harvesting of the yellow-spotted Amazon river turtle (Podocnemis unifilis) for human consumption has contributed to the species’ decline, according to scientists. It is currently classified as vulnerable by the IUCN.
- A series of raids in mid-2017 saw authorities seize more than 50,000 river turtle eggs from poachers in the Beni department of Bolivia.
- A conservation project is trying to help river turtle populations recover, and has released 70,000 baby turtles into the Maniqui River since 1992.
Europe’s beetle species plummet as trees disappear
- A new report by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) finds nearly 18 percent of saproxylic beetles are threatened with extinction in Europe. That number goes up to almost 22 percent for the EU as a whole.
- Of Europe’s threatened species, the 2018 report finds five are critically endangered, up from two in 2010. Of these, four are endemic, meaning they are found nowhere else in the world. In the EU overall, the IUCN lists seven species as critically endangered, up from three in 2010.
- Saproxylic beetles live in and eat dead and decaying wood, and play important ecological roles such as nutrient recycling, pollination and as an important food source for birds and other wildlife.
- The IUCN says that to stave of greater declines and help saproxylic beetles bounce back, land management should make sure each square kilometer of land contains a mix of trees of different ages, including standing and fallen dead trees.
Seychelles home to new species of caecilian, a legless amphibian
- The Petite Praslin caecilian (Hypogeophis pti) is the world’s newest — and possibly the smallest — caecilian, a type of legless amphibian.
- Scientists discovered the animal on the island of Praslin in the Seychelles, an archipelago in the Indian Ocean.
- The new species is the seventh caecilian species found in the Seychelles, where the amphibians have been evolving for 64 million years.
Study maps out reptiles’ ranges, completing the ‘atlas of life’
- The study’s 39 authors, from 30 institutions around the world, pulled together data on the habitats of more than 10,000 species of reptiles.
- They found little overlap with current conservation areas, many of which have used the numbers of mammal and bird species present as proxies for overall biodiversity.
- In particular, lizards and turtles aren’t afforded much protection under current schemes.
- The authors report that they’ve identified high-priority areas for conservation that protects reptile diversity, ranging from deserts in the Middle East, Africa and Australia, to grass- and scrublands in Asia and Brazil.
Five promising stories for Global Tiger Day
- Since the last Global Tiger Day in 2016, researchers have discovered tiger populations in unexpected areas, such as forested corridors along riverbanks and in areas that recently served as theaters of war.
- Several countries have worked to protect the tigers that live within their borders, including the creation of a massive national park and taking steps to end tiger farming.
- Camera trap surveys continue to prove invaluable to wildlife researchers in tracking down tigers and other species that can range over huge areas.
First ‘intrusions’ into unbroken forests drive pulses of biodiversity loss
- The study examined ‘initial intrusions’ into tropical forests and their effect on the threat status of species.
- The researchers found that deforestation at current rates in high-priority areas such as Borneo, the Congo Basin, and the Amazon could push 121 to 219 species closer to extinction in the next 30 years.
- While the authors point out that their conclusions are not a call to protect only intact landscapes, the data could help policymakers working with limited resources to decide where to place new protected areas.
How the World Heritage Convention could save more wilderness: Q&A with World Heritage expert Cyril Kormos
- Since its inception in the 1970s, the UNESCO World Heritage Convention has officially recognized 1,052 sites of cultural or ecological importance around the planet.
- Making the list as a World Heritage site can help provide a location with increased protection and attention.
- The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), an advisor to the World Heritage Committee, released a study showing that 1.8 percent of wilderness areas are covered under World Heritage protection.
- The IUCN recommends a more methodical approach to the designation of World Heritage sites to help fill these gaps.
‘Crunch time for biodiversity’: Farming, hunting push thousands of species toward extinction
- Eighty percent of threatened animals are losing ground – literally, in the form of habitat loss – to agriculture.
- Up to 50 percent of threatened birds and mammals face extinction at the hands of hunters.
- In a study published in the journal Nature, a team of scientists explores solutions to avoid destroying the habitats of these animals, such as increasing yields in the developed world and minimizing fertilizer use.
Jane Goodall on zoos and tech as conservation tools
 Famed conservationist Jane Goodall, DBE, founder of the Jane Goodall Institute (JGI), UN Messenger of Peace, and Mongabay.com advisory board member visited Hawai’i last month for the World Conservation Congress, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s latest global gathering. She and her team kept a busy schedule as usual, giving press conferences and speaking about […]
Famed conservationist Jane Goodall, DBE, founder of the Jane Goodall Institute (JGI), UN Messenger of Peace, and Mongabay.com advisory board member visited Hawai’i last month for the World Conservation Congress, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s latest global gathering. She and her team kept a busy schedule as usual, giving press conferences and speaking about […]
Voluntary certification standards have far to go, say experts
- Certification should be combined with other standard public policies to promote sustainable forest management principles, say experts.
- Experts point to a need for more relationship building between voluntary certification schemes and public institutions.
- Effective certification requires the cooperation of policy makers, certification schemes, companies, academics and other stakeholders.
Good news for Giant Panda, Tibetan Antelope in updated IUCN Red List
- The latest update of The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species reports that species like the Giant Panda, Tibetan Antelope, the Bridled Nailtail Wallaby, and the Greater Stick-nest rate have improved in their conservation status thanks to effective conservation efforts.
- However, over-hunting is wiping out many mammals such as the Plains Zebra and Duikers, which have moved from Least Concern to a threatened status.
- The updated list also has some new entrants such as the recently described Psychedelic Rock Gecko and the Chiku Bent-toed Gecko.
More than half of the Amazon’s tree species may be threatened with extinction
- Of the Amazon’s 15,000 tree species, thousands are at risk. Those in the southern and eastern parts of the Amazon, where deforestation rates are highest, are the most threatened.
- The present network of protected areas and indigenous territories, which covers over 50 percent of the Amazon, could offer a ray of hope, researchers say.
- While the results are still preliminary, researchers say that the study provides the size, urgency, and feasibility of undertaking the task of evaluating the Amazon tree species on a case-by-case basis.
ASAP: reversing decline of critically endangered species in Southeast Asia
- Southeast Asian countries face the highest rate of habitat loss, and have the highest proportion of species that are threatened with extinction.
- Given the urgency to save these species, the IUCN Species Survival Commission, together with other international conservation organizations have come together to form the Asian Species Action Partnership (ASAP!).
- ASAP prioritizes conservation of critically endangered species in Southeast Asia.
New study re-assesses conservation status of Peruvian amphibians
- The conservation status of 38 amphibian species that had been previously determined to possibly meet IUCN criteria for being listed as Threatened species was re-assessed.
- Researchers found that the status of 14 of the 38 species should be changed.
- The major threat to the re-assessed amphibians is habitat loss due to logging and agriculture, with significant dangers presented by disease, pollution, and illegal harvesting for consumption and the pet trade.
World Rhino Day arrives this year with a new cause for celebration
- September 22 is World Rhino Day.
- The Sumatran Rhino is listed as being critically endangered on the IUCN red list.
- A Sumatran Rhino at the Sumatran Rhino Sanctuary in Indonesia is pregnant with her second baby.
Does conservation work? Using the IUCN Red List to evaluate groups’ performance
- Researchers came up with a new method to determine whether a conservation group’s programs work.
- The method involves tracking the status of species over time to see whether their risk of extinction increases or decreases, then comparing the outcome to a hypothetical “what if” scenario in which no conservation interventions took place.
- The study, conducted by researchers at UK-based Durrell Wildlife Conservation Trust, examined 17 species subjected to Durrell’s own conservation interventions, and found that of the nine species whose status changed over time, eight improved and one worsened.
Chameleon crisis: extinction threatens 36% of world’s chameleons
 World’s chameleons facing potential extinction crisis The lesser chameleon (Furcifer minor) is listed as Endangered. This species is only found in Madagascar. Photo by: Christopher V. Anderson. Chameleons are an unmistakable family of wonderfully bizarre reptiles. They sport long, shooting tongues; oddly-shaped horns or crests; and a prehensile tail like a monkey’s. But, of course, […]
World’s chameleons facing potential extinction crisis The lesser chameleon (Furcifer minor) is listed as Endangered. This species is only found in Madagascar. Photo by: Christopher V. Anderson. Chameleons are an unmistakable family of wonderfully bizarre reptiles. They sport long, shooting tongues; oddly-shaped horns or crests; and a prehensile tail like a monkey’s. But, of course, […]
Gone for good: world’s largest earwig declared extinct
 A female common earwig (Forficula auricularia) in defensive posture. The world’s largest earwig has been declared extinct. Photo by: Public Domain. The world has lost a giant: this week the IUCN Red List officially declared St. Helena giant earwig (Labidura herculeana) extinct. While its length of 80 millimeters (3.1 inches) may not seem like much, […]
A female common earwig (Forficula auricularia) in defensive posture. The world’s largest earwig has been declared extinct. Photo by: Public Domain. The world has lost a giant: this week the IUCN Red List officially declared St. Helena giant earwig (Labidura herculeana) extinct. While its length of 80 millimeters (3.1 inches) may not seem like much, […]
Of bluefin and pufferfish: 310 species added to IUCN Red List
 Overfishing has pushed the Pacific bluefin tuna from Least Concern to Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Photo by: © Monterey Bay Aquarium – Randy Wilder. Today, 22,413 species are threatened with extinction, according to the most recent update of the IUCN Red List. This is a rise of 310 species from the last update […]
Overfishing has pushed the Pacific bluefin tuna from Least Concern to Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Photo by: © Monterey Bay Aquarium – Randy Wilder. Today, 22,413 species are threatened with extinction, according to the most recent update of the IUCN Red List. This is a rise of 310 species from the last update […]
Is there hope for the vaquita? IUCN calls for action to save world’s smallest, rarest porpoise
 Fishing industry propelling tiny cetacean to extinction Since the baiji was declared extinct in the early aughts, the vaquita has taken its unenviable position as the world’s most threatened cetacean. The tiny porpoise currently numbers around 100, with accidental entanglement in gillnets primarily responsible for its decline. In response, the IUCN recently issued a statement […]
Fishing industry propelling tiny cetacean to extinction Since the baiji was declared extinct in the early aughts, the vaquita has taken its unenviable position as the world’s most threatened cetacean. The tiny porpoise currently numbers around 100, with accidental entanglement in gillnets primarily responsible for its decline. In response, the IUCN recently issued a statement […]
Desperate measures: researchers say radical approaches needed to beat extinctions
 Introduction of non-native species, de-extinction may work better than traditional conservation practices Today, in the midst of what has been termed the “Sixth Great Extinction” by many in the scientific community, humans are contributing to dizzying rates of species loss and ecosystem changes. A new analysis published in Science refutes the value of common conservation […]
Introduction of non-native species, de-extinction may work better than traditional conservation practices Today, in the midst of what has been termed the “Sixth Great Extinction” by many in the scientific community, humans are contributing to dizzying rates of species loss and ecosystem changes. A new analysis published in Science refutes the value of common conservation […]
Over 350 species added to the IUCN Red List’s threatened categories in the last six months
 The number of threatened species on the IUCN Red List has grown by 352 since this summer, according to an update released today. Currently, 21,286 species are now listed as threatened with extinction out of the 71,576 that have been evaluated. The new update comes with both good and bad news for a number of […]
The number of threatened species on the IUCN Red List has grown by 352 since this summer, according to an update released today. Currently, 21,286 species are now listed as threatened with extinction out of the 71,576 that have been evaluated. The new update comes with both good and bad news for a number of […]
Ground zero for endangered species: new program to assist animals on the brink across Southeast Asia
 Organizations within the international conservation community are joining forces to minimize impending extinctions in Southeast Asia, where habitat loss, trade and hunting have contributed to a dramatic decline in wildlife. The coalition is aptly named ASAP, or the Asian Species Action Partnership. “ASAP began as a response to alarming results revealed in a 2008 comprehensive […]
Organizations within the international conservation community are joining forces to minimize impending extinctions in Southeast Asia, where habitat loss, trade and hunting have contributed to a dramatic decline in wildlife. The coalition is aptly named ASAP, or the Asian Species Action Partnership. “ASAP began as a response to alarming results revealed in a 2008 comprehensive […]
Over 700 species added to the threatened categories on the IUCN Red List (photos)
 In another sign of the global biodiversity crisis, the IUCN Red List has added 715 species to its threatened categories of Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered in this year’s update. Some of these species were evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time while others saw their conditions deteriorate, such as the the […]
In another sign of the global biodiversity crisis, the IUCN Red List has added 715 species to its threatened categories of Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered in this year’s update. Some of these species were evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time while others saw their conditions deteriorate, such as the the […]
Working to save the mystery antelope that’s little bigger than a pet cat (photos)
 Little is known about the silver dik-dik (Madoqua piacentinii) population that roams the dense coastal bushlands of eastern Africa, but experts are working to learn more about the mysterious species. Weighing little more than a domestic cat, the small antelopes are found in a long, narrow coastal strip spreading across 250 kilometers (155 miles) from […]
Little is known about the silver dik-dik (Madoqua piacentinii) population that roams the dense coastal bushlands of eastern Africa, but experts are working to learn more about the mysterious species. Weighing little more than a domestic cat, the small antelopes are found in a long, narrow coastal strip spreading across 250 kilometers (155 miles) from […]
Bizarre, little-known carnivore sold as illegal pet in Indonesian markets (photo)
 Few people have ever heard of the Javan ferret-badger, but that hasn’t stopped this animal—little-known even to scientists—from being sold in open markets in Jakarta according to a new paper in Small Carnivore Conservation. The Javan ferret-badger (Melogale orientalis) is one of five species in the ferret-badger family, which are smaller than proper badgers with […]
Few people have ever heard of the Javan ferret-badger, but that hasn’t stopped this animal—little-known even to scientists—from being sold in open markets in Jakarta according to a new paper in Small Carnivore Conservation. The Javan ferret-badger (Melogale orientalis) is one of five species in the ferret-badger family, which are smaller than proper badgers with […]
Pictures: 20% of the world’s reptiles endangered
 Green iguana in Colombia. Photo by Rhett A. Butler Nearly a fifth the planet’s reptiles are threatened with extinction, warns a new assessment published in the journal Biological Conservation. The analysis, carried out by experts with the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) and the IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC), is based on the extinction risk […]
Green iguana in Colombia. Photo by Rhett A. Butler Nearly a fifth the planet’s reptiles are threatened with extinction, warns a new assessment published in the journal Biological Conservation. The analysis, carried out by experts with the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) and the IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC), is based on the extinction risk […]
IUCN to kick-off Green List for ‘fully conserved’ species
 Aerial view of African buffalo herd in the Okavango Delta. With a population numbering several hundred thousand will the African buffalo find itself on the Green List? Or will hunting, especially bushmeat hunting of the forest buffalo subspecies, keep it off? These are the questions scientists with the Green List will have to answer. Photo […]
Aerial view of African buffalo herd in the Okavango Delta. With a population numbering several hundred thousand will the African buffalo find itself on the Green List? Or will hunting, especially bushmeat hunting of the forest buffalo subspecies, keep it off? These are the questions scientists with the Green List will have to answer. Photo […]
96 percent of the world’s species remain unevaluated by the Red List
 The IUCN Red List releases its 2012 update, adding 247 species to its threatened categories. The king cobra has been evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time and listed as Vulnerable. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Nearly 250 species have been added to the threatened categories—i.e. Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered—in this […]
The IUCN Red List releases its 2012 update, adding 247 species to its threatened categories. The king cobra has been evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time and listed as Vulnerable. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Nearly 250 species have been added to the threatened categories—i.e. Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered—in this […]
Chemotherapy tree facing extinction
 A yew tree in the Himalayas that produces the chemotherapy drug, Taxol, is in danger of extinction. An update to the IUCN Red List, has moved the tree, named Taxus contorta, from Vulnerable to Endangered. Overharvesting for medicine and fuelwood have placed the species in serious danger. Craig Hilton-Taylor with the Red List told the […]
A yew tree in the Himalayas that produces the chemotherapy drug, Taxol, is in danger of extinction. An update to the IUCN Red List, has moved the tree, named Taxus contorta, from Vulnerable to Endangered. Overharvesting for medicine and fuelwood have placed the species in serious danger. Craig Hilton-Taylor with the Red List told the […]
Over 80 percent of rediscovered species still face extinction
 Imagine if your job was to locate extinct species. In 2010, biologists with The Search for Lost Frogs set out on a tropical mission hoping to confirm the existence of frog species not seen in decades. The team recovered proof of four out of a hundred missing species, including a toad among the expedition’s Top […]
Imagine if your job was to locate extinct species. In 2010, biologists with The Search for Lost Frogs set out on a tropical mission hoping to confirm the existence of frog species not seen in decades. The team recovered proof of four out of a hundred missing species, including a toad among the expedition’s Top […]
The glass is half-full: conservation has made a difference
 Focused conservation efforts, including reintroduction of captive individuals into the wild, have saved the golden lion tamarin from extinction. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Don’t despair: that’s the message of a new paper in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, which argues that decades of conservation actions at multiple scales have had a positive impact for […]
Focused conservation efforts, including reintroduction of captive individuals into the wild, have saved the golden lion tamarin from extinction. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Don’t despair: that’s the message of a new paper in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, which argues that decades of conservation actions at multiple scales have had a positive impact for […]
Over 900 species added to endangered list during past year
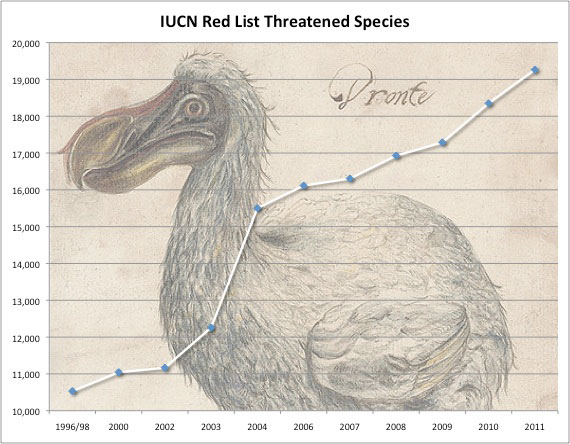 Previously unpublished 17th Century Dutch sketch of the dodo, taken from a real specimen, either alive or stuffed. Dronte means dodo in Dutch. The past twelve months have seen 914 species added to the threatened list by the world’s authority of species endangerment, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List. Over […]
Previously unpublished 17th Century Dutch sketch of the dodo, taken from a real specimen, either alive or stuffed. Dronte means dodo in Dutch. The past twelve months have seen 914 species added to the threatened list by the world’s authority of species endangerment, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List. Over […]
Hyenas discovered in Armenia? Researchers find carcass, tracks
 On October 1, 2010, the carcass of a striped hyena was found entangled in barbed wire surrounding an orchard in southern Armenia. The find represents the nation’s first confirmed hyena observation in over 60 years. Although they may be doglike in appearance, hyenas are actually more related to cats than dogs, with their closest relatives […]
On October 1, 2010, the carcass of a striped hyena was found entangled in barbed wire surrounding an orchard in southern Armenia. The find represents the nation’s first confirmed hyena observation in over 60 years. Although they may be doglike in appearance, hyenas are actually more related to cats than dogs, with their closest relatives […]
Malaysian customs seizes 1,800 trafficked reptiles
 Malaysia contains an amazing array of plants and animals, including this water monitor. Photo taken in Sabah by Rhett A. Butler Malaysia ended 2010 with the confiscation of 4.3 metric tons of reptiles near the Thai border on December 20th, reports the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network, TRAFFIC. The confiscation was the largest of the year […]
Malaysia contains an amazing array of plants and animals, including this water monitor. Photo taken in Sabah by Rhett A. Butler Malaysia ended 2010 with the confiscation of 4.3 metric tons of reptiles near the Thai border on December 20th, reports the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network, TRAFFIC. The confiscation was the largest of the year […]
Red pandas may be threatened by small-scale trade
 Two studies investigated the scale and potential threat of continued trade in red pandas and found that while reports are low, the occurrence of isolated incidents may be enough to threaten species survival. The red panda, Ailurus fulgens, is a cat-sized, arboreal mammal which lives in temperate forests in the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. […]
Two studies investigated the scale and potential threat of continued trade in red pandas and found that while reports are low, the occurrence of isolated incidents may be enough to threaten species survival. The red panda, Ailurus fulgens, is a cat-sized, arboreal mammal which lives in temperate forests in the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. […]
The march to extinction accelerates
 A fifth of the world’s vertebrate species (i.e. mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish) are threatened with extinction, according to a massive new study by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN); and the situation is worsening for the world’s wildlife: on average 52 species of mammals, birds, and amphibians move one category […]
A fifth of the world’s vertebrate species (i.e. mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish) are threatened with extinction, according to a massive new study by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN); and the situation is worsening for the world’s wildlife: on average 52 species of mammals, birds, and amphibians move one category […]
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
 Famed conservationist Jane Goodall, DBE, founder of the Jane Goodall Institute (JGI), UN Messenger of Peace, and Mongabay.com advisory board member visited Hawai’i last month for the World Conservation Congress, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s latest global gathering. She and her team kept a busy schedule as usual, giving press conferences and speaking about […]
Famed conservationist Jane Goodall, DBE, founder of the Jane Goodall Institute (JGI), UN Messenger of Peace, and Mongabay.com advisory board member visited Hawai’i last month for the World Conservation Congress, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s latest global gathering. She and her team kept a busy schedule as usual, giving press conferences and speaking about […] World’s chameleons facing potential extinction crisis The lesser chameleon (Furcifer minor) is listed as Endangered. This species is only found in Madagascar. Photo by: Christopher V. Anderson. Chameleons are an unmistakable family of wonderfully bizarre reptiles. They sport long, shooting tongues; oddly-shaped horns or crests; and a prehensile tail like a monkey’s. But, of course, […]
World’s chameleons facing potential extinction crisis The lesser chameleon (Furcifer minor) is listed as Endangered. This species is only found in Madagascar. Photo by: Christopher V. Anderson. Chameleons are an unmistakable family of wonderfully bizarre reptiles. They sport long, shooting tongues; oddly-shaped horns or crests; and a prehensile tail like a monkey’s. But, of course, […] A female common earwig (Forficula auricularia) in defensive posture. The world’s largest earwig has been declared extinct. Photo by: Public Domain. The world has lost a giant: this week the IUCN Red List officially declared St. Helena giant earwig (Labidura herculeana) extinct. While its length of 80 millimeters (3.1 inches) may not seem like much, […]
A female common earwig (Forficula auricularia) in defensive posture. The world’s largest earwig has been declared extinct. Photo by: Public Domain. The world has lost a giant: this week the IUCN Red List officially declared St. Helena giant earwig (Labidura herculeana) extinct. While its length of 80 millimeters (3.1 inches) may not seem like much, […] Overfishing has pushed the Pacific bluefin tuna from Least Concern to Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Photo by: © Monterey Bay Aquarium – Randy Wilder. Today, 22,413 species are threatened with extinction, according to the most recent update of the IUCN Red List. This is a rise of 310 species from the last update […]
Overfishing has pushed the Pacific bluefin tuna from Least Concern to Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Photo by: © Monterey Bay Aquarium – Randy Wilder. Today, 22,413 species are threatened with extinction, according to the most recent update of the IUCN Red List. This is a rise of 310 species from the last update […] Fishing industry propelling tiny cetacean to extinction Since the baiji was declared extinct in the early aughts, the vaquita has taken its unenviable position as the world’s most threatened cetacean. The tiny porpoise currently numbers around 100, with accidental entanglement in gillnets primarily responsible for its decline. In response, the IUCN recently issued a statement […]
Fishing industry propelling tiny cetacean to extinction Since the baiji was declared extinct in the early aughts, the vaquita has taken its unenviable position as the world’s most threatened cetacean. The tiny porpoise currently numbers around 100, with accidental entanglement in gillnets primarily responsible for its decline. In response, the IUCN recently issued a statement […] Introduction of non-native species, de-extinction may work better than traditional conservation practices Today, in the midst of what has been termed the “Sixth Great Extinction” by many in the scientific community, humans are contributing to dizzying rates of species loss and ecosystem changes. A new analysis published in Science refutes the value of common conservation […]
Introduction of non-native species, de-extinction may work better than traditional conservation practices Today, in the midst of what has been termed the “Sixth Great Extinction” by many in the scientific community, humans are contributing to dizzying rates of species loss and ecosystem changes. A new analysis published in Science refutes the value of common conservation […] The number of threatened species on the IUCN Red List has grown by 352 since this summer, according to an update released today. Currently, 21,286 species are now listed as threatened with extinction out of the 71,576 that have been evaluated. The new update comes with both good and bad news for a number of […]
The number of threatened species on the IUCN Red List has grown by 352 since this summer, according to an update released today. Currently, 21,286 species are now listed as threatened with extinction out of the 71,576 that have been evaluated. The new update comes with both good and bad news for a number of […] Organizations within the international conservation community are joining forces to minimize impending extinctions in Southeast Asia, where habitat loss, trade and hunting have contributed to a dramatic decline in wildlife. The coalition is aptly named ASAP, or the Asian Species Action Partnership. “ASAP began as a response to alarming results revealed in a 2008 comprehensive […]
Organizations within the international conservation community are joining forces to minimize impending extinctions in Southeast Asia, where habitat loss, trade and hunting have contributed to a dramatic decline in wildlife. The coalition is aptly named ASAP, or the Asian Species Action Partnership. “ASAP began as a response to alarming results revealed in a 2008 comprehensive […] In another sign of the global biodiversity crisis, the IUCN Red List has added 715 species to its threatened categories of Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered in this year’s update. Some of these species were evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time while others saw their conditions deteriorate, such as the the […]
In another sign of the global biodiversity crisis, the IUCN Red List has added 715 species to its threatened categories of Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered in this year’s update. Some of these species were evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time while others saw their conditions deteriorate, such as the the […] Little is known about the silver dik-dik (Madoqua piacentinii) population that roams the dense coastal bushlands of eastern Africa, but experts are working to learn more about the mysterious species. Weighing little more than a domestic cat, the small antelopes are found in a long, narrow coastal strip spreading across 250 kilometers (155 miles) from […]
Little is known about the silver dik-dik (Madoqua piacentinii) population that roams the dense coastal bushlands of eastern Africa, but experts are working to learn more about the mysterious species. Weighing little more than a domestic cat, the small antelopes are found in a long, narrow coastal strip spreading across 250 kilometers (155 miles) from […] Few people have ever heard of the Javan ferret-badger, but that hasn’t stopped this animal—little-known even to scientists—from being sold in open markets in Jakarta according to a new paper in Small Carnivore Conservation. The Javan ferret-badger (Melogale orientalis) is one of five species in the ferret-badger family, which are smaller than proper badgers with […]
Few people have ever heard of the Javan ferret-badger, but that hasn’t stopped this animal—little-known even to scientists—from being sold in open markets in Jakarta according to a new paper in Small Carnivore Conservation. The Javan ferret-badger (Melogale orientalis) is one of five species in the ferret-badger family, which are smaller than proper badgers with […] Green iguana in Colombia. Photo by Rhett A. Butler Nearly a fifth the planet’s reptiles are threatened with extinction, warns a new assessment published in the journal Biological Conservation. The analysis, carried out by experts with the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) and the IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC), is based on the extinction risk […]
Green iguana in Colombia. Photo by Rhett A. Butler Nearly a fifth the planet’s reptiles are threatened with extinction, warns a new assessment published in the journal Biological Conservation. The analysis, carried out by experts with the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) and the IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC), is based on the extinction risk […] Aerial view of African buffalo herd in the Okavango Delta. With a population numbering several hundred thousand will the African buffalo find itself on the Green List? Or will hunting, especially bushmeat hunting of the forest buffalo subspecies, keep it off? These are the questions scientists with the Green List will have to answer. Photo […]
Aerial view of African buffalo herd in the Okavango Delta. With a population numbering several hundred thousand will the African buffalo find itself on the Green List? Or will hunting, especially bushmeat hunting of the forest buffalo subspecies, keep it off? These are the questions scientists with the Green List will have to answer. Photo […] The IUCN Red List releases its 2012 update, adding 247 species to its threatened categories. The king cobra has been evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time and listed as Vulnerable. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Nearly 250 species have been added to the threatened categories—i.e. Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered—in this […]
The IUCN Red List releases its 2012 update, adding 247 species to its threatened categories. The king cobra has been evaluated by the IUCN Red List for the first time and listed as Vulnerable. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Nearly 250 species have been added to the threatened categories—i.e. Vulnerable, Endangered, and Critically Endangered—in this […] A yew tree in the Himalayas that produces the chemotherapy drug, Taxol, is in danger of extinction. An update to the IUCN Red List, has moved the tree, named Taxus contorta, from Vulnerable to Endangered. Overharvesting for medicine and fuelwood have placed the species in serious danger. Craig Hilton-Taylor with the Red List told the […]
A yew tree in the Himalayas that produces the chemotherapy drug, Taxol, is in danger of extinction. An update to the IUCN Red List, has moved the tree, named Taxus contorta, from Vulnerable to Endangered. Overharvesting for medicine and fuelwood have placed the species in serious danger. Craig Hilton-Taylor with the Red List told the […] Imagine if your job was to locate extinct species. In 2010, biologists with The Search for Lost Frogs set out on a tropical mission hoping to confirm the existence of frog species not seen in decades. The team recovered proof of four out of a hundred missing species, including a toad among the expedition’s Top […]
Imagine if your job was to locate extinct species. In 2010, biologists with The Search for Lost Frogs set out on a tropical mission hoping to confirm the existence of frog species not seen in decades. The team recovered proof of four out of a hundred missing species, including a toad among the expedition’s Top […] Focused conservation efforts, including reintroduction of captive individuals into the wild, have saved the golden lion tamarin from extinction. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Don’t despair: that’s the message of a new paper in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, which argues that decades of conservation actions at multiple scales have had a positive impact for […]
Focused conservation efforts, including reintroduction of captive individuals into the wild, have saved the golden lion tamarin from extinction. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Don’t despair: that’s the message of a new paper in Trends in Ecology and Evolution, which argues that decades of conservation actions at multiple scales have had a positive impact for […] Previously unpublished 17th Century Dutch sketch of the dodo, taken from a real specimen, either alive or stuffed. Dronte means dodo in Dutch. The past twelve months have seen 914 species added to the threatened list by the world’s authority of species endangerment, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List. Over […]
Previously unpublished 17th Century Dutch sketch of the dodo, taken from a real specimen, either alive or stuffed. Dronte means dodo in Dutch. The past twelve months have seen 914 species added to the threatened list by the world’s authority of species endangerment, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN)’s Red List. Over […] On October 1, 2010, the carcass of a striped hyena was found entangled in barbed wire surrounding an orchard in southern Armenia. The find represents the nation’s first confirmed hyena observation in over 60 years. Although they may be doglike in appearance, hyenas are actually more related to cats than dogs, with their closest relatives […]
On October 1, 2010, the carcass of a striped hyena was found entangled in barbed wire surrounding an orchard in southern Armenia. The find represents the nation’s first confirmed hyena observation in over 60 years. Although they may be doglike in appearance, hyenas are actually more related to cats than dogs, with their closest relatives […] Two studies investigated the scale and potential threat of continued trade in red pandas and found that while reports are low, the occurrence of isolated incidents may be enough to threaten species survival. The red panda, Ailurus fulgens, is a cat-sized, arboreal mammal which lives in temperate forests in the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. […]
Two studies investigated the scale and potential threat of continued trade in red pandas and found that while reports are low, the occurrence of isolated incidents may be enough to threaten species survival. The red panda, Ailurus fulgens, is a cat-sized, arboreal mammal which lives in temperate forests in the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. […] A fifth of the world’s vertebrate species (i.e. mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish) are threatened with extinction, according to a massive new study by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN); and the situation is worsening for the world’s wildlife: on average 52 species of mammals, birds, and amphibians move one category […]
A fifth of the world’s vertebrate species (i.e. mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish) are threatened with extinction, according to a massive new study by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN); and the situation is worsening for the world’s wildlife: on average 52 species of mammals, birds, and amphibians move one category […]