Sites: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
topic: Clean Energy
Social media activity version | Lean version
Impunity and pollution abound in DRC mining along the road to the energy transition
- In the DRC’s copper belt, pollution from the mining of cobalt and copper, critical minerals for the energy transition, is on the rise and polluters are ignoring their legal obligations to clean it up.
- Cases of pollution have caused deaths, health problems in babies, the destruction of crops, contaminated water and the relocation of homes or an entire village, residents and community organizations say.
- Mining is the economic lifeblood of the region and the state-owned mining company, Gécamines, is a shareholder in several other companies — some accused of these same rights abuses.
- Mongabay visited several villages in Lualaba province affected by pollution and human rights violations to assess the state of the unresolved damage — and whether companies are meeting their legal obligations.
Indonesia civil society groups raise concerns over proposed Borneo nuclear reactor
- Indonesia’s largest environmental advocacy group, Walhi, staged demonstrations in Jakarta and West Kalimantan province to raise awareness about a proposed nuclear power plant in West Kalimantan’s Bengkayang district.
- In 2021, a U.S. agency signed a partnership agreement with Indonesia’s state-owned power utility to explore possibilities for a reactor in the province. Survey work is currently being conducted to determine the project’s viability and safety.
- Some environmental groups have questioned the merit of the plan on safety grounds and the availability of alternative renewable sources.
Multilateral development banks must prioritize clean & community-led energy projects (commentary)
- Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), governments, and corporations across 160 countries consider or approve more than one investment per day in the energy sector.
- Despite commitments to tackle the climate crisis, many of these investments support the fossil fuel industry, while others invest in false clean energy solutions like hydropower which often cause harm to local communities.
- “To achieve a just energy transition, MDBs and governments must prioritize sustainable renewable energy models that empower communities and ensure inclusive energy access,” a new op-ed argues.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors, not necessarily Mongabay.
Tribes turn to the U.N. as major wind project plans to cut through their lands in the U.S.
- Last week a United States federal judge rejected a request from Indigenous nations to stop SunZia, a $10 billion dollar wind transmission project that would cut through traditional tribal lands in southwestern Arizona.
- Indigenous leaders and advocates are turning to the U.N. to intervene and are calling for a moratorium on green energy projects for all U.N. entities “until the rights of Indigenous peoples are respected and recognized.”
- Indigenous leaders say they are not in opposition to renewable energy projects, but rather projects that don’t go through the due process and attend their free, prior and informed consent.
- According to the company, the wind transmission project is the largest clean energy infrastructure initiative in U.S. history, and will provide power to 3 million Americans, stretching from New Mexico to as far as California.
Consent and costs are key questions on extraction of ‘energy transition’ minerals
- The many environmental, social, and health impacts of extracting minerals that power renewable energy, mobile phones and electric vehicles need more debate and detailed media coverage, an Indigenous rights activist and journalist say on the podcast.
- Mongabay speaks with Galina Angarova, Indigenous executive director of the SIRGE Coalition, and environmental journalist Ian Morse about critical questions to ask about the demand for certain minerals and who benefits from their extraction.
- Research indicates as much as 54% of all transition minerals are on or near Indigenous land, however, no nation has properly implemented the protocols of Free Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC), a framework that’s key to ensuring that local communities are aware of, benefit from – and especially are not harmed by – such activities.
- The risk of global supply chain disruptions due to the concentration of minerals in relatively few countries, or the potential formation of cartels restricting their supply, adds further complexity to the situation, the two podcast guests say.
Locals slam Zimbabwe for turning a blind eye to Chinese miner’s violations
- Mining workers and villagers near the Bikita Minerals lithium mine in Zimbabwe accuse the government and Chinese mining company Sinomine Resource Group of sidelining environmental and social standards in the scramble for lithium.
- After a series of displacements, spills, labor abuses, a death, and little action by authorities, locals and experts accuse the government of failing to enforce its own laws and letting bad mining practices run loose.
- According to industry experts, in theory, Chinese investments come with an increasingly robust set of ESG standards, but in practice these aren’t followed if host countries “shy away” from making such demands from their new partners.
- Zimbabwe, under economic stress, holds Africa’s largest lithium reserves and sees potential for an economic boost from mining the critical mineral, which represents the country’s fastest growing industry, with companies from China as the largest share of investors
Soraida Chindoy: the Indigenous guardian defending the sacred Putumayo mountains
- An Indigenous woman from the Inga community in the Condagua reservation in Putumayo, Colombia, is leading the struggle against a Canadian mining company that plans to mine the community’s sacred mountains for copper and molybdenum.
- Within Soraida Chindoy’s territory is the Doña Juana-Chimayoy páramo, where eight rivers have their source and where there are 56 lagoons. The site, where the Amazon rainforest and the Andes meet, is sacred to the Indigenous population.
- Her campaign against mining was borne of tragedy. In 2017, she and her family were among the almost 22,000 people affected by the landslide in Mocoa, when Mother Earth provided a stark warning as to why it is so important to take care of her.
We need a better understanding of how crops fare under solar panels, study shows
- In agrivoltaics, farmers grow crops beneath or between solar panels.
- Proponents say the technology can help achieve clean energy goals while maintaining food production, but experts caution that careful analysis and guidelines are needed if we’re not to compromise agricultural production.
- A new synthesis of previously published studies finds that overall crop yields decline as the amount of land covered by solar panels increases.
- This ground cover ratio is a convenient, easily measured and reproducible metric that can be used to predict crop yields and better evaluate agrivoltaic systems.
Conservation ‘setback’ looms as Nepal opens protected areas to hydropower projects
- Nepal’s government has approved a controversial new proposal allowing the development of large-scale hydropower plants within protected areas, prompting concerns about conservation setbacks.
- The “Construction of Physical Infrastructure Inside Protected Areas” procedures was officially approved Jan. 4, permitting hydropower developers to build projects entirely within protected areas, release minimal water during the dry season, and acquire land more easily.
- Conservationists, lawyers and Indigenous communities have opposed the policy, calling it legally flawed and warning that it threatens conservation achievements in the face of climate change.
- More than two dozen conservationists submitted feedback during the policy’s public consultation phase, but these weren’t accommodated to any significant degree in the final document.
Report: Rush for ‘clean energy’ minerals in Africa risks repeating harmful extractivist model
- The nonprofit Global Witness investigated lithium mining projects in Zimbabwe, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and Namibia, which appear to reproduce the same model of extractivism that has impoverished African countries for centuries.
- In March, residents of the Namibian town of Uis took to the streets to protest the activities of Chinese miner Xinfeng, alleging the company was carrying out large-scale industrial mining without the proper permits or social license.
- In Zimbabwe, activist Farai Maguwu from the Centre for Natural Resource Governance described a similar experience of exclusion and exploitation at Chinese miner Sinomine’s Bikita lithium operation, calling it “typical extractivism.”
- One of the ways to prevent exploitation is to shut out companies that “socialize the costs and privatize the profits,” Maguwu said, adding he remains hopeful that encouraging competition between companies from across the world is the way to ensure better outcomes for Zimbabweans.
New dams in Cambodia pit ‘green’ hydropower against REDD+ project
- The recent approval of two hydropower dams in Cambodia’s Cardamom Mountains could undermine a REDD+ carbon project in the area.
- The Southern Cardamom REDD+ Project relies on keeping the forests in this region standing — a goal researchers say is “completely incompatible” with the forest clearing and flooding necessitated by the new dams.
- The lack of transparency inherent in both the carbon market and the Cambodian government means that the fate of the Cardamoms remains unclear for now.
Little achieved for Indigenous groups at U.N. climate summit, delegates say
- At this year’s U.N. climate conference, COP28, Indigenous delegates numbered more than 300, but were left generally disappointed with the outcomes of the event.
- The final agreement had little inclusion of Indigenous rights and excluded an Indigenous representative from sitting on the board of the newly launched loss and damage fund.
- Indigenous groups say two big climate mitigation strategies, the clean energy transition and carbon markets, should include robust protection of Indigenous rights and consent.
- Despite setbacks, Indigenous leaders say they’re working on increasing their presence and influence at the next climate conferences, including upping their numbers to 3,000 delegates, creating a large international Indigenous Commission, and taking part in the summit’s decision-making.
A lithium ‘gold mine’ is buried under one of Europe’s last heritage farming systems
- The hilly Barroso region of northern Portugal has been recognized for its centuries-old and “globally important” farming system that combines agricultural biodiversity, resilient ecosystems and a valuable cultural heritage.
- But the region is also home to what’s believed to be one of Europe’s largest deposits of lithium, an element that will be critical in the ongoing clean energy transition, with EU and Portuguese officials saying mining projects in Barroso will be key to securing domestic supplies of the metal.
- Residents and environmental activists, however, warn the mines will scar the landscape, contaminate the water, erode the soil, disrupt local livelihoods, and deprive them of communal lands.
- Yet even as they continue to oppose the planned mines, the state can declare lithium projects to be of strategic public interest to force residents to lease the lands needed for the mining projects.
Nickel mine threatens Philippines biodiversity hotspot on Sibuyan Island (analysis)
- The pursuit of cleaner sources of energy could lead to the destruction of a biodiversity hotspot of global significance — the ‘Galapagos of Asia’ — a new analysis argues.
- Communities on Sibuyan Island have opposed mining for over 50 years but need decisive action from the government to safeguard their forests and rivers via a permanent mining ban.
- Demand for nickel and other ‘energy transition metals’ is set to increase, requiring long-term planning and rigorous, independent and participatory assessment of environmental & social impacts.
- This post is an analysis. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Indonesia pushes carbon-intensive ‘false solutions’ in its energy transition
- Indonesia’s newly revised plan for a $20 billion clean energy transition has come under criticism for offering “false solutions” that would effectively cancel out any gains it promises.
- One of its most controversial proposals is to not count emissions from off-grid coal-fired power plants that supply industrial users without feeding into the grid.
- Emissions from these so-called captive plants alone would exceed any emissions reductions projected under the rest of the Just Energy Transition Partnership.
- The plan also puts a heavy emphasis on “false” renewables solutions such as biomass cofiring and replacing diesel generators with natural gas ones.
Circular economy poised to go beyond outdated oil, gas and coal, experts say
- The exploitation of oil, gas and coal is now destabilizing all nine planetary boundaries and driving a triple crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss and pollution. The solution, experts say, is to move from a hydrocarbon-based linear economy to a diversified circular economy. This is Part 3 of a three-part miniseries.
- To step back from dangerous environmental thresholds, humanity needs to cut its use of fossil fuels, petroleum-based synthetic fertilizers and petrochemicals (especially plastics), with many analysts unequivocal about the unlikelihood of utilizing oil, gas and coal resources to implement a global circular economy.
- To achieve a circular economy, fossil fuels need to be phased out and alternative energy sources put in place. Bio-fertilizers need to be adopted and scaled up, and nitrogen fertilizers must be managed better to prevent overuse. Plastic production needs to be curbed, with a ban of single-use plastics as a start.
- Unfortunately, the world isn’t on target to achieve any of these goals soon, with surging oil and natural gas production by the U.S., Saudi Arabia and Russia expected to push the planet past the maximum 2° C (3.6° F) temperature increase agreed to in the 2015 Paris Accord — putting Earth at risk of climate catastrophe.
Colombian wind farm end-of-life raises circularity and Indigenous questions
- Jepírachi, Colombia’s first wind farm, is waiting to be dismantled after reaching its end of life, but the process itself and the project’s legacy remain uncertain.
- Across the world, first-generation wind projects are becoming obsolete, and disposing of the equipment, especially of the wind blades, is challenging circularity goals; currently, most blades are used in cement factories.
- Three Wayuu communities depend on the desalination plant created by the wind farm company for their clean water, but now the communities question the future of their water security.
Can carbon markets solve Africa’s climate finance woes?
- The African Carbon Markets Initiative, a consortium of Global North donors, corporate representatives, conservation groups and energy lobbyists, is pushing to expand carbon markets on the continent.
- The effort has gained the vocal support of Kenyan President William Ruto, along with a number of other African heads of state, who see carbon markets as a way to generate badly needed climate finance.
- But African environmental groups have sharply criticized carbon markets, saying they represent a “false solution” to the climate crisis and will mostly enrich bankers and traders based outside the continent.
- The drive to scale up carbon markets in Africa and elsewhere is set to be a major agenda item at this month’s COP28 climate summit in Dubai.
Mine in ‘world cobalt capital’ displaces locals and monks under questionable circumstances
- Local residents living in the DRC’s ‘cobalt capital of the world’ are being forced to relocate in order to make way for a mine owned by Chinese company COMMUS (Compagnie miniere de Musonie).
- The relocation process is being done under questionable circumstances, including providing compensation payments under the table which don’t always meet amounts needed to buy a decent home, contradictory statements, lack of consultation, and few traces of written documentation to fact-check claims made by local government officials, the mining company and displaced people.
- The demand for cobalt, a critical mineral for the clean energy transition, is expected to increase and lead to the eviction of communities who find themselves living above their deposits, say energy experts.
- The mining company’s lawyer says the relocation process is happening fairly, payments are calculated alongside officials and civil society groups, and the land and buildings, like schools, rather belong to the company’s owners.
Study: Tricky balancing act between EV scale-up and mining battery metals
- A recent study finds rapidly switching to electric vehicles could significantly cut emissions but also increase demand for critical battery metals like lithium and nickel.
- Mining metals like lithium has major environmental impacts including deforestation, high water use, and toxic waste.
- Electrifying heavy-duty vehicles requires substantially more critical metals than other EVs and could account for 62% of critical metal demand in coming decades despite making up just 4-11% of vehicles.
- The researchers recommend policies to support recycling, circular economies, alternative battery chemistries, and coordinated action to balance environmental and material needs.
Pacific alliance adopts moratorium on deep-sea mining, halting resurgent PNG project
- The Melanesian Spearhead Group put in place a moratorium on deep-sea mining within its member countries’ territorial water in a declaration signed Aug. 24.
- Leaders from Fiji, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and an alliance of pro-independence political parties known as FLNKS from the French territory of New Caledonia said more research is needed to establish whether mining the seabed below 200 meters (660 feet) is possible without damaging ecosystems and fisheries.
- The moratorium ostensibly thwarts the return of Nautilus Minerals, a Canadian company, to Papua New Guinea and its Solwara 1 project in the Bismarck Sea, where it had hoped to mine gold and copper from sulfide deposits on the seafloor.
- Proponents of deep-sea mining say that minerals found deep beneath the ocean are necessary for the production of batteries used in electric vehicles and thus are critical in the global transition away from fossil fuels.
Indonesian voters want a clean energy plan, but candidates haven’t delivered
- Candidates running in Indonesia’s presidential election next year must make clear their plans for transition the country away from fossil fuels and toward clean energy, policy experts say.
- A survey shows young Indonesians, who make up the majority of potential voters, view environmental issues in general, and a just energy transition in particular, as crucial issues for a new president to tackle.
- However, none of the three hopefuls who have declared their candidacies to date have addressed these issues, with the survey reflecting a sense of pessimism among respondents.
- Indonesia, a top greenhouse gas emitter, has said it aims to hit net-zero emissions by 2060 and retire its existing fleet of coal-fired power plants, but continues to build more coal plants to serve its growing metal-processing sector.
In Brazil, rural communities are caught in the eye of the wind farm storm
- In Brazil’s semiarid Caatinga biome, wind power farms have brought dirt, noise and disruption to the livelihood of local communities.
- Many locals say the project developers have failed to properly consult them before building roads, infrastructure and turbines in the region.
- Wind power is considered a clean energy source in Brazil, which qualifies developers for access to easier financing and licensing, often at the expense of conflicts with local villages.
- From loss of livelihoods to damaged houses, this investigation by the Marco Zero news outlet shows how the development model that Brazil has adopted for wind power expansion has come at a high cost to rural communities.
Nuclear pioneers press ahead with plans for Indonesia island frontier
- PT ThorCon Power Indonesia is moving closer toward building an experimental nuclear reactor on a remote island in a strait bisecting the islands of Sumatra and Borneo.
- The company says the electricity generated by a thorium-powered reactor could generate electricity at 3 cents per kilowatt hour while emitting close to zero greenhouse gases.
- Some worry the project could threaten delicate marine ecosystems on an island that was, until recently, protected as a conservation area.
A just energy transition requires better governance & equity in the DRC
- The global energy transition has increased demand for critical minerals involved in the making of products such as lithium-ion batteries, solar panels and other renewable energy sources.
- In the Democratic Republic of Congo, this demand has fueled a poorly regulated mining sector that has forced Indigenous communities off their land, polluted water and air, and given little back in the way of infrastructure or development.
- The DRC has also recently opened 27 blocks of land for oil exploration under the auspices of lifting the nation out of poverty, but our guests say the handling of these other mineral revenues doesn’t bode well for an equitable oil boom.
- Joseph Itongwa Mukumo, an Indigenous community member of Walikale in the North Kivu province and director of ANAPA-DRC, and Christian-Géraud Neema Byamungu, Francophone editor at the China Global South Project, speak with Mongabay about the impacts of mining on local and Indigenous communities and what DRC residents need for a just energy transition.
Forests in the furnace: Can fashion brands tackle illegal logging in their Cambodian supply chains?
- Global fashion brands touting sustainability claims continue to buy from their contract factories in Cambodia that burn illegally logged wood in their boilers.
- Mongabay reached out to 14 international brands that listed factories identified in a report as using illegal forest wood, but they either didn’t respond or evaded questions on illegal logging in their supply chains.
- One prominent brand, Sweden’s H&M, has developed an app that allows its partner factories to identify deliveries of forest wood, but industry insiders say there are ways to circumvent it, and that the government should be playing a bigger role in the issue.
- This story was supported by the Pulitzer Center’s Rainforest Investigations Network where Gerald Flynn was a fellow. *Names have been changed to protect sources who said they feared reprisals from the authorities.
Over a third of conflicts over development projects affect Indigenous people: Study
- Roughly one-third of all environmental conflicts documented in an online crowd-sourced atlas affect Indigenous peoples, researchers have found.
- The mining of transition minerals has been linked to hundreds of allegations of abuse with multi-faceted impacts on the environment and communities, according to a new report.
- Some Indigenous organizations are calling for Indigenous rights and free, prior and informed consent to be central to the transition to a green economy in light of the global rush to secure clean energy minerals.
U.N. climate chief calls for end to fossil fuels as talks head to Dubai
- International climate talks began in Bonn, Germany, on June 5.
- A key part of the discussion will be the global stocktake, assessing progress toward the emissions cuts pledged by nations as part of the 2015 Paris climate agreement.
- Discussions will work to provide the technical details of the stocktake, but the consensus is that the world is not on track to cut emissions by 50% by 2030, which scientists say is key to keeping the global temperature rise below 1.5°C (2.7°F) over pre-industrial levels.
- The talks are a precursor to COP28, the annual U.N. climate conference, scheduled to begin Nov. 30 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, which is a major oil- and gas-producing nation.
Report: Forest-razing biomass plant in Indonesia got millions in green funds
- An Indonesian oil and gas company is using government money to clear rainforest for a biomass power plant, according to a new report.
- The project has received a total of $9.4 million from two Ministry of Finance agencies, including one tasked with managing environmental protection funds from international donors.
- Criticism of Medco’s activities reflects a broader debate over whether clear-cutting rainforest can ever be considered sustainable, even when done in the name of transitioning a major coal-producing country away from fossil fuels.
From palm oil waste to cellulosic ethanol: Indonesia’s opportunity (commentary)
- Many Indonesian farmers say they haven’t seen benefits from the country’s biofuel program. Cellulosic ethanol could help fix the problem, a new op-ed says.
- Tenny Kristiana of the International Council on Clean Transportation argues Indonesia could develop a domestic cellulosic ethanol industry that would use leftover plant residues such as palm trunks, empty palm fruit bunches and palm press fiber.
- Currently, Indonesia exports these leftovers to countries like Japan, but developing an industry at home could aid local farmers and create new jobs in factories, transportation and plantation work.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Scramble for clean energy metals confronted by activist calls to respect Indigenous rights
- At the world’s largest gathering of Indigenous peoples in New York, mining for critical minerals is at the top of the agenda as the push for the clean energy transition gains steam worldwide.
- Indigenous leaders are calling on countries and companies to create binding policies and guidelines requiring the free, prior, and informed consent (FPIC) of communities over clean energy mining projects that seek to explore and extract these minerals on their lands or in ways that affect their livelihoods.
- Such binding policies will be very difficult for government, companies and investors to abide by, says an executive, as it gives communities the capability to decline on highly-profitable projects and strategies part of national energy transition goals.
- Indigenous leaders also highlight FPIC as a framework for partnership with such projects, including options for equitable benefit-sharing agreements or memorandum of understanding, collaboration or conservation.
Floating solar project on Philippines natural lake brings hope — and questions
- Laguna Lake in the Philippines is home to a pilot project for a floating solar photovoltaic (FPV) installation that could provide energy to surrounding communities as the country faces pressure to transition away from fossil fuels.
- “Floatovoltaic” installations already exist in other parts of Asia, but none are currently on natural lakes like Laguna; researchers say further research is needed to determine the long-term effects on the environment and local communities.
- In Laguna, local fishing communities hope their voices are heard as the project develops, especially since their livelihoods could be affected by the FPV installations; however, the project could also bring new jobs to the area.
Indonesia’s Just Energy Transition Partnership must increase transparency (commentary)
- Last year, Indonesia obtained a $20 billion international financing commitment to fund the country’s transition to clean energy via the Just Energy Transition Partnership (JETP).
- This year, Transparency International reported Indonesia’s susceptibility to corruption increased from the previous year, which could affect the JETP scheme as well.
- A new op-ed argues that the JETP should increase transparency and public inclusion in its planning processes to avoid falling victim to corruption which would slow the country’s transition to a renewable energy future.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
What’s black and white and spins? Wind turbines that don’t kill birds
- A new study suggests a way to stop seabirds from colliding with wind turbines: painting a black-and-white pattern on all three blades and the pylon to produce a flickering effect.
- This strategy has yet to be tested or implemented, but experts believe it has promise and would create its desired effect.
- However, getting approval for painting wind turbines can be difficult, and this mitigation strategy might generate the unintended effect of displacing seabirds, one expert says.
- It’s estimated that wind turbines kill thousands of birds in the U.K. alone.
Will clean-energy minerals provoke a shift in how mining is done in Africa?
- Meeting the Paris climate goals to curb global warming could quadruple demand for metals like lithium, cobalt and nickel by 2040, according to the International Energy Agency. About a fifth of these critical reserves are found in Africa.
- With mining activity ramping up across Africa, civil society organizations are asking for concrete changes in how mining is done and whose needs it addresses.
- Many activists who work with communities in Africa fear that far from benefiting from their mineral wealth, countries that hold reserves for critical minerals will pay the steepest price for their extraction, a replication of the mining footprint without a transformation in the way mining is done.
- While most activists and observers agree about the need to pursue the highest environmental, social and governance standards, many CSOs say it doesn’t have to happen as part of a superpower-led geopolitical race but be part of a globally accepted framework.
Plan to mine ‘clean energy’ metals in Colombian Amazon splits communities
- Libero Copper, a Canadian company, plans to mine copper, molybdenum and other metals in the richly biodiverse Andean-Amazon Piedmont, which has led to strong divisions within Indigenous and local communities.
- The copper and molybdenum project is framed as a green project that could contribute much-needed minerals for the country’s energy transition, a proposal that aligns with the goals of the new left-wing government of Gustavo Petro.
- However, some communities and environmental activists oppose the mining project over concerns of deforestation, landslides and loss of forest-based livelihoods in the region.
- Others support the clean energy transition and the company’s promise of jobs in the historically neglected region.
‘They paid for it with misery’: Q&A with Chile dam critic Jose Marihuan Ancanao
- Jose Marihuan Ancanao, president of the Ayin Mapu La Peña community, spoke to Mongabay’s Maxwell Radwin about the impact of hydropower plants in parts of the Chilean Andes that are home to Indigenous people with a spiritual connection to rivers and the surrounding mountains.
- Marihuan was relocated in the early 2000s by a different hydropower plant and, although relocation isn’t a threat this time around, is witnessing the construction of another mega dam near his community.
- The 90-megawatt Rucalhue power plant has resulted in the felling of nationally protected trees sacred to the Pehuenche and, once finished, would flood some ancestral land.
Dam construction ignites Indigenous youth movement in southern Chile
- Dam construction on the Bío Bío watershed has plagued Indigenous Mapuche-Pehuenche communities in south-central Chile for decades, with many families having to relocate due to flooding of ancestral lands.
- The 90-megawatt Rucalhue hydropower plant, located near the town of Santa Bárbara, is the latest project causing controversy among local communities, who say they’re sick of battling infrastructure projects that disrespect their culture and traditions.
- Young people have been particularly outspoken against the project, staging sit-ins at the work site, sending petitions to government agencies, and helping organize a local plebiscite.
- Hydropower plants, while less polluting than many other forms of energy generation, still require the clearing of trees and the disrupting of river flows, which can have a significant impact on surrounding ecosystems.
“Largest of its kind” dam in Cameroon faces backlash from unimpressed fishmongers
- Cameroon is constructing a new 420-megawatt capacity hydroelectric dam in Batchenga, aiming to reduce the country’s significant energy deficit by 30%.
- The massive dam project is impacting several villages where fishing is an essential part of the local economy. Several professional bodies, including fishmongers, fishermen and restaurant owners, have lost their livelihoods due to the dam’s construction.
- Fishmongers in one nearby village, Ndji, are becoming increasingly desperate for proper compensation as the amounts paid by the Nachtigal Hydro Power Company is not enough to make ends meet, they say.
- Civil society organizations are also accusing Nachtigal of seriously violating environmental standards during dam construction, despite the company continuously receiving environmental compliance certificates by the government.
Why Russia should not win the bid for Bolivia’s lithium (commentary)
- The government of Bolivia is currently negotiating with various foreign companies from countries including Argentina, the United States, China, and Russia, for the handling of its lithium extraction.
- Results of the bidding process should be announced within the next two weeks. A top contender is Russia: Moscow-based Uranium One Group has offered to extract Bolivia’s lithium reserves, operated by state-owned energy and mining giant Rosatom.
- Joseph Bouchard, a Canadian analyst focusing on geopolitics and security in Latin America, argues that Bolivia should not accept the Russian bid.
- This article is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Contorted energy politics of the Ukraine crisis (commentary)
- The Russian invasion of Ukraine has driven energy prices to the highest levels in years, spurring a global energy crisis.
- Nikolas Kozloff, a writer who authored “No Rain in the Amazon: How South America’s Climate Change Affects the Entire Planet,” examines America’s response, which he argues is so far shaping up to be a missed opportunity to transition toward greener energy sources.
- “The Ukraine crisis has the potential to finally nudge the world towards a long overdue clean energy future,” he writes. “However, the Biden administration seems to have calculated that pursuing short-term political gains must take priority.”
- This article is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Sluggish growth of renewables threatens Bangladesh’s clean-energy goals
- The development of renewable energy in Bangladesh continues to be outpaced by non-renewables such as coal, gas and nuclear.
- This threatens the country’s ability to meet both its commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions under the Paris Agreement, and its goal under the U.N. SDGs of ensuring that at least 10% of energy consumption by 2030 comes from renewable sources.
- Renewables today account for just 2% of the power flowing into the grid, or 3.49% of total consumption if off-grid sources are included.
- While the country is embarking on a spate of renewable energy projects, including one solar and four wind farms, these are overshadowed by the seven coal plants, 13 gas plants, and one — possibly two — nuclear plants in the works.
International funding nowhere near enough for Indonesia to cut emissions: Study
- Indonesia will have to come up with its own funding schemes to have any chance of achieving its carbon emissions reduction target by 2030, a new study says.
- The government has calculated that it needs $323 billion in funding from the international community to slash emissions by 41%, but received just $6.4 million between 2007 and 2019, the study found.
- It found that Indonesia faced difficulties accessing international climate grants, with donors often prioritizing their own interests or preferring countries with lower incomes than Indonesia.
- A potential source of funding could be the sale of government debt that’s a combination of environmental (green) bonds and Islamic-compliant bonds, known as sukuk, the study says.
Analysis: Elite power struggle sees Vietnam abandon coal, but leaves collateral damage
- Vietnam’s energy establishment attempted last year to flout top-level instructions to undo the nation’s growing dependence on coal and other fossil fuels.
- However, after more than a decade of failures by bureaucrats and managers to deliver clean energy and clean air, there is broad sentiment for maximal exploitation of Vietnam’s plentiful endowment of wind and sunshine.
- At COP26, the prime minister left no doubt which way the nation is headed: Vietnam, he pledged, will be carbon neutral by 2050.
- But the recent developments have also seen a leading advocate for the clean energy transition jailed after publishing a letter warning of the risks of clinging to coal.
Climate-positive, high-tech metals are polluting Earth, but solutions await
- Green energy technology growth (especially wind, solar and hydropower, along with electric vehicles) is crucial if the world is to meet Paris climate agreement goals. But these green solutions rely on technology-critical elements (TCEs), whose production and disposal can be environmentally harmful.
- Mining and processing of TCEs requires huge amounts of energy. Mines use gigantic quantities of fresh water; can drive large-scale land-use change; and pollute air, soil and water — threatening biodiversity. TCEs may also become pollutants themselves when they are disposed of as waste.
- We know relatively little about what happens to TCEs after manufacture and disposal, but trace levels of many critical elements have been detected in urban air pollution, waterways and ice cores. Also of concern: Rare-earth elements have been detected in the urine of mine workers in China.
- Green mining technologies and new recycling methods may reduce the impacts of TCE production. Plant- and microbe-based remediation can extract TCEs from waste and contaminated soil. But experts say a circular economy and changes at the product design stage could be key solutions.
At a disputed Native massacre site, tribes brace for a new, lithium-driven rush
- The U.S. Bureau of Land Management has approved an open-pit lithium ore mine in northern Nevada, despite protests by Native tribes to protect the disputed sacred site.
- Lithium is in high demand as the key component in batteries that fuel electric vehicles and cellphones, raising environmental concerns about its extraction.
- The U.S. government is ramping up production of lithium all along the domestic supply chain to meet its clean energy goals.
As blackouts loom, Indonesia’s energy crisis highlights its addiction to coal
- Coal miners in Indonesia have been shirking their obligation to allocate 25% of their output for the domestic market, leading to a critical shortage of the fossil fuel for power generation.
- That’s prompted the government to impose a ban on coal exports throughout January, but energy policy experts say this doesn’t address the root of the problem: Indonesia’s overreliance on coal in its energy mix.
- They say the energy crunch, the fifth in 15 years, should ring alarm bells about the need to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels and toward renewable energy.
- They point out that years of coddling the coal industry have led to the current situation, and that there’s no real sense of urgency about moving away from coal.
In the Brazilian Amazon, solar energy brings light — and new opportunities
- A village on the banks of Brazil’s Negro River is running 132 solar panels as part of a pilot project aimed at bringing clean energy and economic opportunity to remote communities in the Amazon.
- The scheme promises to bring reliable energy to the community of Santa Helena do Inglês, in northern Amazonas state, addressing frequent power cuts that have long plagued the remote village and thwarted efforts to develop sustainable income streams.
- The solar energy supply is helping the community — a former logging hub that now lies within a protected reserve — generate income from fishing and ecotourism, without encroaching on the forest.
There is no climate solution without China and America, says Li Shuo
- China and the United States account for nearly half the world’s carbon dioxide emissions from energy, while the two countries’ resource consumption is among the biggest threats to global biodiversity. These issues make China and the U.S. major targets for environmental activists like Greenpeace.
- Despite the difference in political systems between China and the U.S., Li Shuo, Senior Climate and Energy Policy Officer at Greenpeace China, says the approach Greenpeace uses in China, like other places, is based on building trust.
- Li Shuo says the countries share another similarity: They are lagging behind on their climate commitments: “There is no climate solution without the G2 rolling towards the same direction,” Li Shuo told Mongabay. “The U.S. can do all it can to reduce emissions. It won’t solve the problem as long as China doesn’t comply, and vice versa.”
- Beyond climate, China and the U.S. have another near-term opportunity to collaborate: averting the global extinction crisis via strong action and commitment at the upcoming U.N. Conventional on Biological Diversity (CBD).
Turning Kenya’s problematic invasive plants into useful bioenergy
- The shores of Lake Victoria are clogged with water hyacinth, a South American invasive plant that is hurting Kenya’s freshwater fishery, economy and people’s health. While manual removal is effective, it is labor intensive and can’t keep up with the spreading plant.
- Kenyans are innovating to find ways to reduce water hyacinth by finding practical uses for the invader. In 2018, a program was launched to turn the exotic species into biogas which is then offered to economically vulnerable households to use as a biofuel for cooking.
- One proposal being considered: a scaled up industrial biogas plant that would use water hyacinth as a primary source of raw material. Efforts are also underway to convert another invasive plant, prickly pear into biogas used for cooking. A biocontrol insect is also proving effective, though slow, in dealing with prickly pear.
- These economically viable and sustainable homegrown solutions are chipping away at Kenya’s invasive species problem, though to be truly effective, these various projects would need to be upscaled.
Biofuel in Mexico: Uphill battle against bureaucracy, organized crime
- Biofuels based on pressed plant oils, and made especially from used cooking oil, could help Mexico’s public transport sector transition to a cleaner and climate-friendly energy era, according to researchers and industry entrepreneurs.
- But there is a lack of government regulatory support, while the nation’s new president is betting on fossil fuels and neglecting biodiesel options and nature-based climate solutions.
- As a result, small biodiesel producers have to operate in a legal gray zone, while industry entrepreneurs are held back in the development of the technology and the market.
- Mexico isn’t alone: Many nations large and small are struggling with hurdles imposed by fossil fuel-friendly governments and a lack of supportive regulations to create a level playing field for the rapid development and deployment of biodiesel and other climate-friendly alternative energy solutions.
Converting biowaste to biogas could power cleaner, sustainable Earth future
- Biogas made from organic materials — including food and agricultural waste, and animal or human manure — is a renewable, sustainable, affordable and inclusive energy alternative becoming increasingly available to households, farms, municipalities and nations.
- Converting biowaste into biogas, via anaerobic digestion technology, is a strategy that could contribute to multiple U.N. Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris climate agreement. Biodigesters are already in use to meet a range of energy needs around the world.
- Current limiting factors to the sector’s growth include technical and adaptive challenges, lack of awareness in many regions, and unsupportive policy instruments that can discourage biogas adoption.
- Ahead of COP26, the critically important U.N. climate meeting coming this November, the World Biogas Association is urging governments to integrate biogas into their Nationally Determined Contributions — their voluntary emissions reduction targets, as agreed to under the Paris Agreement.
Coal phase-out plan gets pushback in power-hungry Indonesia
- Officials and industry in Indonesia have questioned a plan by the national utility to phase out all coal-fired power plants, while clean energy advocates have welcomed the proposal.
- The main objections to the plan include the high cost of prematurely retiring coal-fired power plants that haven’t achieved a return on investment, and the persistently high price of renewable energy compared to coal in Indonesia.
- Supporters of the plan say it’s not just economically feasible, but over the long term would work out cheaper than maintaining coal plants, while creating millions of jobs in the renewable energy sector.
- A glaring inconsistency in the plan, however, is that the utility is at the same time also planning to bring 117 under-construction and planned coal-fired power plants online, negating any notion of a “phase-out.”
ADB declares coal exit in Asia Pacific, but gas remains in play
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) plans to exit financing coal, oil and natural gas exploration and extraction activities, according to its draft energy policy released May 7.
- The bank says it also intends to deliver climate finance worth $80 billion between 2019 and 2030 to ensure that at least 75% of its projects address climate change issues.
- While green groups have welcomed the transition, they note that the draft energy policy has a loophole by potentially allowing fossil gas investments.
- ADB is set to release its final energy policy by October this year.
‘We’re at a tipping point with coal’: Q&A with Bloomberg’s Antha Williams
- Former New York mayor Michael Bloomberg was key in marshaling city and state governments across the U.S. to ramp up their climate action after the Trump administration pulled the country out of the Paris Agreement.
- With the climate-focused Biden administration now in office, Bloomberg Philanthropies is going “all-in toward climate solutions,” says Antha N. Williams, head of the foundation’s environment program.
- Among its main initiatives is the Beyond Coal campaign, which seeks to get OECD countries to transition away from coal by 2030 and the rest of the world by 2040.
- In this post-Trump follow-up interview with Mongabay founder Rhett A. Butler, Williams discusses a just energy transition, the role of finance in driving change, and the importance of ocean protection.
Melina Laboucan-Massimo: Catalyzing an Indigenous-led just energy transition
- A Just Transition is the idea that the shift toward low-carbon economies needs to be fair and inclusive, meaning it considers the people that will be most impacted by abandoning fossil fuels.
- Among the groups most likely to be affected by the green energy transition are Indigenous communities, many of whom may be disproportionately dependent on fossil fuels for their day-to-day energy needs and livelihoods, and at the same time are also most likely to bear the brunt of the impacts of climate change.
- Recognizing the need for a Just Transition for Indigenous Peoples, Melina Miyowapan Laboucan-Massimo of the Lubicon Cree First Nation in northern Alberta founded Sacred Earth Solar in 2015 to empower Indigenous communities across Canada to adopt renewable energy.
- Laboucan-Massimo spoke about catalyzing a just energy transition for Indigenous peoples, the legacy of colonization, and more, during a March 2021 conversation with Mongabay founder Rhett Ayers Butler.
New age of sail looks to slash massive maritime carbon emissions
- If ocean shipping were a country, it would be the sixth-largest carbon emitter, releasing more CO2 annually than Germany. International shipping accounts for about 2.2% of all global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the U.N. International Maritime Organization.
- But change is on the way. Wind, solar electric, and hydrogen-powered ships offer innovative low- or no-carbon alternatives to fossil fuel-powered cargo vessels, with wind about to make a huge comeback in shipping, say experts. New experimental sail designs include hard sails, rotating vertical cylinders, and even kites.
- Today, startup companies like Fair Transport (with its retrofitted wooden vessels Tres Hombres and Nordlys); modest sized proof-of-concept firms, with purpose-built vessels like Grain de Sail; and large cargo ship retrofits and purpose-built vessels like Neoline’s new large cargo vessels, are starting to address CO2 emissions.
- Through the late 1940s, huge steel sailing ships carried cargos on some ocean routes. By 2030 — less than 100 years since the end of the last great era of sail — fossil fuel-powered cargo vessels may give way to high- and (s)low-tech sailing ships thanks to a revolution in energy technology, that reduces shipping costs with less emissions.
Philanthropist Wendy Schmidt: ‘Solutions are always local’
- Coming from respective backgrounds of design and technology, Wendy Schmidt and her husband, Eric, are the driving force behind some of the charitable organizations and investment vehicles working to address the challenges of climate change, clean energy, ocean health, and more.
- Wendy Schmidt says they bring a systems-thinking approach to these challenges, to allow stakeholders to see connections that may not be obvious on the surface and work toward more resilient solutions.
- “Humans need to develop new systems that work in harmony with the natural world, that are resilient in the face of a changing planet,” she says.
- In this interview with Mongabay founder and CEO Rhett A. Butler, Schmidt advocates for the role of technology, but also explains why the idea that technology can be “scaled” to meet any challenge is problematic.
Data drives Bloomberg’s support for climate solutions, says Antha N. Williams
- Bloomberg Philanthropies, the foundation launched by businessman and former New York City mayor Michael R. Bloomberg, is one of the world’s largest charitable organizations.
- One of Bloomberg’s priority focal areas is the environment: specifically combating climate change by accelerating the transition to clean energy, greening the world’s cities, and protecting the health and productivity of oceans.
- Heading up the foundation’s environment program is Antha N. Williams, who got her start as a campaigner and organizer before taking up leadership roles in the world of philanthropy. Williams says Bloomberg’s strategy is to develop programs that offer the highest leverage in terms of impact.
- Williams spoke about her background, Bloomberg’s programs, and opportunities to drive progress in addressing critical environmental challenges during an October 2020 conversation with Mongabay founder Rhett A. Butler.
Indian embassy in Madagascar becomes first to go fully solar
- A solar power plant was inaugurated at the Indian embassy in Antananarivo, Madagascar, to mark the 150th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi on October 2.
- It became the first Indian embassy in the world to be run entirely on solar power from the 8 KW plant.
- Madagascar has huge potential to develop solar energy, with almost all regions receiving 2800 hours of sunshine in a year.
- The environment minister acknowledged that with less than 15% of people having access to grid electricity embracing solar power was a way for Madagascar to develop and meet its climate goals.
Podcast: Can the planet support a clean energy transition?
- Combating climate change will require rapidly deploying renewable energy while reducing our use of fossil fuels. But renewable energy technologies like wind turbines, solar panels, batteries, and electric vehicles require large amounts of mined metals and minerals.
- That poses a problem, because the mining process creates significant environmental impacts, from air and water pollution to deforestation, and has led to numerous conflicts with local communities. And now, there’s a concerted effort underway by the mining industry to open up vast areas of the ocean floor to minerals mining. If we’re not careful about how we meet the growing demand for minerals, it could actually imperil the promises of the transition to clean energy.
- To help us dive into all of this, we speak with Ian Morse, a journalist who follows the minerals mining and clean energy beat closely. We also speak with Catherine Coumans of MiningWatch Canada, who discusses the threats posed by deep sea mining and tells us why more mining may not be the best way to meet the demand for minerals.
Analysis: Vietnam’s leadership flex shows how to drive electricity reform
- Vietnam’s Communist Party leadership has instituted a top-down reform of the country’s electricity sector in response to the need to shift away from coal and its growing list of associated problems.
- The country’s new energy strategy puts greater emphasis on renewables, including wind and solar, abandoning a decade-long commitment to investing in and subsidizing coal.
- The move is also helped by recent technological developments that have made generating renewable power at scale more economically feasible than ever.
Burning down the house? Enviva’s giant U.S. wood pellet plants gear up
- An outdated Kyoto Climate Agreement policy, grandfathered into the 2015 Paris Agreement, counts electrical energy produced by burning biomass — wood pellets — as carbon neutral. However, new science demonstrates that burning forests for energy is dirtier than coal and not carbon neutral in the short-term.
- But with the carbon accounting loophole still on the books, European Union nations and other countries are rushing to convert coal plants to burn wood pellets, and to count giant biomass energy facilities as carbon neutral — valid on paper even as they add new carbon emissions to the atmosphere. The forest industry argues otherwise.
- It too is capitalizing on the loophole, building large new wood pellet factories and logging operations in places like the U.S. Southeast — cutting down forests, pelletizing trees, and exporting biomass. A case in point are the two giant plants now being built by the Enviva Corporation in Lucedale, Mississippi and Epes, Alabama.
- Enviva and other firms can only make biomass profitable by relying on government subsidies. In the end, forests are lost, carbon neutrality takes decades to achieve, and while communities may see a short-term boost in jobs, they suffer air pollution and the risk of sudden economic collapse if and when the carbon loophole is closed.
Energy-guzzling McMansions make the American dream a climate nightmare
- A new study finds that wealthy Americans living in spacious houses in upscale neighborhoods are responsible for 25% more greenhouse gas emissions on average than those living in smaller homes in poorer areas.
- The U.S. has one of the highest per capita emissions of any country, and residential properties account for almost a quarter of the country’s total carbon footprint, larger than the total emissions for Germany.
- By looking at energy consumption patterns of nearly 100 million households from 2015, the researchers found out that Maine, Vermont and Wisconsin were the largest consumers of energy that year.
- Only if homes are smaller and more tightly packed together, the power grid is cleaner, and energy consumption is reduced, would the U.S. be able to achieve emissions reductions targets for homes laid down in the Paris Agreement, the study says.
Indonesia’s $300m geothermal play risks being undercut by cheap coal
- The Asian Development Bank has granted Indonesian power developer PT Geo Dipa Energi (GDE) a $300 million loan to expand two geothermal plants in Java.
- But the plants will be supplying the Java-Bali grid that is already 40% overcapacity,thanks to a glut of cheap power from coal-fired power plants.
- Clean-energy observers also say the expansion of the plants carries the risk of environmental damage, including land subsidence from groundwater extraction, and deforestation to build new wells.
- Indonesia plans to generate 23% of its electricity from renewable resources by 2025, but growth in renewables is far outstripped by existing and new coal-fired plants, 10 of which came online last year alone.
No more business as usual: Halt dangerous development projects that put our health at risk (commentary)
- Liberia’s Ebola outbreak provides a cautionary tale of how powerful industries exploit public health crisis for short-term profit.
- Madan argues that international norms of free prior informed consent must be upheld to ensure recovery efforts do not endanger peoples’ or the planet’s health.
- This post is a commentary and does not necessarily reflect the views of Mongabay.
South Korea subsidizing biomass so heavily that wind and solar are being crowded out of the market
- The government of South Korea is subsidizing the development of biomass power so heavily that it’s hindering the adoption of renewable energy technologies like solar and wind, new research finds.
- According to a report issued by Seoul-based NGO Solutions For Our Climate (SFOC), forest biomass is considered a carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels under Korean law, and the country’s government has so aggressively supported the growth of biomass-fueled energy production that it has become one of the most subsidized renewable energy sources in South Korea.
- Soojin Kim, a senior researcher at SFOC and an author of the report, told Mongabay that biomass projects have been so overcompensated by the government that it is causing serious disruption and uncertainties in the Korean renewable energy market, including steep declines in the price of Renewable Energy Credits (RECs). These uncertainties, in turn, are discouraging utilities from investing in renewables such as solar and wind, she said.
Wireless grids and towers of power: Engineering our way out of dirty energy
- Engineers have explored harnessing gravity, tapping the unique structures of smelly fruit, and shrinking a planetary idea down to household size.
- Meeting current energy demands with renewable energies is vital to meet climate goals and prevent ecological collapse, but energy technologies rely on hundreds of years of fossil fuel innovation.
- Mongabay explored some intriguing new approaches and talked with innovators who are helping to think our way out of the climate crisis.
A wave-powered ferry aims to forge a new path for shipping in the Philippines
- A Filipino marine engineer is building a hybrid trimaran, powered by both a traditional motor and wave energy, as an alternative to the decades-old shipping vessels that ply transnational routes in the Visayas region in the Philippines.
- The Philippines’ transport sector is the second-biggest contributor to the country’s greenhouse gas emissions, thanks to a large fleet of aging ships burning dirty fuel.
- The multi-hull boat now being built is expected to move more efficiently on the sea, cut average travel times by half, and have a lower carbon footprint.
In Indonesian renewables bill, activists see chance to move away from coal
- Indonesia’s parliament is drafting a bill on renewable energy that will be included in its docket of priority legislation for passage this year.
- Energy industry observers and activists have welcomed the move and called for policies to transition the country away from its heavy reliance on coal.
- Coal accounts for the majority of Indonesia’s energy mix, and looks to remain that way through to at least 2025, even though the country has vast untapped potential to generate power from geothermal, solar, wind and wave.
- Observers are also wary of the government’s definition of what constitutes new and renewable energy, which includes nuclear, gasified and liquefied coal, hydrogen, and even palm oil biodiesel.
COP25: EU officials say biomass burning policy to come under critical review
- At a COP25 climate summit press conference on Thursday, December 12, Frans Timmermans, executive vice president of the EU and a Dutch politician answered a Mongabay question concerning the UN biomass carbon accounting loophole.
- When asked if the EU would close the loophole, he said: “The issue of biofuels needs to be looked at very carefully. We have to make sure that what we do with biofuels is sustainable and does not do more harm than that it does good.” A second EU official expressed a similar view. The issue won’t likely be reviewed until after 2020.
- This is perhaps the first acknowledgement by a top developed world official that the biomass loophole is a potential problem. The loophole encourages power plants that burn coal (whose carbon emissions are counted) to be converted to biomass — the burning of wood pellets (whose carbon emissions are counted as carbon neutral).
- Recent science shows that burning wood pellets is worse than burning coal, since more pellets must be burned to produce equivalent energy levels to coal. Also replacing plantation forests to achieve carbon neutrality takes many decades, time not available to a world that needs to quickly cut emissions over the next 20 years.
COP25: Wood pellet CEO claims biomass carbon neutrality, despite science
- Research has conclusively shown that burning biomass for energy is not carbon neutral. However, a biomass carbon accounting loophole currently enforced by the UN and the Paris Agreement says that burning trees in the form of wood pellets produces zero emissions, and so is classified with solar and wind power.
- Mongabay gained an exclusive interview with Will Gardiner, CEO of Drax, the United Kingdom’s largest biomass energy plant. He dismisses the science and asserts that his firm and $7.6 billion industry are meeting “a responsibility to our community, our shareholders and our colleagues to be a part of the escalating climate crisis.”
- Bill Moomaw — an international researcher on biomass-for-energy, and author of forest reports for the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change — counters Gardiner’s arguments: “It’s all about the money. The wood pellet industry is a monster out of control,” he said when interviewed at COP25.
- Despite repeated pleas from scientists, COP25 climate summit negotiators in Madrid failed to address the biomass carbon accounting loophole, as they did at COP24 — a lapse that, if allowed to persist, could help push emissions above a 2 degree Celsius planetwide average increase that the UN says could bring climate catastrophe.
COP25 may put climate at greater risk by failing to address forests
- COP25, originally slated for Brazil, then Chile, but starting today in Madrid comes as global temperatures, sea level rise, wildfires, coral bleaching, extreme drought and storms break new planetary records.
- But delegates have set a relatively low bar for the summit, with COP25’s primary goal to determine rules under Article 6 of the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement for creating carbon markets among nations, cities and corporations as a means of incentivizing emission-reduction strategies.
- Policy experts warn that global forest conservation is not yet being actively incentivized as part of carbon market discussions, a possible lapse apparently backed by Brazil and the government of Jair Bolsonaro which has declared its plan to develop the Amazon basin — the world’s largest remaining rainforest and vital to sequestering carbon to curb climate change.
- COP25 also seems unlikely to address the UN biomass carbon accounting loophole, which allows nations to convert obsolete coal plants to burn wood pellets to produce energy, with the carbon emitted counted as “zero emissions” equivalent to solar and wind. Scientists warn that biomass burning, far from being carbon neutral, is actually worse than burning coal.
In surprise move, Brazil has removed restrictions on Amazon sugarcane production
- Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro has signed a decree revoking a zoning regulation for the sugarcane industry, effectively allowing for cultivation of the crop in the Amazon and other areas of primary forest.
- The measure is controversial because it wasn’t requested by the industry, which, under the previous regulation, was permitted to expand onto degraded land and cattle pasture covering six times the area currently planted with sugarcane.
- The government has justified the move as necessary to boost the ethanol industry in Amazonian states, but experts warn the end of the zoning restriction could present an obstacle to ethanol exports to the European Union, damaging the biofuel sector.
- To date, the sugarcane industry has remained dissociated from the deforestation linked to the cattle and soy industries. Environmentalists say this new decree could end that exception, while also sending the message that the government sees no value in protecting standing forests.
UN and policymakers, wake up! Burning trees for energy is not carbon neutral (commentary)
- On September 23, the signatories of the Paris Climate Agreement will gather at the United Nations for a Climate Action Summit to step up their carbon reduction pledges in order to prevent catastrophic climate change, while also kicking off Climate Week events in New York City.
- However, the policymakers, financiers, and big green groups organizing these events will almost certainly turn a blind eye toward renewable energy policies that subsidize forest wood burned for energy as if it is a zero emissions technology like wind or solar.
- Scientists have repeatedly warned that burning forests is not in fact carbon neutral, and that doing so puts the world at risk of overshooting the Paris Agreement’s 1.5°C target.
- But that message has fallen on deaf ears, as lucrative renewable energy subsidies have driven exponential growth in use of forest wood as fuel. The world’s nations must stop subsidizing burning forest biomass now to protect forests, the climate, and our future. This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author.
New UN report takes stock of renewable energy’s decade-long growth spurt
- 2018 was the ninth year in a row in which renewable energy capacity investments exceeded $200 billion and the fifth year in a row in which they exceeded $250 billion, according to a report released by the UN ahead of the Climate Action Summit to be held in New York City later this month.
- That means that, by the time it’s over, the current decade — 2010 to 2019 — will have seen a total of $2.6 trillion in renewable energy investments and a four-fold increase in global renewable energy capacity (excluding large hydroelectric dams, i.e. those with electricity generation capacity of 50 megawatts or more).
- Of all the major generating technologies, including those that burn fossil fuels, solar accounts for 638 GW of new power capacity installed since 2010, the largest single share claimed by any technology. Coal-fired power comes in second at 529 GW, wind in third at 487 GW, and gas in fourth at 438 GW.
Japan builds coal plants abroad that wouldn’t be allowed at home: Report
- Japan is investing heavily in building coal-fired power plants overseas that would fall short of its own domestic emissions standards, according to a Greenpeace report.
- Pollution from these plants, in places such as India, Indonesia, Vietnam and Bangladesh, could potentially lead to 410,000 premature deaths over the 30-year lifetime of the plants.
- Japan is the only country in the G7 group of wealthiest nations still actively building coal-fired plants domestically and overseas, which threatens international efforts to reduce carbon emissions and stall global warning.
- Activists say by building on its own renewable energy potential, Japan can set a positive example for the countries in which it’s investing in energy infrastructure.
When rich economies cut emissions, poor ones stand to benefit, study says
- If higher and middle-income countries cut their greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2050, reduced demand could lower oil costs and boost economic growth for low-income countries, according to a study published in the journal Climatic Change in April.
- To benefit from that cheaper oil, low-income countries would have to be exempted from emissions requirements until they reach middle-income status.
- However, emissions last year hit an all-time high, and without drastic emissions reductions, low-income countries currently face economic, social and environmental catastrophe.
From flaming to free-flowing: The full lesson of the recovery of the Cuyahoga River (commentary)
- As we approach the 50th anniversary of the fire on the Cuyahoga River, it’s heartening to see my hometown flip the script and the national media focus on the river’s remarkable recovery as a testament to how restored nature can spark urban revitalization.
- The river’s recovery from pollution is an important story. But as someone who works in international river conservation, I see the Cuyahoga as demonstrating a lesson that is even more remarkable, and equally needed, today: There is great value in protecting a river, not just protecting the quality of the water within it.
- The future could be much brighter for rivers and the people that depend on them. Due to the renewable revolution — the dramatically dropping costs for electricity from wind and solar — the world can indeed power its future with systems that are low-carbon, low-cost, and low-conflict with rivers and communities.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
Carbon to burn: UK net-zero emissions pledge undermined by biomass energy
- The United Kingdom and the European Union are setting goals to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. But that declaration is deeply flawed, analysts say, due to a long-standing United Nations carbon accounting loophole that turns a blind eye toward the conversion of coal burning power plants to burning wood pellets.
- While the cutting of trees to convert them to wood pellets to produce energy is ultimately carbon neutral — if an equal number of new trees are planted — the regrowth process requires 50 to 100 years. That means wood pellets burned today, and in coming decades, will be adding a massive carbon load to the atmosphere.
- That carbon will add significantly to global warming — bringing more sea level rise, extreme weather, and perhaps, climate catastrophe — even as official carbon counting by the UN provides a false sense of security that we are effectively reducing emissions to curb climate change.
- Unless the biomass loophole is dealt with, the risk is very real that the world could easily overshoot its Paris Agreement targets, and see temperatures rise well above the 1.5 degrees Celsius safe limit. At present, there is no official move to address the biomass loophole.
Shift to renewable energy could have biodiversity cost, researchers caution
- Climate change has widely reported negative consequences, and innovations in renewable energy technologies are central to achieving the Paris climate treaty goals to mitigate these effects.
- A new report cautions that mining of metals used in manufacturing renewable technologies like wind turbines, solar power, and electric vehicles has costs, including for biodiversity.
- Negative effects from the mining of metals like aluminum, cobalt and rare earths could impact a range of creatures from flamingoes to gorillas, plants, and even deep sea creatures.
- Until widespread recycling and reuse of these materials becomes a feasible alternative to mining, these activities should be monitored and verified via certification schemes such as the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance, researchers say.
No need to dam free-flowing rivers to meet world’s climate and energy targets
- In a comment article published in the Nature last month, scientists argue that an “energy future in which both people and rivers thrive” is possible with better planning.
- The hydropower development projects now underway threaten the world’s last free-flowing rivers, posing severe threats to local human communities and the species that call rivers home. A recent study found that just one-third of the world’s 242 largest rivers remain free-flowing.
- The benefits of better planning to meet increasing energy demands could be huge: A report released by WWF and The Nature Conservancy ahead of the World Hydropower Congress, held in Paris last month, finds that accelerating the deployment of non-hydropower renewable energy could prevent the fragmentation of nearly 165,000 kilometers (more than 102,500 miles) of river channels.
Indonesia electricity chief charged with bribery over coal-fired power plant
- Indonesian anti-graft investigators have charged the head of state-owned power utility PLN, Sofyan Basir, with bribery in connection to a coal-fired plant on the island of Sumatra.
- Sofyan was responsible for awarding contracts for the $900 million Riau-1 plant, whose construction has been suspended following a raft of corruption allegations and arrests.
- Among those already tried and convicted in the case are a government minister, a member of parliament, and a shareholder in one of the companies awarded the Riau-1 contract; Sofyan himself faces up to 20 years in prison if convicted.
- Environmental activists have praised the anti-graft commission for pursuing the case, which they say should spur the government to move away from coal and shift toward renewable energy.
EU sued to stop burning trees for energy; it’s not carbon neutral: plaintiffs
- Plaintiffs in five European nations and the U.S. filed suit Monday, 4 March, in the European General Court in Luxembourg against the European Union. At issue is the EU’s rapid conversion of coal-burning powerplants to burn wood pellets and chips, a process known as bioenergy. Activists see the EUs bioenergy policies as reckless and endangering the climate.
- Bioenergy was classified as carbon neutral under the Kyoto Protocol, meaning that nations don’t need to count wood burning for energy among their Paris Agreement carbon emissions. However, studies over the last 20 years have found that bioenergy, while technically carbon neutral, is not neutral within the urgent timeframe in which the world must cut emissions.
- In essence, it takes many decades for new tree growth to re-absorb the amount of carbon released from burning mature trees in a single day. But the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change last October said that the world has just 12 years – not decades – to drastically cut emissions or face likely disastrous temperature rise and climate impacts.
- The activists filing suit face a difficult fight. Only EU member states and EU institutions are generally given standing to challenge legislative acts. To gain standing, they will have to prove that they are being impacted by the EU’s bioenergy policies. The activists say that ending bioenergy coal plant conversions is vital if the world is to avoid catastrophic climate change.
Will Malaysia become Southeast Asia’s clean energy leader? (commentary)
- Malaysia sits at a unique crossroads. Last year’s election was a wake-up call for the powers that be, with more than 60 years of entrenched power coming to an unexpected and abrupt end. While much of our region, Australia included, slips further into the pockets of fossil fuel interests, Malaysia has the opportunity to position itself as Southeast Asia’s clean energy and renewable industries leader.
- Australia now has the highest proportion of households with PV systems on their roof of any country in the world, in spite of the current Government’s hopeless commitment to fossil fuels. The Australian legislation of 2012 is a template for other countries intent on responding to the climate crisis.
- Malaysia can be a champion for our region. Where it chooses to sit on this spectrum between leader and follower in the new geopolitical relationships evolving from the transition to renewable energy is yet to be seen, but the opportunity to lead in the transformation in South-East Asia is wide open.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the author, not necessarily Mongabay.
For Indonesian presidential hopefuls, burning coal is business as usual
- Indonesia relies for more than half of its electricity on coal-fired power plants, and has plans to build dozens more in the coming years, bucking a worldwide shift away from fossil fuels and toward renewable sources of energy.
- Activists have called on President Joko Widodo and his challenger, Prabowo Subianto, to address the issue at their presidential debate on Feb. 17.
- Neither camp, however, has made any meaningful policy gestures on environmental issues, with a Widodo campaign spokesman even disputing the science on coal’s central role in climate change as merely “an opinion.”
- Instead, the incumbent, who enjoys a solid lead on his challenger, looks set to deepen Indonesia’s reliance on coal as the primary energy source.
With no oil cleanup in sight, Amazon tribes harvest rain for clean water
- The Siona, Secoya and Kofan indigenous peoples have been living with the consequences of oil drilling in Ecuador’s northeastern Sucumbíos province for several generations.
- Many communities say the oil industry has polluted their sources of water for drinking, cooking and bathing, with grave consequences for their health.
- With the communities, the Ecuadoran government and the U.S. oil company Chevron locked in legal battle over who will pay for a cleanup, and oil still being pumped from beneath the rainforest, the communities are now forging a path around their pollution problems.
- Indigenous communities, with help from a U.S. NGO, have installed more than 1,100 rainwater collection and filtration systems in 70-plus villages to supply clean water. They’ve also set up dozens of solar panels to ensure ample electricity that does not rely on the fossil fuel industry they say has irreparably harmed their home and way of life.
COP24: Summit a step forward, but fails to address climate urgency
- COP24 ran into overtime over the weekend as delegates rushed to approve the Paris rulebook to set up a detailed mechanism for accomplishing and gauging the carbon reduction pledges made by the world’s nations in Paris at the end of 2015.
- But considering the urgency of action needed – with just 12 years left to act decisively to significantly cut emissions, according to an October IPCC science report – the COP24 summit proved to be less successful than many participants had hoped.
- On the negative side: the U.S., Russia and Saudi Arabia tried to undermine the gravity of the IPCC science report. Brazil successfully scuttled plans for an international carbon market. And COP24 failed to address the bioenergy carbon counting loophole, which incentivizes the harvesting and burning of trees to make energy by calling the process carbon neutral.
- On the positive side, “1,000 tiny steps” were made, including an improved transparency framework for reporting emissions; regular assessments called Global Stocktake to gauge emissions-reduction effectiveness at national levels starting in 2023; and an agreement to set new finance goals in 2020 to help vulnerable nations adapt to a warming world.
COP24: Nations complicit in ignoring bioenergy climate bomb, experts say
- Twenty years ago science told policymakers that bioenergy – the burning of woody biomass – was a sustainable form of energy that was carbon neutral. The current United Nations carbon accounting system follows that guidance. However, new science has found the hypothesis to be wrong: bioenergy has been found to add significantly to carbon emissions.
- However, national delegations at the UN climate summit in Poland, COP24, as they wordsmith the Paris Rulebook, are stonewalling on the matter, doing nothing to close the bioenergy carbon accounting loophole. But nature can’t be fooled, which means that the undercounting of emissions could push the world past a climate catastrophe tipping point.
- Still, with the problem unaddressed, developed nations in the European Union and elsewhere continue burning woody biomass as energy, with the U.S., Canada and other nations happy to profit from the accounting error. Tropical nations like Brazil and Peru are eager to jump on the bioenergy bandwagon, a potential disaster for rainforests and biodiversity.
- Meanwhile, NGOs and scientists at COP24 have sought earnestly to alert the media and COP delegations to the bioenergy climate bomb and its looming risks, even going so far as to write language closing the loophole that could be inserted into the Paris Rulebook now being negotiated, but to no avail.
‘Light for everyone’: Indigenous youth mount a solar-powered resistance
- Among the cloud forests of northern Puebla, Mexico, an indigenous cooperative is training its youth to install solar panels.
- The initiative was born of the cooperative’s contentious fight with the federal and local government over plans to build an electricity substation that the co-op members believed would only benefit industry, not local communities.
- The panels are part of a plan hatched by these mountain communities to unhook from Mexico’s federal power company, provide their youth with meaningful employment, and reclaim control of their land and resources.
- The initiative appears to be well aligned with the renewable-energy plans of Mexico’s new president, Andrés Manuel López Obrador.
COP24: Coal casts a shadow over U.N. climate talks in Poland
- Activists have questioned the integrity and effectiveness of the U.N. climate talks in Poland, in light of its close associations with the coal industry.
- Among the event’s sponsors are three Polish coal companies, and in his opening speech, the Polish president said his country’s continued use of coal did not go against efforts to tackle climate change.
- Activists say the influence of the coal lobby at the conference amounts to greenwashing and could undermine the effectiveness of any outcome from the discussions.
‘Drifters of opportunity’: Seabirds track energy in tidal currents
- A recent study used location data from GPS-tagged seabirds called razorbills to track currents in the Irish Sea.
- When a team of biologists compared the movements of resting birds on the surface of the water with a mathematical model that lays out the currents, they found that the birds provided solid information on the speed and direction of the flow of water.
- The researchers suggest that similar research using data from resting seabirds could help identify areas for the harvest of renewable tidal energy.
Dam project pushes threatened orangutans from forest to farms
- Critically endangered Tapanuli orangutans are starting to flee from their only known habitat in Sumatra and encroaching on plantations, as the development of a controversial hydropower project in the Batang Toru forest gets underway.
- The finding comes just days after the project developer joined forces with the local government and a prominent university to speed up the pace of development ahead of the 2022 deadline.
- Indonesia’s environment ministry has ordered the developer to revise its environmental impact assessment, but conservationists say there are far too many problems with the project for it to continue.
- A key risk that remains unaddressed is the proposed dam’s location along a known fault line, which critics of the project say could have disastrous consequences in a region known for its high level of seismic activity.
California targets fossil fuel-free electricity by 2045
- On Monday, California Governor Jerry Brown signed into law Senate Bill 100, which sets a goal of generating 100 percent of the state’s electricity from carbon-free sources by 2045. The same day, Governor Brown issued an executive order committing California to full, economy-wide carbon neutrality by 2045.
- California was already known as a leader in climate action prior to SB 100, but the new law significantly accelerates its emissions-reduction timeline by requiring the state to get 50 percent of its electricity from renewable sources by 2025 and 60 percent by 2030 — the latter target being 10 percent higher than California’s previous clean energy commitments.
- Electricity generation is only responsible for 16 percent of California’s annual greenhouse gas emissions, however. That’s why Governor Brown issued the executive order, as well, committing the state to achieving carbon neutrality by 2045 and net negative greenhouse gas emissions thereafter.
Graft and government policy align to keep Indonesia burning coal
- Antigraft investigators arrested a member of parliament and a coal businessman, among others, in July in connection with a contract to build a $900 million power plant in Indonesia.
- The case has shone a spotlight on the country’s boom in mine-mouth power plants, which burn the lowest-quality coal available and are awarded to developers in an opaque process that makes them ripe for corruption.
- Indonesia continues to plow millions into subsidies for coal-fired power plants, and plans to keep relying on the fossil fuel to generate the bulk of its energy mix beyond 2027.
- This is despite ample studies and evidence showing it can reduce power generation costs and cut greenhouse gas emissions significantly by reallocating those subsidies to renewable energy projects.
On an island in the sun, coal power is king over abundant solar
- Locals and environmentalists have opposed a plan to expand a coal-fired power plan in northern Bali, Indonesia.
- They are worried that the expansion will exacerbate the existing impact of the plant on the environment and locals’ health and livelihoods.
- A particular concern focuses on the survival of dolphins and endemic species living in close proximity to the plant, with Greenpeace saying the dolphins have particularly been affected since the plant came on line in 2015.
- Another major worry is air pollution, with many locals complaining of respiratory ailments as a result of the fumes and coal dust emitted from the plant.
Indonesia turns to green finance for development projects
- Indonesia, one of the world’s biggest greenhouse gas emitters, is turning to green finance markets to fund new development projects it promises will be both environmentally and socially friendly.
- In issuing these ‘green’ and ‘sustainable’ bonds, Indonesia joins a growing number of developing countries seeking to appeal to ecologically and socially conscious international investors.
- But critics question just how green and sustainable these bonds really are, highlighting concerns about greenwashing.
In a country long wary of nuclear, an Indonesian chases the thorium dream
- The image of nuclear energy took a huge hit after the catastrophic accident at the Fukushima Daiichi plant in Japan in 2011. Some countries are phasing out their nuclear power programs.
- Around the world, however, proponents of an alternative type of reactor billed as safer and more efficient are gaining steam with their ideas. One of them is Bob Effendi, a native of Indonesia.
- Indonesia has long been skeptical of nuclear power. But at the country struggles to meet its targets for renewable energy, some within the government appear to be listening to the thorium pitch.
UN forest accounting loophole allows CO2 underreporting by EU, UK, US
- Emissions accounting helps determine whether or not nations are on target to achieve their voluntary Paris Agreement reduction goals. Ideally, the global community’s CO2 pledges, adjusted downward over time, would, taken together, help keep the world from heating up by 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100 from a 1900 baseline.
- But scientists are raising the alarm that this goal may already be beyond reach. One reason: a carbon accounting loophole within UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) guidelines accepting the burning of wood pellets (biomass) as a carbon neutral replacement for coal — with wood now used in many European Union and United Kingdom power plants.
- Scientists warn, however, that their research shows that replacing coal with wood pellets in power plants is not carbon neutral. That’s partly because burning wood, which is celebrated by governments as a renewable and sustainable energy resource, is less efficient than coal burning, so it actually produces more CO2 emissions than coal.
- Also, while wood burning and tree replanting over hundreds of years will end up carbon neutral, that doesn’t help right now. Over a short timeframe, at a historical moment when we require aggressive greenhouse gas reductions, wood burning is adding to global emissions. Analysts say that this loophole needs to be closed, and soon, to avoid further climate chaos.
Indonesia may achieve renewables target, but still favors coal for power
- Indonesia is set to achieve its target for renewables portion in the national energy mix by 2025, but the country will still rely heavily on coal in the next 10 years, according to revisions in the national electricity plan.
- The new plan also sees cuts to the country’s target to install additional electricity capacity across the archipelago by 2027 amid stagnant demand, slower-than-projected economic growth, and state utility PLN’s financial concerns over the glut of idle power in some parts of the nation.
- Energy activists, however, argue that the trims are still not enough to solve PLN’s financial woes or to reduce Indonesia’s dependence on health- and environment-damaging coal.
Red Cloud’s Revolution: Oglalla Sioux freeing themselves from fossil fuel
- Henry Red Cloud, like so many Oglalla Sioux young men, left the reservation to work in construction. When he returned home in 2002, he needed a job, and also wanted to make a difference. He attended a solar energy workshop and saw the future.
- Today, Red Cloud runs Lakota Solar and the Red Cloud Renewable Energy Center, which have become catalysts for an innovative new economic network – one that employs locals and connects tribes, while building greater energy independence among First Nations.
- The company is building and installing alternative energy systems, and training others to do the same, throughout remote areas of U.S. reservations, thus allowing the Sioux and others to leap past outdated fossil fuel technology altogether.
- Henry Red Cloud’s company has another more radical purpose: it helps provide energy to remote Water Protector camps, like the one at Standing Rock protesting the Dakota Access Pipeline (DAPL). Solar power and other alternative energy sources are vital at such remote sites, as they power up cellphones, connecting resistors to the media and outside world.
A tale of two policies: climate change, Trump, and the U.S. military
- The U.S. military is preparing for a changing climate, but not in order to protect the Earth’s environment. The Pentagon’s first and foremost concern is to respond to global warming only in so far as that response enhances the military’s “operational effectiveness” – its ability to fight.
- Jim Mattis, President Trump’s own Secretary of Defense, has spoken out about the dangers of climate change, running contrary to the commander-in-chief whose recently announced National Security Strategy omitted it as a threat. Analysts expect the military to continue with its climate change adaptation and preparedness programs, despite the President’s denialism.
- However, even as the U.S. military takes steps to make itself more fuel and energy efficient, the Department of Defense remains the world’s largest institutional fossil fuel guzzler.
- Critics say the greening of the military is positive, but not if its growth comes at the expense of U.S. climate programs at EPA and the State Department. Big increases in the military’s size, pushed by Trump and Congress, are only going to make the Pentagon’s and the world’s carbon emissions worse – which could ultimately impact national security and “operational effectiveness.”
COP23: Trump team leads ‘surreal’ coal-gas-nuke climate summit panel
- The only U.S. presentation to be offered at the COP23 climate summit was led by Trump administration energy advisors, along with coal, natural gas and nuclear industry representatives.
- The panel argued that fossil fuel production at high, subsidized levels is vital to “energy security and economic development.” Panel members made only infrequent references to climate change, and they made no mention of the dire impacts from burning fossil fuels.
- The presentation was likely one of the most uproarious in the history of COP. Two U.S. state governors burst in at the start to give impromptu speeches, attacking Trump’s climate denialist policies.
- A memorable highlight occurred when a chorus of young people arose en masse during the panel’s opening remarks, and to the tune of Lee Greenwood’s patriotic hit “God Bless the USA” sang: “So you claim to be an American. But we see right through your greed.” Their song lasted seven minutes, after which they peacefully departed the hall.
Indonesia coal power push neglects rural households, chokes urban ones
- The Indonesian government’s push to generate an additional 35 GW of electricity capacity by 2019 relies heavily on building new coal-fired power plants.
- Observers say the program focuses too much on the already saturated Java-Bali grid, while ignoring millions of households in more remote areas.
- The preference for generating power from coal could also threaten the health of up to 30 million people living in areas slated for power plant construction, a recent study from Greenpeace says.
COP23: Voices from America’s Pledge; in their own words
- A U.S. non-federal delegation led by Gov. Jerry Brown of California and former New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg, and including 15 U.S. states, 455 cities, 1,747 businesses and 325 universities, represents nearly half the United States economy.
- This U.S. subnational delegation is at COP23 in Bonn, Germany, to commit to keeping the U.S. Paris Agreement emissions reduction goal set by the Obama administration in Paris in 2015 – a commitment made in defiance of President Donald Trump.
- On Saturday, a standing-room-only event was held at COP23 where Bloomberg, Brown, Gore, and others spoke rousingly of emission cut achievements so far, and to come. Their words and photos are presented here.
U.S. subnationals shoulder climate role in Bonn, Trump sidelined
- The United States government under Donald Trump now stands alone, a rogue nation. Aligned against it at COP23 in Bonn, Germany, is every other nation in the world – all committed to meeting national emissions goals set in Paris in 2015.
- Completely bypassing Trump and the federal government at COP23 is the U.S. subnational delegation, led by Gov. Jerry Brown of California and former New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg.
- The U.S. subnational delegation in Bonn represents non-federal actors in 15 states, 455 cities, 1,747 businesses and 325 universities. Combined they represent nearly half the U.S. economy. It remains to be seen if the delegation will be formally seated at COP23 as negotiators – a potential slap in the face to Trump’s tiny U.S. State Department delegation.
- The U.S. subnationals are committed to keeping America’s Paris goal of a 28 percent reduction in carbon emissions (over 2005 levels) by 2025. Supporters of America’s Pledge say they’re nearly halfway there. But it will take a far bigger push, and deeper cuts, to avoid the threat of escalating climate change, as heatwaves, extreme storms, and sea levels surge.
Even as Trump and Modi clash on energy, India and U.S. are partnering
- In the past, and under Pres. Trump and Prime Minister Modi, the U.S. and India have often been at odds environmentally, especially regarding climate change, with the U.S. saying that developing nations need to do more to cut emissions, while India says that the U.S, as biggest historical carbon emitter, must take a primary role.
- However, the two countries, under Obama and now under Trump, have quietly done trade agreements to enhance the transfer of liquid natural gas and nuclear power plant technology via sales from U.S. high tech companies to India.
- India’s Modi, a proponent of solar energy, was also convinced in talks with Pres. Obama to be a big supporter of the Paris Climate Agreement. Though, with the ascendance of Pres. Trump, and his rejection of the landmark accord, the two countries have again parted ways.
- Trump’s plan to renege on a US $2 billion Green Climate Fund (GCF) commitment made by Pres. Obama could somewhat slow India’s drive to quickly embrace green technologies.
Cross currents: Mega-dams and micro-hydro offer two different futures for rural Borneo
- Rural villages along the Papar River in Sabah, Malaysia are getting electrical infrastructure for the first time by building micro-hydropower systems.
- The proposed Kaiduan Dam would flood the Ulu Papar Valley, displacing villagers in order to provide a water source to the state capital, Kota Kinabalu, and its environs.
- Villages share what they have learned about managing their new hydropower systems, and work together to try to block plans for the dam.
The financial case against coal power in Indonesia
- A recent report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) warns that Indonesia’s coal-based electricity strategy risks wasting $76 billion over the next 25 years.
- IEEFA is among a small group of non-profits focusing on the economics of fossil fuels, rather than emphasizing environment and public health concerns.
- Indonesia, a major coal producer, relies heavily on large, fossil-fueled power plants for electricity, but there are some signs that policymakers are increasingly open to developing small-scale and renewable options.
Renewable energy to power 139 countries? Scientists say it’s possible
- The research looked at the impacts of a 100-percent switch to renewable energy in 139 countries by 2050 on the climate, as well as air pollution and the economy.
- They calculated that the transition to wind, solar and hydropower will generate around 24 million net jobs.
- Switching to renewable sources of energy that don’t emit carbon into the atmosphere will also save trillions of dollars in the costs we would otherwise incur due to air pollution and the changing climate.
Protests over geothermal development heat up in Central Java
- The people of Karangtengah Village in Central Java learned in January one of their key sources of freshwater had been contaminated by debris from the development of a planned $1 billion geothermal energy plant at a nearby volcano.
- Indonesia, which is estimated to have the largest geothermal capacity in the world, is eager to tap into the renewable energy source.
- The government says work will continue despite mounting demands from locals to stop the project over claims it has contaminated rivers, cleared forests and damaged the local tourism industry.
Trump’s policies could put Cambodia’s environment on chopping block
- Under President Donald Trump’s proposed 2018 budget, Cambodia could experience a 70 percent cut in aid from the United States.
- For Cambodia, this would mean a combined cut of $11.7 million from the budgets of the U.S. State Department and USAID, with the latter involved in a host of projects meant to help sustain and protect the Cambodian environment and help curb and adapt to climate change.
- Trump’s isolationism and “America First” policies could create a political vacuum in Southeast Asia, with China stepping in to replace the U.S., with major repercussions. China has historically been less transparent and less concerned about environmental impacts in nations where its government and corporations are at work.
- Trump’s authoritarian and anti-environmental policies are possibly being interpreted as a green light by autocratic leaders in the developing world. Cambodia, for example, has lately stepped up dissident arrests and sought transnational corporate partnerships to build large infrastructure projects — such projects often see high levels of corruption and do major environmental harm.
Facing oversupply, Indonesia scales back its coal-based electricity plan
- In 2014, Indonesian President Joko Widodo announced plans to generate an additional 35,000 megawatts of electricity by 2019, much of it to be fueled by coal.
- Last month, energy minister Ignasius Jonan said only 15,000 additional megawatts will be required by 2019.
- Jonan cited lower-than-expected economic growth, leading to lower energy demand.
Thousands of anti-coal activists march in Jakarta, deliver complaints to anti-graft agency
- Around 2,000 people, including convoys from communities affected by coal mining and coal-fired power plants, marched in Jakarta on March 23.
- A delegation from the protest was received by Indonesia’s Corruption Eradication Commission (KPK), where they presented reports on cases of alleged corruption.
- Demonstrators also rallied in solidarity with farmers from Kendeng, West Java, who have encased their feet in cement and are staging a sit-in to protest the construction of a cement factory in the Kendeng karst mountain area.
These Indonesian villages are powered by locally sourced sustainable energy
- An estimated 1.6 million poor households in Indonesia are not connected to the electricity grid.
- Indonesia’s national energy plan, which targets 35,000 megawatts of new generating capacity, relies primarily on coal and other fossil fuels.
- In rural, off-grid areas, the government has shown more support for renewable energy generation, but progress remains slow.
- In the meantime, villages like Reno on Flores Island have built their own small-scale renewable energy sources.
U.S. president energizes pipeline projects
- Conservation groups argue that the pipelines would move oil harvested through ‘dirty’ extraction methods from oil sands and shale formations.
- The Obama Administration opposed both projects, saying that they represented a step backward in ending our dependence on carbon-based energy.
- President Trump told reporters during the signing at the White House that the Keystone XL pipeline would create 28,000 jobs.
Trump vows Paris Agreement pull out; world unites behind green economy
- Climate delegates and NGOs meeting in Marrakesh, Morocco, responded to threats this week by Donald Trump to quickly renege on the US commitment to uphold the Paris Climate Agreement. While the US under Pres. Obama led the way to the accord, COP22 summit attendees say that China is now likely to fill the leadership vacuum created by Trump.
- COP22 participants also say that the world’s nations are now united in moving toward decarbonizing their economies with 21st century technologies to slow the rate of global warming, while creating millions of new green-energy jobs. Meanwhile, a US under Trump is on the path to re-embracing coal, a 19th century technology in rapid decline.
- Summit attendees have discussed repercussions for a US withdrawal from the accord reached in December 2015 by nearly 200 nations. Beyond the loss of US standing on the world stage, backlash could come in the form of faltering trade agreements, failed military cooperation, economic sanctions, or a carbon tax levied on the US for failing its carbon-reduction pledges.
- “Even though we are in a time of uncertainty because of the US election, there is no way to turn away from what [climate] scientists have shown us. Failure to act now will lead to catastrophic consequences,” said Peru’s Manuel Pulgar-Vidal, a key organizer of the Lima and Paris climate summits.
California governor signs landmark climate and clean energy bills into law
- California Governor Jerry Brown had threatened to take the measure directly to voters via ballot initiative as he approaches the end of his fourth and final term, but in the end, Senate Bill 32 (SB 32) was approved by the California legislature on August 25.
- Governor Brown signed the bill into law last Thursday.
- SB 32 extends the climate targets adopted by California under Assembly Bill 32 (AB 32), also known as the Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006, which required California to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by 2020.
Canada, Mexico, US announce joint clean energy, climate commitments
- The North American Climate, Clean Energy, And Environment Partnership was announced by Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, Mexican President Enrique Peña Nieto, and U.S. President Barack Obama while meeting at the North American Leaders Summit in Ottawa.
- The plan contains a range of measures aimed at curbing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and spurring the growth of low-carbon energy technologies.
- In addition to the clean energy goal, the countries have committed to phasing out “inefficient” fossil fuel subsidies by 2025, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants from light- and heavy-duty vehicles, and drawing down methane emissions from the oil and gas industry 40 to 45 percent by 2025, among other initiatives.
These countries are growing their economies and lowering emissions at the same time
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) recently reported that global GDP has grown the past two years even as greenhouse gas emissions have fallen.
- Researchers at the World Resources Institute (WRI) found that 21 countries have managed to decouple GDP growth from energy production-related CO2 emissions for some period of time between 2000 and 2014.
- “The United States is the largest country to experience multiple consecutive years in which economic growth has been ‘decoupled’ from growth in carbon dioxide emissions,” WRI’s Nate Aden wrote in a blog post.
Unhealthy environment kills 12.6 million people every year: WHO study
- Scientists estimate that in 2012, 12.6 million people died because of working or living in unhealthy environmental conditions.
- Children, aged less than five years, and adults between 50 and 75 years, are most negatively impacted by unhealthy environment, the study found
- Regionally, lower and middle-income countries seem to bear the greatest burden of environment-related diseases and injuries, the study found, although some environment-related noncommunicable diseases like cancers and cardiovascular diseases are on the rise in high-income countries.
The week in environmental news – Dec 4, 2015
- The House has voted against Obama’s plan to curb greenhouse gas.
- The coast of southern Chile has turned into a mass grave for more than 330 whales.
- Unilever, a multinational consumer goods company has vowed to become “carbon positive” by 2030.
Solar energy boom has put natural areas at risk
- Study found that most big solar installations in California were located in biologically-sensitive desert lands — comprising of scrublands and shrublands — for installations, covering about 145 square miles.
- Nearly one-third of the big solar installations were located in crop lands, the team found.
- Study also identified around 8,500 square miles of areas in less-sensitive, already-developed land that is compatible for solar energy installations.
Powered by the land: The Sumatran village that conserves forest for electricity
- Residents of Kinangkung rely on water from the surrounding forest to power their homes.
- The microgrid is the consequence of years of a focused drive by a community to protect its ecological wealth.
- Kinangkung is just one sign that microgeneration is beginning to concentrate minds in the archipelago’s outlying areas.
Companies Pledge $140 Billion Toward Resolving Climate Change
 More than a dozen leading U.S. companies have committed to investing a total of $140 billion in new funds to combat climate change in a White House-organized effort.
More than a dozen leading U.S. companies have committed to investing a total of $140 billion in new funds to combat climate change in a White House-organized effort.
Accounting for natural capital on financial exchanges
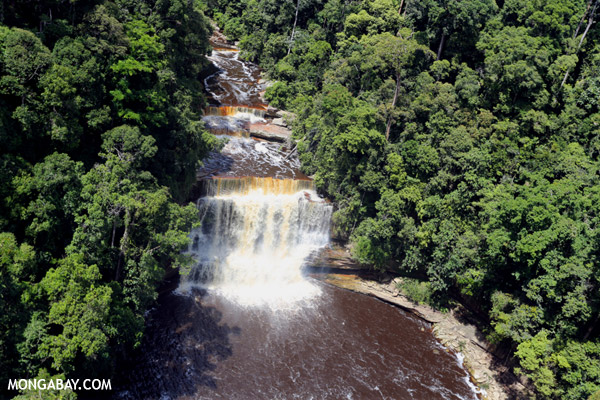 Maliau Falls in Borneo. The global economy depends on natural capital such as freshwater. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last month, Norway’s stock exchange, the Oslo Børs, introduced a way for investors to use their money to promote sustainability. A new list by the stock exchange highlights green bonds, financial products issued by companies to […]
Maliau Falls in Borneo. The global economy depends on natural capital such as freshwater. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last month, Norway’s stock exchange, the Oslo Børs, introduced a way for investors to use their money to promote sustainability. A new list by the stock exchange highlights green bonds, financial products issued by companies to […]
Climate change solution? UN touts ambitious (but cheap) investment in renewable energy
 The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
Offshore wind farms could blunt hurricane damage
 Massive offshore wind turbine arrays would reduce hurricane wind speeds and storm surge, reports a study published this week in Nature Climate Change. And while the size (tens of thousands of turbines) and cost (hundreds of billions of dollars) is difficult to imagine, the reduction in storm damage and value of electricity produced would effectively […]
Massive offshore wind turbine arrays would reduce hurricane wind speeds and storm surge, reports a study published this week in Nature Climate Change. And while the size (tens of thousands of turbines) and cost (hundreds of billions of dollars) is difficult to imagine, the reduction in storm damage and value of electricity produced would effectively […]
Indigenous groups protest hydropower congress as controversy hits meeting in Malaysia
 The opening of the International Hydropower Association (IHA) World Congress in the Malaysian state of Sarawak was marred today by indigenous protests and controversy after a local indigenous leader was barred from attending a pre-conference workshop. Over 300 people from local indigenous people protested the ongoing construction of around a dozen mega-dams in the state […]
The opening of the International Hydropower Association (IHA) World Congress in the Malaysian state of Sarawak was marred today by indigenous protests and controversy after a local indigenous leader was barred from attending a pre-conference workshop. Over 300 people from local indigenous people protested the ongoing construction of around a dozen mega-dams in the state […]
‘Carbon bubble’ could cause next global financial crisis
 The world could be heading for a major economic crisis as stock markets inflate an investment bubble in fossil fuels to the tune of trillions of dollars, according to leading economists. “The financial crisis has shown what happens when risks accumulate unnoticed,” said Lord (Nicholas) Stern, a professor at the London School of Economics. He […]
The world could be heading for a major economic crisis as stock markets inflate an investment bubble in fossil fuels to the tune of trillions of dollars, according to leading economists. “The financial crisis has shown what happens when risks accumulate unnoticed,” said Lord (Nicholas) Stern, a professor at the London School of Economics. He […]
Proposed coal plant threatens Critically Endangered Philippine cockatoo
 One kilometer off the Philippine island of Palawan lies the Rasa Island Wildlife Sanctuary; here forest grows unimpeded from a coral island surrounded by mangroves and coral reefs. Although tiny, over a hundred bird species have been recorded on the island along with a major population of large flying foxes, while in the waters below […]
One kilometer off the Philippine island of Palawan lies the Rasa Island Wildlife Sanctuary; here forest grows unimpeded from a coral island surrounded by mangroves and coral reefs. Although tiny, over a hundred bird species have been recorded on the island along with a major population of large flying foxes, while in the waters below […]
Featured video: moving green, local energy forward in Southeast Asia
 Rainforest in Sabah, Malaysia on the island of Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A new video highlights the work and drive of renewable energy proponents at the inaugural meeting of Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) in the Malaysian state of Sabah. Held last year, the meeting brought together 80 organizations from 12 […]
Rainforest in Sabah, Malaysia on the island of Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A new video highlights the work and drive of renewable energy proponents at the inaugural meeting of Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) in the Malaysian state of Sabah. Held last year, the meeting brought together 80 organizations from 12 […]
Looking bright: solar power passes 100 gigawatts worldwide
 Solar power on Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. Photo by: U.S. Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class Nadine Y. Barclay. The world’s installed solar capacity hit 101 gigawatts last year, according to new data from the European Photovoltaic Industry Association (EPIA). Last year alone, saw nearly 30 gigawatts of solar power added around the world. […]
Solar power on Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. Photo by: U.S. Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class Nadine Y. Barclay. The world’s installed solar capacity hit 101 gigawatts last year, according to new data from the European Photovoltaic Industry Association (EPIA). Last year alone, saw nearly 30 gigawatts of solar power added around the world. […]
New wind power cheaper than coal or gas in Australia
 Electricity supplied from a new wind farm is cheaper than that from a new gas or coal-fired power plant in Australia, reports a new analysis published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. According to the study, wind-generated electricity costs AU$80 ($83) per megawatt hour compared with compared to AU$143/MWh ($148) from a new coal plant or […]
Electricity supplied from a new wind farm is cheaper than that from a new gas or coal-fired power plant in Australia, reports a new analysis published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. According to the study, wind-generated electricity costs AU$80 ($83) per megawatt hour compared with compared to AU$143/MWh ($148) from a new coal plant or […]
Paradigm shift needed to avert global environmental collapse, according to author of new book The Blueprint: Averting Global Collapse
 Scientists and experts are increasingly concerned that we are entering an age of ecological collapse with untold impacts for future generations. In Daniel Rirdan’s new book, The Blueprint, he outlines how to avoid this fate. Author, global strategist, and speaker Daniel Rirdan set out to create a plan addressing the future of our planet. His […]
Scientists and experts are increasingly concerned that we are entering an age of ecological collapse with untold impacts for future generations. In Daniel Rirdan’s new book, The Blueprint, he outlines how to avoid this fate. Author, global strategist, and speaker Daniel Rirdan set out to create a plan addressing the future of our planet. His […]
Sarawak minister tells clean energy activists to ‘stop breathing’
 Bakun dam during construction. Photo by: Mohamad Shoox. A top minister in the Malaysian state of Sarawak has told activists campaigning for cleaner energy to ‘stop breathing’, reports The Borneo Post. “I would like to throw a challenge at them (critics) on two fronts,” Land Development Minister Tan Sri Dr James Jemut Masing told the […]
Bakun dam during construction. Photo by: Mohamad Shoox. A top minister in the Malaysian state of Sarawak has told activists campaigning for cleaner energy to ‘stop breathing’, reports The Borneo Post. “I would like to throw a challenge at them (critics) on two fronts,” Land Development Minister Tan Sri Dr James Jemut Masing told the […]
Micro-hydro and decentralized green energy goals set in Borneo
 Participants from diverse backgrounds and groups marking on a map the creation of partnerships through identified projects at the end of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo by: Suzanne Chong/LEAP. The first ever meeting of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) ended […]
Participants from diverse backgrounds and groups marking on a map the creation of partnerships through identified projects at the end of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo by: Suzanne Chong/LEAP. The first ever meeting of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) ended […]
After defeating coal plant, Borneo hosts renewable energy meeting
 A participant sharing a story at the inaugural Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo courtesy of SEAREPA. Last year, a coalition of environmentalists and locals won a David-versus-Goliath battle against a massive coal plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo. After facing a […]
A participant sharing a story at the inaugural Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo courtesy of SEAREPA. Last year, a coalition of environmentalists and locals won a David-versus-Goliath battle against a massive coal plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo. After facing a […]
Tigers vs. coal in India: when big energy meets vanishing cats
 Surface coal mining in Bihar, India. Around 70-80 percent of India’s power is currently provided by coal. Burning coal fuels climate change, causes acid rain, and spreads toxic pollutants into the environment, but now a new Greenpeace report warns that coal may also imperil the world’s biggest feline: the tiger. Home to world’s largest population […]
Surface coal mining in Bihar, India. Around 70-80 percent of India’s power is currently provided by coal. Burning coal fuels climate change, causes acid rain, and spreads toxic pollutants into the environment, but now a new Greenpeace report warns that coal may also imperil the world’s biggest feline: the tiger. Home to world’s largest population […]
Consumption, population, and declining Earth: wake-up call for Rio+20
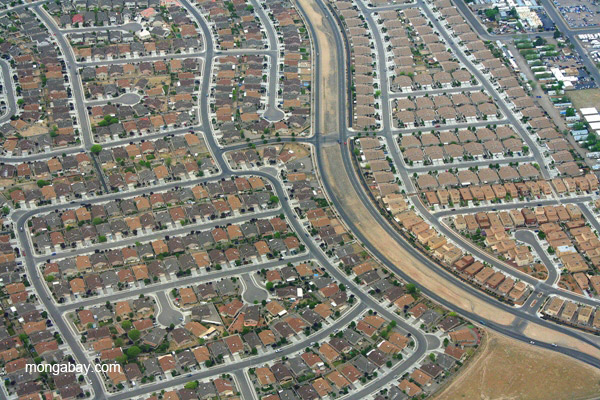 Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Mexico passes aggressive climate bill
 Sunrise in Cancun, Mexico, where the 2010 UN Climate Summit was held. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last week, Mexico’s Senate passed an aggressive and comprehensive climate change bill, making it the first developing nation and only the second country to do so, after the UK. The bill, which far outshines anything achieved by its […]
Sunrise in Cancun, Mexico, where the 2010 UN Climate Summit was held. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last week, Mexico’s Senate passed an aggressive and comprehensive climate change bill, making it the first developing nation and only the second country to do so, after the UK. The bill, which far outshines anything achieved by its […]
Solar cells cross new threshold
 Imagine powering your cell phone by leaving it on the window sill. Sounds like science fiction? Actually, this might soon turn into reality. Scientists have been exploring the potential of solar energy for decades. One of the cheapest ways to turn solar energy into electricity is by creating solar cells from organic polymers, which are […]
Imagine powering your cell phone by leaving it on the window sill. Sounds like science fiction? Actually, this might soon turn into reality. Scientists have been exploring the potential of solar energy for decades. One of the cheapest ways to turn solar energy into electricity is by creating solar cells from organic polymers, which are […]
California sets tough new clean car standards
The U.S. state that takes climate change most seriously—California—has unanimously approved new rules dubbed the Advanced Clean Cars program to lower carbon emissions, reduce oil dependence, mitigate health impacts from pollution, and save consumers money in the long-term. According to the new standards, by 2025 cars sold in California must cut greenhouse gas emissions by […]
Sarah Laskow: even renewable energy has a dark side
 Sarah Laskow is a freelance writer who has covered environmental issues for Grist, GOOD, and Newsweek.com, among others. Raised in New Jersey and educated at Yale where she studied literature, Sarah now lives across the river in Manhattan with her partner. She’s done extensive traveling in West Africa, Europe, and Central America. Sarah can be […]
Sarah Laskow is a freelance writer who has covered environmental issues for Grist, GOOD, and Newsweek.com, among others. Raised in New Jersey and educated at Yale where she studied literature, Sarah now lives across the river in Manhattan with her partner. She’s done extensive traveling in West Africa, Europe, and Central America. Sarah can be […]
Top 10 Environmental Stories of 2011
 Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
Facebook pledges to go green…someday soon
After a massive campaign by Greenpeace to get everyone’s favorite social media site to quit coal energy, Facebook has announced a new energy policy and a partnership with Greenpeace. The policy includes a goal “to power all of our operations with clean and renewable energy,” however does not go so far as to state it […]
IEA warns: five years to slash emissions or face dangerous climate change
 Not known for alarmism and sometimes criticized for being too optimistic, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned that without bold action in the next five years the world will lock itself into high-emissions energy sources that will push climate change beyond the 2 degrees Celsius considered relatively ‘safe’ by many scientists and officials. “As […]
Not known for alarmism and sometimes criticized for being too optimistic, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned that without bold action in the next five years the world will lock itself into high-emissions energy sources that will push climate change beyond the 2 degrees Celsius considered relatively ‘safe’ by many scientists and officials. “As […]
Activists worldwide push for leaving the fossil fuel age behind
 Young people rally in Kiev, Ukraine at apart of the Moving Planet campaign. Photo by: Maxm Gorpenyuk. On six continents, in over 75 percent of the world’s countries, people came out en masse yesterday to attend over 2,000 events to demonstrate the power of renewable energy to combat global climate change. As apart of the […]
Young people rally in Kiev, Ukraine at apart of the Moving Planet campaign. Photo by: Maxm Gorpenyuk. On six continents, in over 75 percent of the world’s countries, people came out en masse yesterday to attend over 2,000 events to demonstrate the power of renewable energy to combat global climate change. As apart of the […]
Has the green energy revolution finally arrived?
 When historians look back at the fight to combat climate change—not to mention the struggle to overcome our global addiction to fossil fuels—will 2011 be considered a watershed moment? Maybe. In the last couple months, three countries—each in the top ten in terms of GDP—have suddenly made major renewable energy promises. Germany, Japan, and, just […]
When historians look back at the fight to combat climate change—not to mention the struggle to overcome our global addiction to fossil fuels—will 2011 be considered a watershed moment? Maybe. In the last couple months, three countries—each in the top ten in terms of GDP—have suddenly made major renewable energy promises. Germany, Japan, and, just […]
Violent protests follow approval of massive dam project in Patagonia
 The wild rivers of Patagonia may soon never be the same. Last week, Chile’s Aysén Environmental Review Commission approved the environmental assessment of a five dam proposal on two rivers. The approval, however, is marred in controversy and has set off protests in many cities, including Santiago. Critics say the series of dams will destroy […]
The wild rivers of Patagonia may soon never be the same. Last week, Chile’s Aysén Environmental Review Commission approved the environmental assessment of a five dam proposal on two rivers. The approval, however, is marred in controversy and has set off protests in many cities, including Santiago. Critics say the series of dams will destroy […]
Obama focuses on climate change in Earth Day proclamation
After a long absence of speaking directly to the issue of climate change—he did not mention it once in his State of the Union speech in January—US President Barack Obama used his Earth Day proclamation to focus on it. “The United States can be a leader in reducing the dangerous pollution that causes global warming […]
Bats worth billions
 US agriculture stands to lose billions in free ecosystem services from the often-feared and rarely respected humble bat. According to a recent study in Science bats in North America provide the US agricultural industry at least $3.7 billion and up to a staggering $53 billion a year by eating mounds of potentially pesky insects. Yet […]
US agriculture stands to lose billions in free ecosystem services from the often-feared and rarely respected humble bat. According to a recent study in Science bats in North America provide the US agricultural industry at least $3.7 billion and up to a staggering $53 billion a year by eating mounds of potentially pesky insects. Yet […]
Sustainability takes only cents
Real economic global results from decoupling economic growth from unsustainable natural resource management and inefficient industrial processes are the central themes of Cents and Sustainability. Implementing wealth creation strategies at the local, national, and international level is the primary economic theme, or modus operandi, of the 21st Century, as opposed to 20th Century wealth appropriation […]
Clean energy investments rise 630% in 7 years
According to a report by the US Pew Environment Group global clean energy investments, which do not include nuclear power, jumped 630% since 2004. The report detailing 2010 clean energy investments found that China remains the global leader in clean energy, while the US fell from 2nd to 3rd. This is the second year in […]
Coal’s true cost in the US: up to half a trillion
According to the global market coal is cheap, yet a new study in the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences finds that the hidden costs of coal are expensive, very expensive. Estimating the hidden costs of coal, such as health and environmental impacts, the study found that burning coal costs the US up […]
Is Obama’s clean energy revolution possible?
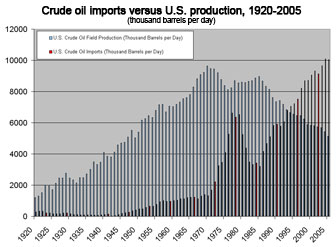 Recent studies point to the feasibility of a global clean energy revolution. Last night US President Barack Obama called for a massive green energy make-over of the world’s largest economy. Describing the challenge as ‘this generation’s Sputnik moment’ the US president set a goal of producing 80 percent of America’s energy by clean sources by […]
Recent studies point to the feasibility of a global clean energy revolution. Last night US President Barack Obama called for a massive green energy make-over of the world’s largest economy. Describing the challenge as ‘this generation’s Sputnik moment’ the US president set a goal of producing 80 percent of America’s energy by clean sources by […]
Prairie grass-based biofuels could meet half current fuel demand without affecting forests, food
Biofuels could meet up to half the world’s current fuel consumption without affecting food production or forests, argues a study published last month in the journal Environmental Science and Technology. Analyzing the extent of marginal grasslands, including abandoned and degraded grassland, using data on soil, topography, climate and current land use, Ximing Cai of the […]
Indonesia to open protected forests to geothermal power
The Indonesian government will soon issue a decree allowing geothermal mining in protected forests, reports The Jakarta Post. Mining of any kind is currently prohibited in protected forest areas, but because the government says geothermal mining is “environmentally friendly” it would be allowed. Geothermal would enable Indonesia to reduce its dependence on oil, reserves of […]
New Zealand: Can you sink a rainbow?
 25 years on from Greenpeace’s joint stand with New Zealand’s government against potentially environmentally devastating practices, the country is at a Crossroads The Rainbow Warrior after the bombing by French commandos. Image courtesy of Greenpeace In light of the subject of this article, condolences go out to the families of the 29 miners who died […]
25 years on from Greenpeace’s joint stand with New Zealand’s government against potentially environmentally devastating practices, the country is at a Crossroads The Rainbow Warrior after the bombing by French commandos. Image courtesy of Greenpeace In light of the subject of this article, condolences go out to the families of the 29 miners who died […]
U.S. Department of Energy makes $1.5B loan to massive solar plant
 The U.S. Department of Energy has finalized a guarantee to provide a loan of $1.45 billion to Abengoa Solar Inc. which will fund the world’s largest parabolic trough concentrating solar plant. The plant is expected to serve 70,000 households and avoid 475,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. The plant, called Solana, will be […]
The U.S. Department of Energy has finalized a guarantee to provide a loan of $1.45 billion to Abengoa Solar Inc. which will fund the world’s largest parabolic trough concentrating solar plant. The plant is expected to serve 70,000 households and avoid 475,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. The plant, called Solana, will be […]
US elects barrage of climate change deniers, threatening support for green energy
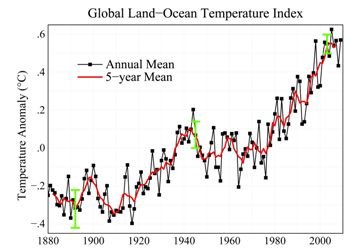 The US midterm election, which won Republicans the House but safeguarded the Senate for Democrats, has brought in a number of self-proclaimed climate change deniers, ending any likelihood that an energy bill will be passed over the next two years and essentially stumbling the White House’s strategy on climate change. Newly elected Republican Senators Rand […]
The US midterm election, which won Republicans the House but safeguarded the Senate for Democrats, has brought in a number of self-proclaimed climate change deniers, ending any likelihood that an energy bill will be passed over the next two years and essentially stumbling the White House’s strategy on climate change. Newly elected Republican Senators Rand […]
Majority of Americans confused on climate change basics
 Most Americans don’t understand the basics of climate change, according to a new poll by researchers with Yale. The poll found that over half of Americans deserve an ‘F’ on basic understanding of climate science and climate change, while only 1% would receive an ‘A’. While 63% of Americans say that the globe is warming, […]
Most Americans don’t understand the basics of climate change, according to a new poll by researchers with Yale. The poll found that over half of Americans deserve an ‘F’ on basic understanding of climate science and climate change, while only 1% would receive an ‘A’. While 63% of Americans say that the globe is warming, […]
New Google wind project moves clean energy forward in US
 While the US has fallen far behind China and Europe in clean energy power, an announcement by Google today brings hope to green energy backers. Google is putting its considerable name and a lot of cash behind a $5 billion energy transmission line that would link up proposed wind turbines off the US’s East Coast […]
While the US has fallen far behind China and Europe in clean energy power, an announcement by Google today brings hope to green energy backers. Google is putting its considerable name and a lot of cash behind a $5 billion energy transmission line that would link up proposed wind turbines off the US’s East Coast […]
Farms in the sky, an interview with Dickson Despommier
 To solve today’s environmental crises—climate change, deforestation, mass extinction, and marine degradation—while feeding a growing population (on its way to 9 billion) will require not only thinking outside the box, but a “new box altogether” according to Dr. Dickson Despommier, author of the new book, The Vertical Farm. Exciting policy-makers and environmentalists, Despommier’s bold idea […]
To solve today’s environmental crises—climate change, deforestation, mass extinction, and marine degradation—while feeding a growing population (on its way to 9 billion) will require not only thinking outside the box, but a “new box altogether” according to Dr. Dickson Despommier, author of the new book, The Vertical Farm. Exciting policy-makers and environmentalists, Despommier’s bold idea […]
Citizens of 188 countries challenge leaders on climate change
 As world leaders continue to fumble a coherent, rapid, and comprehensive response to climate change, citizens from around the world yesterday sent a message to inert politicians by participating in over 7,300 events against climate change, according to 350.org, the head organizer of the day dubbed the ‘Global Work Party’. “The fossil fuel industry may […]
As world leaders continue to fumble a coherent, rapid, and comprehensive response to climate change, citizens from around the world yesterday sent a message to inert politicians by participating in over 7,300 events against climate change, according to 350.org, the head organizer of the day dubbed the ‘Global Work Party’. “The fossil fuel industry may […]
Do wind farms drive local warming?
 Using decades-old data researchers have proven a long-suspected effect of wind turbines: under certain conditions large-scale wind farms can change local weather. Temperatures recorded from a wind farm in San Gorgonio, California in 1989 shows that turbines cooled local temperatures during the day, but warmed them at night. However, researchers in the paper published in […]
Using decades-old data researchers have proven a long-suspected effect of wind turbines: under certain conditions large-scale wind farms can change local weather. Temperatures recorded from a wind farm in San Gorgonio, California in 1989 shows that turbines cooled local temperatures during the day, but warmed them at night. However, researchers in the paper published in […]
Dapatkah Biochar Selamatkan Dunia?
 Sebuah wawancara dengan Laurens Rademakers dari Biochar Fund. Biochar – penggunaan arang yang diproduksi dari membakar biomassa untuk pertanian – mungkin merupakan saru dari revolusi lingkungan dan sosial yang terpenting di abad ini. Praktek yang sepertinya sederhana ini – sebuah teknologi yang kembali ke ribuan tahun yang lalu – memiliki potensi untuk membantu mengurangi sebagian […]
Sebuah wawancara dengan Laurens Rademakers dari Biochar Fund. Biochar – penggunaan arang yang diproduksi dari membakar biomassa untuk pertanian – mungkin merupakan saru dari revolusi lingkungan dan sosial yang terpenting di abad ini. Praktek yang sepertinya sederhana ini – sebuah teknologi yang kembali ke ribuan tahun yang lalu – memiliki potensi untuk membantu mengurangi sebagian […]
Could biochar save the world?
 An interview with Laurens Rademakers of Biochar Fund. Biochar—the agricultural application of charcoal produced from burning biomass—may be one of this century’s most important social and environmental revolutions. This seemingly humble practice—a technology that goes back thousands of years—has the potential to help mitigate a number of entrenched global problems: desperate hunger, lack of soil […]
An interview with Laurens Rademakers of Biochar Fund. Biochar—the agricultural application of charcoal produced from burning biomass—may be one of this century’s most important social and environmental revolutions. This seemingly humble practice—a technology that goes back thousands of years—has the potential to help mitigate a number of entrenched global problems: desperate hunger, lack of soil […]
Fishermen express doubts about coal plant overlooking their fishing grounds
 Local fishermen in the Malaysian state of Sabah are uncertain of their future, if the government pushes ahead to build a 300 megawatt coal power plant. They have been told they will be moved from their current seaside village to one deeper inland, and while the coal plant will provide manual labor work in its […]
Local fishermen in the Malaysian state of Sabah are uncertain of their future, if the government pushes ahead to build a 300 megawatt coal power plant. They have been told they will be moved from their current seaside village to one deeper inland, and while the coal plant will provide manual labor work in its […]
Foto-foto tunjukkan daerah mirip-surga untuk lokasi pembangkit listrik batu bara di Borneo
 Dengan seluruh perhatian dunia sedang mengarah pada bencana lingkungan di Teluk Meksiko, banyak yang mulai merenungkan kebenaran dari tidak hanya Amerika, tapi ketergantungan dunia akan bahan bakar fossil. Meski begitu proyek-proyek pengadaan energi berbahan bakar fosil skala besar terus berjalan maju, termasuk di kota Sabah, Malaysia di Borneo yang akan membangun 300 MW pembangkit listrik […]
Dengan seluruh perhatian dunia sedang mengarah pada bencana lingkungan di Teluk Meksiko, banyak yang mulai merenungkan kebenaran dari tidak hanya Amerika, tapi ketergantungan dunia akan bahan bakar fossil. Meski begitu proyek-proyek pengadaan energi berbahan bakar fosil skala besar terus berjalan maju, termasuk di kota Sabah, Malaysia di Borneo yang akan membangun 300 MW pembangkit listrik […]
Bill Gates: larang batu bara dan berinvestasi di teknologi energi bersih
Planet membutuhkan “keajaiban energi” untuk mengatasi tantangan ganda dari memenuhi permintaan energi dan mengatasi perubahan iklim, ujar penemu Microsoft Bill Gates dalam pidato Jumat di Konferensi TED di Long Beach, California. “Yang akan harus kita lakukan dalam skala global adalah menciptakan sistem baru,” ungkap Gates. “Sehingga kita membutuhkan keajaiban energi.” Hanya beberapa minggu setelah yayasannya […]
Photos reveal paradise-like site for coal plant in Borneo
 With the world’s eyes on the environmental catastrophe in the Gulf of Mexico, many are beginning to ponder the rightness of not just America’s, but the world’s dependence on fossil fuels. Yet large-scale fossil-fuel energy projects continue to march ahead, including one in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo to build a 300 MW […]
With the world’s eyes on the environmental catastrophe in the Gulf of Mexico, many are beginning to ponder the rightness of not just America’s, but the world’s dependence on fossil fuels. Yet large-scale fossil-fuel energy projects continue to march ahead, including one in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo to build a 300 MW […]
Who’s to blame for the oil spill?
 Why we get the oil spill we deserve. America, we deserve the oil spill now threatening the beautiful coast of Louisiana. This disaster is not natural, like the earthquake that devastated Haiti or tsunami that swept Southeast Asia in 2006; this disaster is man-made, American-made in fact, pure and simple. So, while in the upcoming […]
Why we get the oil spill we deserve. America, we deserve the oil spill now threatening the beautiful coast of Louisiana. This disaster is not natural, like the earthquake that devastated Haiti or tsunami that swept Southeast Asia in 2006; this disaster is man-made, American-made in fact, pure and simple. So, while in the upcoming […]
US emissions from coal could be stopped in 20 years
A new study in Environmental Science and Technology (ES&T) concludes that the US could stop all emissions from coal-fired plants within 20 years time using only existing technologies and some that will be ready within the next decade. Such an accomplishment would go a long way toward lowering the US’s carbon emissions and mitigating the […]
U.S. approves first offshore wind farm
 The Obama Administration has approved the nation’s first offshore wind farm after more than eight years of legal challenges, reports the Associated Press. Speaking Wednesday in Boston, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar said the $2 billion Cape Wind project marks “a new direction in our nation’s energy future.” The 130-turbine, 420-megawatt wind farm will generate […]
The Obama Administration has approved the nation’s first offshore wind farm after more than eight years of legal challenges, reports the Associated Press. Speaking Wednesday in Boston, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar said the $2 billion Cape Wind project marks “a new direction in our nation’s energy future.” The 130-turbine, 420-megawatt wind farm will generate […]
Analysis shows Borneo can say ‘no’ to coal power
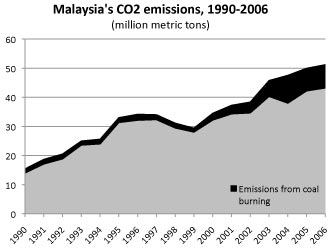 Plans for a coal power plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah in northern Borneo have run into stiff opposition. Environmentalists say the coal plant could damage extensive coral reef systems, pollute water supplies, open rainforests to mining, and contribute to global climate change, undercutting Sabah’s image as a ‘green’ destination. The federal government contends […]
Plans for a coal power plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah in northern Borneo have run into stiff opposition. Environmentalists say the coal plant could damage extensive coral reef systems, pollute water supplies, open rainforests to mining, and contribute to global climate change, undercutting Sabah’s image as a ‘green’ destination. The federal government contends […]
Bill Gates: ban coal and invest in clean energy technology
The planet needs “energy miracles” to overcome the dual challenges of meeting energy demand and addressing climate change, said Microsoft founder Bill Gates during a speech Friday at the TED Conference in Long Beach, California. “What we’re going to have to do at a global scale is create a new system,” Gates said. “So we […]
China leaves US (and Europe) in the dust on renewable energy
 This year China has become the world’s largest manufacturer of solar panels and wind turbines, doubling its wind capacity since 2005. The economically booming nation—and the world’s most populous—has also invested heavily in nuclear power and the world’s most efficient coal plants, according to the New York Times. Still, even with massive investments in green […]
This year China has become the world’s largest manufacturer of solar panels and wind turbines, doubling its wind capacity since 2005. The economically booming nation—and the world’s most populous—has also invested heavily in nuclear power and the world’s most efficient coal plants, according to the New York Times. Still, even with massive investments in green […]
Iceland leads world on environmental issues, but China, US, and Canada plummet
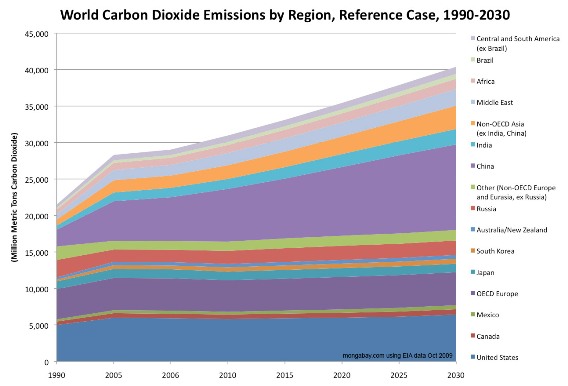 Evaluating 163 nations on their environmental performance, the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) has named Iceland the most environmental nation. Released every two years, the EPI also found that the world’s two largest super-powers—China and the US—have both fallen behind on confronting environmental challenges. Despite being at the top of the list, Iceland continues to face […]
Evaluating 163 nations on their environmental performance, the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) has named Iceland the most environmental nation. Released every two years, the EPI also found that the world’s two largest super-powers—China and the US—have both fallen behind on confronting environmental challenges. Despite being at the top of the list, Iceland continues to face […]
New report: world must change model of economic growth to avert environmental disaster
 For decades industrialized nations have measured their success by the size of their annual GDP (Gross Domestic Product), i.e. economic growth. The current economic model calls for unending growth—as well as ever-rising consumerism—just to remain stable. However, a new report by the New Economics Foundation (nef) states that if countries continue down a path of […]
For decades industrialized nations have measured their success by the size of their annual GDP (Gross Domestic Product), i.e. economic growth. The current economic model calls for unending growth—as well as ever-rising consumerism—just to remain stable. However, a new report by the New Economics Foundation (nef) states that if countries continue down a path of […]
Could space technology save our planet?
A new book, Paradise Regained: the Regreening of Earth argues that the solutions to the world’s current environmental crises—including climate change—could be lying far beyond our planet. “As a scientist and an advocate for space development, I believe that those that are in the environmental movement and space advocates should be working together to help […]
United States to speed up green technology patents
 Green technology patents will see a year shaved off the average forty month wait time to approve new patents in the US. The US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is implementing a one-year pilot program to push green technology patent applications through the process more quickly, so that the technologies can reach the market faster. […]
Green technology patents will see a year shaved off the average forty month wait time to approve new patents in the US. The US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is implementing a one-year pilot program to push green technology patent applications through the process more quickly, so that the technologies can reach the market faster. […]
US provides 3 billion in subsidies for Exxon-mobil project in Papua New Guinea
While officials from around their world are working night-and-day to come up with an international agreement to combat climate change in Copenhagen, the US Export-Import Bank confirmed it will subsidize a natural gas project in Papua New Guinea to the tune of 3 billion dollars—a record for the bank. Critics say the project will clear […]
New rating systems seeks to promote sustainable landscapes from shopping malls to city parks
 The Sustainable Sites Initiative has developed the United States’ first rating system for the design, construction, and on-going maintenance of a wide-variety of landscapes, both with and without buildings, including shopping malls, subdivisions, university campuses, corporate buildings, transportation centers, parks and other recreation areas, and single-family homes. “While carbon-neutral performance remains the holy grail for […]
The Sustainable Sites Initiative has developed the United States’ first rating system for the design, construction, and on-going maintenance of a wide-variety of landscapes, both with and without buildings, including shopping malls, subdivisions, university campuses, corporate buildings, transportation centers, parks and other recreation areas, and single-family homes. “While carbon-neutral performance remains the holy grail for […]
US subsidies of oil and coal more than double the subsidies of renewable energy
 During the fiscal years of 2002-2008 the United States handed out subsidies to fossil fuel industries to a tune of 72 billion dollars, while renewable energy subsidies, during the same period, reached 29 billion dollars. Conducted by the Environmental Law Institute (ELI) in partnership with the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, the research shows […]
During the fiscal years of 2002-2008 the United States handed out subsidies to fossil fuel industries to a tune of 72 billion dollars, while renewable energy subsidies, during the same period, reached 29 billion dollars. Conducted by the Environmental Law Institute (ELI) in partnership with the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, the research shows […]
Fifteen indigenous leaders arrested in Borneo for protesting dams that would flood their lands
 After attempting to send a memorandum of protest against two dam proposals to the Sarawak Chief Minister Taib Mahmud, fifteen indigenous leaders were arrested in Kuching, Sarawak, reports the non-governmental organization the Burno Manser Fund. Each of the community leaders—including six Penans, four Ibans, three Kenyahs, and two Kayans—were protesting the dams since they will […]
After attempting to send a memorandum of protest against two dam proposals to the Sarawak Chief Minister Taib Mahmud, fifteen indigenous leaders were arrested in Kuching, Sarawak, reports the non-governmental organization the Burno Manser Fund. Each of the community leaders—including six Penans, four Ibans, three Kenyahs, and two Kayans—were protesting the dams since they will […]
Power, profit, and pollution: dams and the uncertain future of Sarawak
Solar powered conservation

Environmental disappointments under Obama

Little hydroelectric dams become all the rage, but do they harm the environment?
Biofuel company eyes dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico for creating fish-powered fuel
‘Dead zones’ in the ocean are called such for a reason. Every year agricultural run-off, especially fertilizer, floods the oceans with an abundance of nutrients leading to algae blooms, i.e. massive explosions of phytoplankton. The demise of these blooms, and the rise of bacteria feeding on them, eventually starves the entire area of oxygen creating […]
Will hydrocarbon biofuels replace gasoline and ethanol?
 In a Perspectives piece in Science, John R. Regalbuto argues that the world will soon see a revolution in biofuels, but not those made from corn. Instead Regalbuto, program director of Catalysis and Biocatalysis at the National Science Foundation, says that the future of biofuels is in substances that can be converted into liquid hydrocarbons, […]
In a Perspectives piece in Science, John R. Regalbuto argues that the world will soon see a revolution in biofuels, but not those made from corn. Instead Regalbuto, program director of Catalysis and Biocatalysis at the National Science Foundation, says that the future of biofuels is in substances that can be converted into liquid hydrocarbons, […]
Wind could power the entire world
 Wind power may be the key to a clean energy revolution: a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science finds that wind power could provide for the entire world’s current and future energy needs. To estimate the earth’s capacity for wind power, the researchers first sectioned the globe into areas of […]
Wind power may be the key to a clean energy revolution: a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science finds that wind power could provide for the entire world’s current and future energy needs. To estimate the earth’s capacity for wind power, the researchers first sectioned the globe into areas of […]
New Yangtze River dam could doom more endangered species
 Eight Chinese environmentalists and scientists have composed a letter warning that a new dam under consideration for the Yangtze River could lead to the extinction of several endangered species. The letter contends that Xiaonanhia Dam, which would be 30 kilometers upstream from the city of Chongqing, will negatively impact the river’s only fish reserve. Spanning […]
Eight Chinese environmentalists and scientists have composed a letter warning that a new dam under consideration for the Yangtze River could lead to the extinction of several endangered species. The letter contends that Xiaonanhia Dam, which would be 30 kilometers upstream from the city of Chongqing, will negatively impact the river’s only fish reserve. Spanning […]
High-flying kites could power New York
 A fleet of kites could harvest enough energy from high-altitude winds to power New York, report researchers from the Carnegie Institution and California State University. Using 28 years of data from the National Center for Environmental Prediction and the Department of Energy, Ken Caldeira of the Carnegie Institution’s Department of Global Ecology and Cristina Archer […]
A fleet of kites could harvest enough energy from high-altitude winds to power New York, report researchers from the Carnegie Institution and California State University. Using 28 years of data from the National Center for Environmental Prediction and the Department of Energy, Ken Caldeira of the Carnegie Institution’s Department of Global Ecology and Cristina Archer […]
Congo biochar initiative will reduce poverty, protect forests, slow climate change
 Congo biochar initiative wins critical funding to support poverty alleviation, climate change mitigation An initiative using soil carbon enrichment techniques to boost agricultural yields, alleviate poverty, and protect endangered forests in Central Africa was today selected as one of six projects to win funding under the Congo Basin Forest Fund (CBFF). The scientific committee of […]
Congo biochar initiative wins critical funding to support poverty alleviation, climate change mitigation An initiative using soil carbon enrichment techniques to boost agricultural yields, alleviate poverty, and protect endangered forests in Central Africa was today selected as one of six projects to win funding under the Congo Basin Forest Fund (CBFF). The scientific committee of […]
Bioelectricity bests ethanol on two fronts: land use and global warming
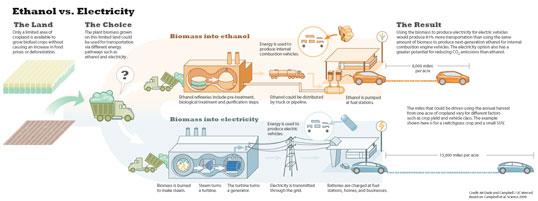 Yesterday the Obama Administration established a Biofuels Interagency Working Group to oversee implementation of new rules and research regarding biofuels. On the group’s first day they would do well to look at a new study in Science Magazine comparing the efficacy of ethanol versus bioelectricity. Researchers compared ethanol and bioelectricity in terms of miles per […]
Yesterday the Obama Administration established a Biofuels Interagency Working Group to oversee implementation of new rules and research regarding biofuels. On the group’s first day they would do well to look at a new study in Science Magazine comparing the efficacy of ethanol versus bioelectricity. Researchers compared ethanol and bioelectricity in terms of miles per […]
Canada and Britain abandon conventional coal
In an effort to curb climate change, both Britain and Canada have announced plans to stop building new conventional coal power plants, a move long-advocated by environmentalists. Both nations have turned their sights to the possibility of clean coal, a controversial and still unproven method that has divided environmentalists, scientists, and policy makers. On Friday, […]
Clean energy investment moving too slowly to avoid irreversible climate change
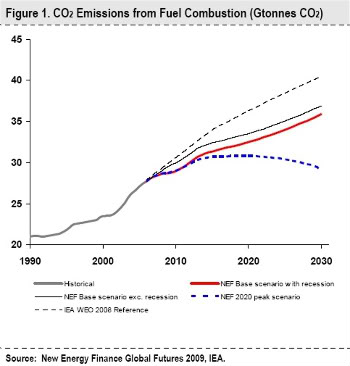
Largest US protest on climate change today
Wind energy jobs now exceed coal mining jobs
Africa eyes geothermal power
Africa eyes geothermal power Africa eyes geothermal power mongabay.com December 12, 2008
Living up to the Pope’s words: the Vatican turns to solar power
Living up to the Pope’s words: the Vatican turns to solar power Living up to the Pope’s words: the Vatican turns to solar power Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com November 28, 2008
Limiting global warming to 2-degree rise will require $180/t carbon price says energy think tank
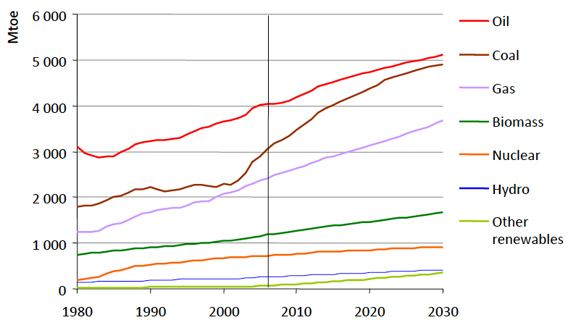 Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency mongabay.com November 13, 2008 Limiting global warming to 2-degree rise will require $180/t carbon price says energy think tank
Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency mongabay.com November 13, 2008 Limiting global warming to 2-degree rise will require $180/t carbon price says energy think tank
Biodiversity of rainforests should not be compared with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief
 Scientists should not compare biodiversity of rainforests with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief Biodiversity of rainforests should not be compared with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief mongabay.com November 11, 2008 Dr. Yusof Basiron, the controversial CEO of the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC), blogs about the sustainability of palm […]
Scientists should not compare biodiversity of rainforests with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief Biodiversity of rainforests should not be compared with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief mongabay.com November 11, 2008 Dr. Yusof Basiron, the controversial CEO of the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC), blogs about the sustainability of palm […]
First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe
 First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe mongabay.com November 10, 2008
First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe mongabay.com November 10, 2008
EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil
 EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil mongabay.com November 7, 2008
EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil mongabay.com November 7, 2008
Rainforest fungus generates biodiesel, may drive energy of the future
Rainforest fungus generates biodiesel, may drive energy of the future Rainforest fungus generates biodiesel, may drive energy of the future Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com November 4, 2008
Green New Deal will spark global economy, create jobs
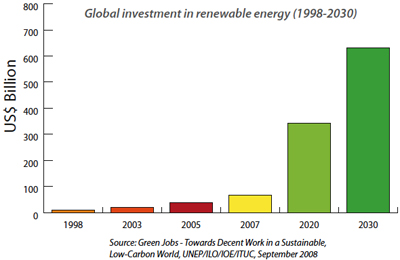 Green New Deal will spark global economy on long-term basis Green New Deal will spark global economy, create jobs mongabay.com October 22, 2008
Green New Deal will spark global economy on long-term basis Green New Deal will spark global economy, create jobs mongabay.com October 22, 2008
Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature
 Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature mongabay.com October 20, 2008 can be used as a 3.8-billion-year-old R&D lab for technology development is gaining momentum. Benyus, author of
Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature mongabay.com October 20, 2008 can be used as a 3.8-billion-year-old R&D lab for technology development is gaining momentum. Benyus, author of
Challenges of starting a green business
 Challenges of starting a green business Challenges facing green business start-ups mongabay.com October 20, 2008
Challenges of starting a green business Challenges facing green business start-ups mongabay.com October 20, 2008
U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels
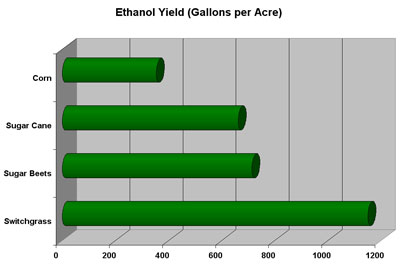 U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels mongabay.com October 2, 2008
U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels mongabay.com October 2, 2008
U.S. Congress passes legislation to boost solar, wind, and geothermal energy
U.S. Congress passes legislation to boost solar, wind, and geothermal energy U.S. Congress passes legislation to boost solar, wind, and geothermal energy mongabay.com September 24, 2008 Tuesday the U.S. Senate passed a bill that will extend tax credits on solar power installations through 2016. The House approved the measure Wednesday. The $17 billion package will […]
Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020
 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 mongabay.com September 12, 2008 The European Union significantly reduces targets for biofuels produced from food sources, while boosting goals for other renewables The E.U. voted to relax biofuels targets following widespread criticism of […]
Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 mongabay.com September 12, 2008 The European Union significantly reduces targets for biofuels produced from food sources, while boosting goals for other renewables The E.U. voted to relax biofuels targets following widespread criticism of […]
Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more
 Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com September 5, 2008 Presidential nominee Barack Obama recently answered fourteen science-related questions for the organization Science Debate 2008. The questions covered a wide-variety of topics, including the importance of innovation, […]
Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com September 5, 2008 Presidential nominee Barack Obama recently answered fourteen science-related questions for the organization Science Debate 2008. The questions covered a wide-variety of topics, including the importance of innovation, […]
Biofuels 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation
 Biofuels up to 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation Biofuels 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation mongabay.com August 27, 2008 The British government should end subsidies for biofuels and instead use the funds to slow destruction of rainforests and tropical peatlands argues a new report […]
Biofuels up to 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation Biofuels 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation mongabay.com August 27, 2008 The British government should end subsidies for biofuels and instead use the funds to slow destruction of rainforests and tropical peatlands argues a new report […]
How do wind turbines kill bats?
Researchers discover why wind turbines are hazardous to bats How do wind turbines kill bats? Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com August 25, 2008 Drop in air pressure, not collisions, devastate bat populations that fly by wind turbines Numerous studies have shown that migratory bats are undergoing large fatalities due to wind turbines. Far more bats die due […]
Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal power production
 Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal power production Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal energy mongabay.com August 20, 2008 Geothermal energy got a big boost this week with Google and the Australian government announcing multi-million initiatives that make use of Earth’s heat as a clean and renewable source of power. Tuesday Google.org, the […]
Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal power production Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal energy mongabay.com August 20, 2008 Geothermal energy got a big boost this week with Google and the Australian government announcing multi-million initiatives that make use of Earth’s heat as a clean and renewable source of power. Tuesday Google.org, the […]
Algae could yield 30 times more biofuel than soybeans, while cleaning the environment
Algae could yield 30 times more biofuel than soybeans, while cleaning the environment Algae could yield 30 times more biofuel than soybeans, while cleaning the environment mongabay.com August 15, 2008 Algae could be used as a biofuel while simultaneously cleaning up the environment, report researchers at the University of Virginia. By feeding algae extra carbon […]
PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant
 PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant mongabay.com August 15, 2008 California electricity producer PG&E Thursday announced a plan to build two giant solar photovoltaic power plants that will cover 12.5 square miles and have a peak generating capacity of 800 megawatts. The plants […]
PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant mongabay.com August 15, 2008 California electricity producer PG&E Thursday announced a plan to build two giant solar photovoltaic power plants that will cover 12.5 square miles and have a peak generating capacity of 800 megawatts. The plants […]
Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests
 Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests mongabay.com July 22, 2008 Biofuels meant to help alleviate greenhouse gas emissions may be in fact contributing to climate change when grown on converted tropical forest lands, warns a comprehensive study […]
Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests mongabay.com July 22, 2008 Biofuels meant to help alleviate greenhouse gas emissions may be in fact contributing to climate change when grown on converted tropical forest lands, warns a comprehensive study […]
Gore launches second campaign… for Earth
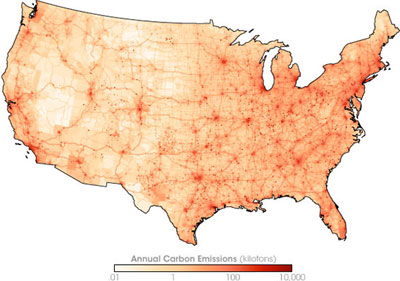 Gore launches second campaign… for Earth Gore launches second campaign mongabay.com July 17, 2008 In a speech Thursday, Al Gore challenged the U.S. to generate 100 percent of its electricity from zero carbon emission sources within 10 years. Speaking at Washington’s Constitution Hall, Gore said America’s security, environmental and economic crises are all related, and […]
Gore launches second campaign… for Earth Gore launches second campaign mongabay.com July 17, 2008 In a speech Thursday, Al Gore challenged the U.S. to generate 100 percent of its electricity from zero carbon emission sources within 10 years. Speaking at Washington’s Constitution Hall, Gore said America’s security, environmental and economic crises are all related, and […]
Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years
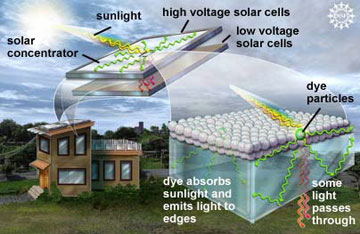 Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com July 10, 2008 The breakthrough scientists have been waiting for to make solar power cheaper, more efficient–and therefore a more […]
Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com July 10, 2008 The breakthrough scientists have been waiting for to make solar power cheaper, more efficient–and therefore a more […]
Oceans hold vast potential for wind power
 Oceans hold vast potential for wind power Oceans hold vast potential for wind power mongabay.com July 9, 2008 The North Pacific, Tasmania, New Zealand, Tierra del Fuego in South America, and the mid-latitudes of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans are potential locations for wind power generation, according to new satellite data from NASA. NASA’s QuikSCAT […]
Oceans hold vast potential for wind power Oceans hold vast potential for wind power mongabay.com July 9, 2008 The North Pacific, Tasmania, New Zealand, Tierra del Fuego in South America, and the mid-latitudes of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans are potential locations for wind power generation, according to new satellite data from NASA. NASA’s QuikSCAT […]
Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels
 Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels mongabay.com July 7, 2008 Britain and the E.U. should exercise caution in pushing for wider use of biofuels, warns a new study commissioned by the U.K. government. The report — dubbed the “Gallagher review” [PDF] for Ed Gallagher, the chair of the government’s […]
Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels mongabay.com July 7, 2008 Britain and the E.U. should exercise caution in pushing for wider use of biofuels, warns a new study commissioned by the U.K. government. The report — dubbed the “Gallagher review” [PDF] for Ed Gallagher, the chair of the government’s […]
Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines
 Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines mongabay.com July 7, 2008 By studying and mimicking the characteristics of the flippers, fins and tails of whales and dolphins, engineers have devised more a efficient way to generate wind power, reports a researcher presenting at the Society for Experimental Biology’s Annual Meeting […]
Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines mongabay.com July 7, 2008 By studying and mimicking the characteristics of the flippers, fins and tails of whales and dolphins, engineers have devised more a efficient way to generate wind power, reports a researcher presenting at the Society for Experimental Biology’s Annual Meeting […]
Clean energy gold rush in 2007
 Clean energy investments rose 60% to $148 billion in 2007 Clean energy gold rush in 2007 mongabay.com July 1, 2008 New investment in renewables and energy efficiency surpassed $148 billion in 2007, rising 60 percent rise from 2006, according to an analysis issued Tuesday July 1 by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). High oil prices […]
Clean energy investments rose 60% to $148 billion in 2007 Clean energy gold rush in 2007 mongabay.com July 1, 2008 New investment in renewables and energy efficiency surpassed $148 billion in 2007, rising 60 percent rise from 2006, according to an analysis issued Tuesday July 1 by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). High oil prices […]
Louisiana signs non-corn ethanol law to produce a better biofuel
Louisiana signs non-corn ethanol law to produce a better biofuel Louisiana signs non-corn ethanol law for to produce a better biofuel mongabay.com July 1, 2008 Louisiana has signed into law legislation to develop an advanced biofuel industry that excludes corn as a feedstock, reports Biopact. The Advanced Biofuel Industry Development Initiative will promote high yielding […]
Brazil signs sustainable ethanol deal with Sweden
Brazil signs sustainable ethanol deal with Sweden Brazil signs sustainable ethanol deal with Sweden mongabay.com June 27, 2008 A group of Brazilian ethanol producers has signed the first deal to export certified sustainable ethanol, reports Reuters. Four firms — Cosan, Guarani, NovAmerica and Alcoeste — will sell 115 million liters of anhydrous ethanol certified to […]
California plan would cut emissions 30% by 2020
California plan would cut emissions 30% by 2020 California plan would cut emissions 30% by 2020 mongabay.com June 27, 2008 California announced a plan to reduce state greenhouse gas emissions by 30 percent by 2020. The measures include a cap and trade program covering 85 percent of the state’s emissions, incentives for utilities to generate […]
94% of Americans support solar energy development
94% of Americans support solar energy development 94% of Americans support solar energy development mongabay.com June 11, 2008 94 percent of Americans say it’s important for the U.S. to develop and use solar energy, according to a new poll that found support for solar power runs across the political spectrum. The SCHOTT Solar BarometerTM survey, […]
Cellulosic biofuels may be viable alternative to gas within 5 years
 Cellulosic biofuels may be viable alternative to gas within 5 years High fuel prices to make cellulosic biofuels increasingly competitive with gas Madolyn Rogers, special to mongabay.com June 2, 2008 A new institute in the San Francisco Bay Area is seeking to make cellulosic biofuel an economically viable alternative to corn ethanol and gasoline within […]
Cellulosic biofuels may be viable alternative to gas within 5 years High fuel prices to make cellulosic biofuels increasingly competitive with gas Madolyn Rogers, special to mongabay.com June 2, 2008 A new institute in the San Francisco Bay Area is seeking to make cellulosic biofuel an economically viable alternative to corn ethanol and gasoline within […]
Will earthquake slow dam-building spree in China?
 Will earthquake slow dam-building spree in China? Will earthquake slow enthusiasm for dam-building in China? mongabay.com May 14, 2008 Monday’s 7.9 magnitude earthquake in Sichuan province left more than 15,000 dead, 26,000 missing, and 64,000 injured, according to state media. The quake also “seriously damaged” two hydroelectric stations in Maoxian county, leading authorities to warn […]
Will earthquake slow dam-building spree in China? Will earthquake slow enthusiasm for dam-building in China? mongabay.com May 14, 2008 Monday’s 7.9 magnitude earthquake in Sichuan province left more than 15,000 dead, 26,000 missing, and 64,000 injured, according to state media. The quake also “seriously damaged” two hydroelectric stations in Maoxian county, leading authorities to warn […]
China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020
 China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 mongabay.com April 29, 2008 China aims to expand its wind power generating capacity to 100,000 megawatts by 2020, more than doubling the current world’s installed capacity, according to the Shanghai Daily and The Wall Street […]
China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 mongabay.com April 29, 2008 China aims to expand its wind power generating capacity to 100,000 megawatts by 2020, more than doubling the current world’s installed capacity, according to the Shanghai Daily and The Wall Street […]
Mutant algae may fuel cars
Mutant algae may fuel cars Mutant algae may fuel cars mongabay.com April 2, 2008 Chemically-modified algae may become key to the production of hydrogen gas which seen by researchers as a next-generation fuel source. “We believe there is a fundamental advantage in looking at the production of hydrogen by photosynthesis as a renewable fuel,” said […]
Global warming solutions are harming indigenous people, says U.N.
 Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. mongabay.com April 2, 2008 Large-scale solutions intended to help mitigate global warming are harming the very indigenous people who are likely to bear the brunt of climate change, warned the United Nations University (UNU) at a conference […]
Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. mongabay.com April 2, 2008 Large-scale solutions intended to help mitigate global warming are harming the very indigenous people who are likely to bear the brunt of climate change, warned the United Nations University (UNU) at a conference […]
Arizona seeks to become the ‘Persian Gulf’ of solar energy
Arizona seeks to become the ‘Persian Gulf’ of solar energy Arizona seeks to become the ‘Persian Gulf’ of solar energy mongabay.com February 22, 2008 With a Spanish company’s plans to dramatically expand solar capacity in the desert southwest of Phoenix, Arizona Governor Janet Napolitano said Arizona could become the “Persian Gulf of solar energy,” according […]
Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech
 Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech mongabay.com February 21, 2008 The private sector is “pumping hundreds of billions of dollars” into cleaner and renewable energies, says a new publication released yesterday by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The report, The UNEP Year Book 2008, […]
Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech mongabay.com February 21, 2008 The private sector is “pumping hundreds of billions of dollars” into cleaner and renewable energies, says a new publication released yesterday by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The report, The UNEP Year Book 2008, […]
New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency
 New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency mongabay.com February 13, 2008 Sandia National Laboratories and Stirling Energy Systems (SES) set a new solar-to-grid system conversion efficiency record by achieving a 31.25 percent net efficiency, nearly a 2 point gain of the previous record of 29.4 percent set in […]
New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency mongabay.com February 13, 2008 Sandia National Laboratories and Stirling Energy Systems (SES) set a new solar-to-grid system conversion efficiency record by achieving a 31.25 percent net efficiency, nearly a 2 point gain of the previous record of 29.4 percent set in […]
Biofuels are worsening global warming
 Biofuels are worsening global warming Biofuels are worsening global warming Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Converting native ecosystems for production of biofuel feed stocks is worsening the greenhouse gas emissions they are intended to mitigate, reports a pair of studies published in the journal Science. The studies follow a series of reports that have […]
Biofuels are worsening global warming Biofuels are worsening global warming Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Converting native ecosystems for production of biofuel feed stocks is worsening the greenhouse gas emissions they are intended to mitigate, reports a pair of studies published in the journal Science. The studies follow a series of reports that have […]
Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks
 Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Driven by booming economic growth and rapid urbanization, China’s carbon dioxide emissions are surging. At the same time, forecasts suggest climate change will have an immense impact on the […]
Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Driven by booming economic growth and rapid urbanization, China’s carbon dioxide emissions are surging. At the same time, forecasts suggest climate change will have an immense impact on the […]
E.U. may ban palm oil biodiesel
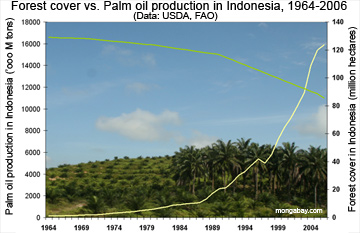 E.U. may restrict palm oil biodiesel due to environmental concerns E.U. may ban palm oil biodiesel Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 15, 2008 The E.U. may ban imports of certain biofuel feedstocks that damage the environment, reports The New York Times. While Europe aims to supply 10 percent of all vehicle fuel from biofuels by […]
E.U. may restrict palm oil biodiesel due to environmental concerns E.U. may ban palm oil biodiesel Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 15, 2008 The E.U. may ban imports of certain biofuel feedstocks that damage the environment, reports The New York Times. While Europe aims to supply 10 percent of all vehicle fuel from biofuels by […]
Indonesia seeks to cut fuel subsidies via biofuels
Indonesia seeks to cut fuel subsidies via biofuels Indonesia seeks to cut fuel subsidies via biofuels Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 15, 2008 Biofuels will make up 10 percent of Indonesia’s fuel transport consumption by 2010 under a plan announced Monday by a senior government official, according to Reuters. The initiative could ease the economic […]
Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn
 Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 7, 2008 Switchgrass yields more than 540 percent more energy than the energy needed to produce and convert it to ethanol, making the grassy weed a far superior source for biofuels than corn ethanol, reports a […]
Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 7, 2008 Switchgrass yields more than 540 percent more energy than the energy needed to produce and convert it to ethanol, making the grassy weed a far superior source for biofuels than corn ethanol, reports a […]
New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel
 New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel mongabay.com December 20, 2007 Chemical engineers at the University of Arkansas have devised a way to convert chicken fat into biodiesel fuel. The process advances efforts to “develop commercially viable fuel out of plentiful, accessible and low-cost feedstocks and other agricultural […]
New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel mongabay.com December 20, 2007 Chemical engineers at the University of Arkansas have devised a way to convert chicken fat into biodiesel fuel. The process advances efforts to “develop commercially viable fuel out of plentiful, accessible and low-cost feedstocks and other agricultural […]
Wind could supply baseline electrical power
 ? Wind could supply baseline electrical power Wind could supply baseline electrical power American Meteorological Society November 22, 2007 Wind power, long considered to be as fickle as wind itself, can be groomed to become a steady, dependable source of electricity and delivered at a lower cost than at present, according to scientists at Stanford […]
? Wind could supply baseline electrical power Wind could supply baseline electrical power American Meteorological Society November 22, 2007 Wind power, long considered to be as fickle as wind itself, can be groomed to become a steady, dependable source of electricity and delivered at a lower cost than at present, according to scientists at Stanford […]
Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation
 Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation: An interview on BECS with Biopact’s Laurens Rademakers mongabay.com November 6, 2007 A proposed mechanism for generating carbon-negative bioenergy — an energy source that reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide levels — could drive large-scale deforestation in the tropics […]
Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation: An interview on BECS with Biopact’s Laurens Rademakers mongabay.com November 6, 2007 A proposed mechanism for generating carbon-negative bioenergy — an energy source that reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide levels — could drive large-scale deforestation in the tropics […]
Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor
 Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor mongabay.com September 12, 2007 Clean energy will help people live longer and healthier lives reports a study published in The Lancet. The research recommends a switch from fossil fuels towards renewable energy and improved access to electricity […]
Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor mongabay.com September 12, 2007 Clean energy will help people live longer and healthier lives reports a study published in The Lancet. The research recommends a switch from fossil fuels towards renewable energy and improved access to electricity […]
Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats
 Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats But learning bat migration patterns may save them from wind turbines Jeremy Hance mongabay.com September 12, 2007 The danger of wind turbines to birds has long been known and well documented. Most recently several studies and articles have attempted […]
Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats But learning bat migration patterns may save them from wind turbines Jeremy Hance mongabay.com September 12, 2007 The danger of wind turbines to birds has long been known and well documented. Most recently several studies and articles have attempted […]
Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment
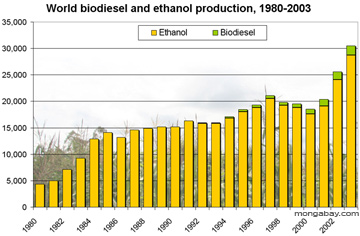 Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment mongabay.com August 30, 2007 Environmentalists have long seen biofuels as a means to improve the sustainability of transportation and energy use since they are a renewable source of energy that can be replenished on an ongoing basis. […]
Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment mongabay.com August 30, 2007 Environmentalists have long seen biofuels as a means to improve the sustainability of transportation and energy use since they are a renewable source of energy that can be replenished on an ongoing basis. […]
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
 More than a dozen leading U.S. companies have committed to investing a total of $140 billion in new funds to combat climate change in a White House-organized effort.
More than a dozen leading U.S. companies have committed to investing a total of $140 billion in new funds to combat climate change in a White House-organized effort. Maliau Falls in Borneo. The global economy depends on natural capital such as freshwater. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last month, Norway’s stock exchange, the Oslo Børs, introduced a way for investors to use their money to promote sustainability. A new list by the stock exchange highlights green bonds, financial products issued by companies to […]
Maliau Falls in Borneo. The global economy depends on natural capital such as freshwater. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last month, Norway’s stock exchange, the Oslo Børs, introduced a way for investors to use their money to promote sustainability. A new list by the stock exchange highlights green bonds, financial products issued by companies to […] The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […]
The world is warming rapidly due to greenhouse gas emissions, threatening everything from our food supply to our ecosystems, but the solution may be surprisingly cheap, according to the third and final report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The report recommends a rapid and aggressive switch from fossil fuel-based energy to renewables. […] Massive offshore wind turbine arrays would reduce hurricane wind speeds and storm surge, reports a study published this week in Nature Climate Change. And while the size (tens of thousands of turbines) and cost (hundreds of billions of dollars) is difficult to imagine, the reduction in storm damage and value of electricity produced would effectively […]
Massive offshore wind turbine arrays would reduce hurricane wind speeds and storm surge, reports a study published this week in Nature Climate Change. And while the size (tens of thousands of turbines) and cost (hundreds of billions of dollars) is difficult to imagine, the reduction in storm damage and value of electricity produced would effectively […] The opening of the International Hydropower Association (IHA) World Congress in the Malaysian state of Sarawak was marred today by indigenous protests and controversy after a local indigenous leader was barred from attending a pre-conference workshop. Over 300 people from local indigenous people protested the ongoing construction of around a dozen mega-dams in the state […]
The opening of the International Hydropower Association (IHA) World Congress in the Malaysian state of Sarawak was marred today by indigenous protests and controversy after a local indigenous leader was barred from attending a pre-conference workshop. Over 300 people from local indigenous people protested the ongoing construction of around a dozen mega-dams in the state […] The world could be heading for a major economic crisis as stock markets inflate an investment bubble in fossil fuels to the tune of trillions of dollars, according to leading economists. “The financial crisis has shown what happens when risks accumulate unnoticed,” said Lord (Nicholas) Stern, a professor at the London School of Economics. He […]
The world could be heading for a major economic crisis as stock markets inflate an investment bubble in fossil fuels to the tune of trillions of dollars, according to leading economists. “The financial crisis has shown what happens when risks accumulate unnoticed,” said Lord (Nicholas) Stern, a professor at the London School of Economics. He […] One kilometer off the Philippine island of Palawan lies the Rasa Island Wildlife Sanctuary; here forest grows unimpeded from a coral island surrounded by mangroves and coral reefs. Although tiny, over a hundred bird species have been recorded on the island along with a major population of large flying foxes, while in the waters below […]
One kilometer off the Philippine island of Palawan lies the Rasa Island Wildlife Sanctuary; here forest grows unimpeded from a coral island surrounded by mangroves and coral reefs. Although tiny, over a hundred bird species have been recorded on the island along with a major population of large flying foxes, while in the waters below […] Rainforest in Sabah, Malaysia on the island of Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A new video highlights the work and drive of renewable energy proponents at the inaugural meeting of Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) in the Malaysian state of Sabah. Held last year, the meeting brought together 80 organizations from 12 […]
Rainforest in Sabah, Malaysia on the island of Borneo. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. A new video highlights the work and drive of renewable energy proponents at the inaugural meeting of Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) in the Malaysian state of Sabah. Held last year, the meeting brought together 80 organizations from 12 […] Solar power on Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. Photo by: U.S. Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class Nadine Y. Barclay. The world’s installed solar capacity hit 101 gigawatts last year, according to new data from the European Photovoltaic Industry Association (EPIA). Last year alone, saw nearly 30 gigawatts of solar power added around the world. […]
Solar power on Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. Photo by: U.S. Air Force photo/Airman 1st Class Nadine Y. Barclay. The world’s installed solar capacity hit 101 gigawatts last year, according to new data from the European Photovoltaic Industry Association (EPIA). Last year alone, saw nearly 30 gigawatts of solar power added around the world. […] Electricity supplied from a new wind farm is cheaper than that from a new gas or coal-fired power plant in Australia, reports a new analysis published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. According to the study, wind-generated electricity costs AU$80 ($83) per megawatt hour compared with compared to AU$143/MWh ($148) from a new coal plant or […]
Electricity supplied from a new wind farm is cheaper than that from a new gas or coal-fired power plant in Australia, reports a new analysis published by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. According to the study, wind-generated electricity costs AU$80 ($83) per megawatt hour compared with compared to AU$143/MWh ($148) from a new coal plant or […] Scientists and experts are increasingly concerned that we are entering an age of ecological collapse with untold impacts for future generations. In Daniel Rirdan’s new book, The Blueprint, he outlines how to avoid this fate. Author, global strategist, and speaker Daniel Rirdan set out to create a plan addressing the future of our planet. His […]
Scientists and experts are increasingly concerned that we are entering an age of ecological collapse with untold impacts for future generations. In Daniel Rirdan’s new book, The Blueprint, he outlines how to avoid this fate. Author, global strategist, and speaker Daniel Rirdan set out to create a plan addressing the future of our planet. His […] Bakun dam during construction. Photo by: Mohamad Shoox. A top minister in the Malaysian state of Sarawak has told activists campaigning for cleaner energy to ‘stop breathing’, reports The Borneo Post. “I would like to throw a challenge at them (critics) on two fronts,” Land Development Minister Tan Sri Dr James Jemut Masing told the […]
Bakun dam during construction. Photo by: Mohamad Shoox. A top minister in the Malaysian state of Sarawak has told activists campaigning for cleaner energy to ‘stop breathing’, reports The Borneo Post. “I would like to throw a challenge at them (critics) on two fronts,” Land Development Minister Tan Sri Dr James Jemut Masing told the […] Participants from diverse backgrounds and groups marking on a map the creation of partnerships through identified projects at the end of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo by: Suzanne Chong/LEAP. The first ever meeting of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) ended […]
Participants from diverse backgrounds and groups marking on a map the creation of partnerships through identified projects at the end of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo by: Suzanne Chong/LEAP. The first ever meeting of the Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) ended […] A participant sharing a story at the inaugural Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo courtesy of SEAREPA. Last year, a coalition of environmentalists and locals won a David-versus-Goliath battle against a massive coal plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo. After facing a […]
A participant sharing a story at the inaugural Southeast Asia Renewable Energy People’s Assembly (SEAREPA) at the Rainforest Discovery Centre in Sandakan, Sabah. Photo courtesy of SEAREPA. Last year, a coalition of environmentalists and locals won a David-versus-Goliath battle against a massive coal plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo. After facing a […] Surface coal mining in Bihar, India. Around 70-80 percent of India’s power is currently provided by coal. Burning coal fuels climate change, causes acid rain, and spreads toxic pollutants into the environment, but now a new Greenpeace report warns that coal may also imperil the world’s biggest feline: the tiger. Home to world’s largest population […]
Surface coal mining in Bihar, India. Around 70-80 percent of India’s power is currently provided by coal. Burning coal fuels climate change, causes acid rain, and spreads toxic pollutants into the environment, but now a new Greenpeace report warns that coal may also imperil the world’s biggest feline: the tiger. Home to world’s largest population […] Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […]
Suburban sprawl in Albuquerque, New Mexico. The average American’s ecological footprint is the fifth highest in the world. Photo by: Jeremy Hance. Human society is consuming natural resources as if there were one-and-a-half Earths, and not just a single blue planet, according to the most recent Living Planet Report released today. If governments and societies […] Sunrise in Cancun, Mexico, where the 2010 UN Climate Summit was held. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last week, Mexico’s Senate passed an aggressive and comprehensive climate change bill, making it the first developing nation and only the second country to do so, after the UK. The bill, which far outshines anything achieved by its […]
Sunrise in Cancun, Mexico, where the 2010 UN Climate Summit was held. Photo by: Rhett A. Butler. Last week, Mexico’s Senate passed an aggressive and comprehensive climate change bill, making it the first developing nation and only the second country to do so, after the UK. The bill, which far outshines anything achieved by its […] Imagine powering your cell phone by leaving it on the window sill. Sounds like science fiction? Actually, this might soon turn into reality. Scientists have been exploring the potential of solar energy for decades. One of the cheapest ways to turn solar energy into electricity is by creating solar cells from organic polymers, which are […]
Imagine powering your cell phone by leaving it on the window sill. Sounds like science fiction? Actually, this might soon turn into reality. Scientists have been exploring the potential of solar energy for decades. One of the cheapest ways to turn solar energy into electricity is by creating solar cells from organic polymers, which are […] Sarah Laskow is a freelance writer who has covered environmental issues for Grist, GOOD, and Newsweek.com, among others. Raised in New Jersey and educated at Yale where she studied literature, Sarah now lives across the river in Manhattan with her partner. She’s done extensive traveling in West Africa, Europe, and Central America. Sarah can be […]
Sarah Laskow is a freelance writer who has covered environmental issues for Grist, GOOD, and Newsweek.com, among others. Raised in New Jersey and educated at Yale where she studied literature, Sarah now lives across the river in Manhattan with her partner. She’s done extensive traveling in West Africa, Europe, and Central America. Sarah can be […] Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […]
Victories won by activists around the world tops our list of the big environmental stories of the year. In this photo: a young woman is placed in handcuffs and arrested for civil disobedience against the Keystone XL Pipeline in the U.S. In all, 1,252 people were arrested in the two week long action. Photo by: […] Not known for alarmism and sometimes criticized for being too optimistic, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned that without bold action in the next five years the world will lock itself into high-emissions energy sources that will push climate change beyond the 2 degrees Celsius considered relatively ‘safe’ by many scientists and officials. “As […]
Not known for alarmism and sometimes criticized for being too optimistic, the International Energy Agency (IEA) has warned that without bold action in the next five years the world will lock itself into high-emissions energy sources that will push climate change beyond the 2 degrees Celsius considered relatively ‘safe’ by many scientists and officials. “As […] Young people rally in Kiev, Ukraine at apart of the Moving Planet campaign. Photo by: Maxm Gorpenyuk. On six continents, in over 75 percent of the world’s countries, people came out en masse yesterday to attend over 2,000 events to demonstrate the power of renewable energy to combat global climate change. As apart of the […]
Young people rally in Kiev, Ukraine at apart of the Moving Planet campaign. Photo by: Maxm Gorpenyuk. On six continents, in over 75 percent of the world’s countries, people came out en masse yesterday to attend over 2,000 events to demonstrate the power of renewable energy to combat global climate change. As apart of the […] When historians look back at the fight to combat climate change—not to mention the struggle to overcome our global addiction to fossil fuels—will 2011 be considered a watershed moment? Maybe. In the last couple months, three countries—each in the top ten in terms of GDP—have suddenly made major renewable energy promises. Germany, Japan, and, just […]
When historians look back at the fight to combat climate change—not to mention the struggle to overcome our global addiction to fossil fuels—will 2011 be considered a watershed moment? Maybe. In the last couple months, three countries—each in the top ten in terms of GDP—have suddenly made major renewable energy promises. Germany, Japan, and, just […] The wild rivers of Patagonia may soon never be the same. Last week, Chile’s Aysén Environmental Review Commission approved the environmental assessment of a five dam proposal on two rivers. The approval, however, is marred in controversy and has set off protests in many cities, including Santiago. Critics say the series of dams will destroy […]
The wild rivers of Patagonia may soon never be the same. Last week, Chile’s Aysén Environmental Review Commission approved the environmental assessment of a five dam proposal on two rivers. The approval, however, is marred in controversy and has set off protests in many cities, including Santiago. Critics say the series of dams will destroy […] US agriculture stands to lose billions in free ecosystem services from the often-feared and rarely respected humble bat. According to a recent study in Science bats in North America provide the US agricultural industry at least $3.7 billion and up to a staggering $53 billion a year by eating mounds of potentially pesky insects. Yet […]
US agriculture stands to lose billions in free ecosystem services from the often-feared and rarely respected humble bat. According to a recent study in Science bats in North America provide the US agricultural industry at least $3.7 billion and up to a staggering $53 billion a year by eating mounds of potentially pesky insects. Yet […] Recent studies point to the feasibility of a global clean energy revolution. Last night US President Barack Obama called for a massive green energy make-over of the world’s largest economy. Describing the challenge as ‘this generation’s Sputnik moment’ the US president set a goal of producing 80 percent of America’s energy by clean sources by […]
Recent studies point to the feasibility of a global clean energy revolution. Last night US President Barack Obama called for a massive green energy make-over of the world’s largest economy. Describing the challenge as ‘this generation’s Sputnik moment’ the US president set a goal of producing 80 percent of America’s energy by clean sources by […] 25 years on from Greenpeace’s joint stand with New Zealand’s government against potentially environmentally devastating practices, the country is at a Crossroads The Rainbow Warrior after the bombing by French commandos. Image courtesy of Greenpeace In light of the subject of this article, condolences go out to the families of the 29 miners who died […]
25 years on from Greenpeace’s joint stand with New Zealand’s government against potentially environmentally devastating practices, the country is at a Crossroads The Rainbow Warrior after the bombing by French commandos. Image courtesy of Greenpeace In light of the subject of this article, condolences go out to the families of the 29 miners who died […] The U.S. Department of Energy has finalized a guarantee to provide a loan of $1.45 billion to Abengoa Solar Inc. which will fund the world’s largest parabolic trough concentrating solar plant. The plant is expected to serve 70,000 households and avoid 475,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. The plant, called Solana, will be […]
The U.S. Department of Energy has finalized a guarantee to provide a loan of $1.45 billion to Abengoa Solar Inc. which will fund the world’s largest parabolic trough concentrating solar plant. The plant is expected to serve 70,000 households and avoid 475,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. The plant, called Solana, will be […] The US midterm election, which won Republicans the House but safeguarded the Senate for Democrats, has brought in a number of self-proclaimed climate change deniers, ending any likelihood that an energy bill will be passed over the next two years and essentially stumbling the White House’s strategy on climate change. Newly elected Republican Senators Rand […]
The US midterm election, which won Republicans the House but safeguarded the Senate for Democrats, has brought in a number of self-proclaimed climate change deniers, ending any likelihood that an energy bill will be passed over the next two years and essentially stumbling the White House’s strategy on climate change. Newly elected Republican Senators Rand […] Most Americans don’t understand the basics of climate change, according to a new poll by researchers with Yale. The poll found that over half of Americans deserve an ‘F’ on basic understanding of climate science and climate change, while only 1% would receive an ‘A’. While 63% of Americans say that the globe is warming, […]
Most Americans don’t understand the basics of climate change, according to a new poll by researchers with Yale. The poll found that over half of Americans deserve an ‘F’ on basic understanding of climate science and climate change, while only 1% would receive an ‘A’. While 63% of Americans say that the globe is warming, […] While the US has fallen far behind China and Europe in clean energy power, an announcement by Google today brings hope to green energy backers. Google is putting its considerable name and a lot of cash behind a $5 billion energy transmission line that would link up proposed wind turbines off the US’s East Coast […]
While the US has fallen far behind China and Europe in clean energy power, an announcement by Google today brings hope to green energy backers. Google is putting its considerable name and a lot of cash behind a $5 billion energy transmission line that would link up proposed wind turbines off the US’s East Coast […] To solve today’s environmental crises—climate change, deforestation, mass extinction, and marine degradation—while feeding a growing population (on its way to 9 billion) will require not only thinking outside the box, but a “new box altogether” according to Dr. Dickson Despommier, author of the new book, The Vertical Farm. Exciting policy-makers and environmentalists, Despommier’s bold idea […]
To solve today’s environmental crises—climate change, deforestation, mass extinction, and marine degradation—while feeding a growing population (on its way to 9 billion) will require not only thinking outside the box, but a “new box altogether” according to Dr. Dickson Despommier, author of the new book, The Vertical Farm. Exciting policy-makers and environmentalists, Despommier’s bold idea […] As world leaders continue to fumble a coherent, rapid, and comprehensive response to climate change, citizens from around the world yesterday sent a message to inert politicians by participating in over 7,300 events against climate change, according to 350.org, the head organizer of the day dubbed the ‘Global Work Party’. “The fossil fuel industry may […]
As world leaders continue to fumble a coherent, rapid, and comprehensive response to climate change, citizens from around the world yesterday sent a message to inert politicians by participating in over 7,300 events against climate change, according to 350.org, the head organizer of the day dubbed the ‘Global Work Party’. “The fossil fuel industry may […] Using decades-old data researchers have proven a long-suspected effect of wind turbines: under certain conditions large-scale wind farms can change local weather. Temperatures recorded from a wind farm in San Gorgonio, California in 1989 shows that turbines cooled local temperatures during the day, but warmed them at night. However, researchers in the paper published in […]
Using decades-old data researchers have proven a long-suspected effect of wind turbines: under certain conditions large-scale wind farms can change local weather. Temperatures recorded from a wind farm in San Gorgonio, California in 1989 shows that turbines cooled local temperatures during the day, but warmed them at night. However, researchers in the paper published in […] Sebuah wawancara dengan Laurens Rademakers dari Biochar Fund. Biochar – penggunaan arang yang diproduksi dari membakar biomassa untuk pertanian – mungkin merupakan saru dari revolusi lingkungan dan sosial yang terpenting di abad ini. Praktek yang sepertinya sederhana ini – sebuah teknologi yang kembali ke ribuan tahun yang lalu – memiliki potensi untuk membantu mengurangi sebagian […]
Sebuah wawancara dengan Laurens Rademakers dari Biochar Fund. Biochar – penggunaan arang yang diproduksi dari membakar biomassa untuk pertanian – mungkin merupakan saru dari revolusi lingkungan dan sosial yang terpenting di abad ini. Praktek yang sepertinya sederhana ini – sebuah teknologi yang kembali ke ribuan tahun yang lalu – memiliki potensi untuk membantu mengurangi sebagian […] An interview with Laurens Rademakers of Biochar Fund. Biochar—the agricultural application of charcoal produced from burning biomass—may be one of this century’s most important social and environmental revolutions. This seemingly humble practice—a technology that goes back thousands of years—has the potential to help mitigate a number of entrenched global problems: desperate hunger, lack of soil […]
An interview with Laurens Rademakers of Biochar Fund. Biochar—the agricultural application of charcoal produced from burning biomass—may be one of this century’s most important social and environmental revolutions. This seemingly humble practice—a technology that goes back thousands of years—has the potential to help mitigate a number of entrenched global problems: desperate hunger, lack of soil […] Local fishermen in the Malaysian state of Sabah are uncertain of their future, if the government pushes ahead to build a 300 megawatt coal power plant. They have been told they will be moved from their current seaside village to one deeper inland, and while the coal plant will provide manual labor work in its […]
Local fishermen in the Malaysian state of Sabah are uncertain of their future, if the government pushes ahead to build a 300 megawatt coal power plant. They have been told they will be moved from their current seaside village to one deeper inland, and while the coal plant will provide manual labor work in its […] Dengan seluruh perhatian dunia sedang mengarah pada bencana lingkungan di Teluk Meksiko, banyak yang mulai merenungkan kebenaran dari tidak hanya Amerika, tapi ketergantungan dunia akan bahan bakar fossil. Meski begitu proyek-proyek pengadaan energi berbahan bakar fosil skala besar terus berjalan maju, termasuk di kota Sabah, Malaysia di Borneo yang akan membangun 300 MW pembangkit listrik […]
Dengan seluruh perhatian dunia sedang mengarah pada bencana lingkungan di Teluk Meksiko, banyak yang mulai merenungkan kebenaran dari tidak hanya Amerika, tapi ketergantungan dunia akan bahan bakar fossil. Meski begitu proyek-proyek pengadaan energi berbahan bakar fosil skala besar terus berjalan maju, termasuk di kota Sabah, Malaysia di Borneo yang akan membangun 300 MW pembangkit listrik […] With the world’s eyes on the environmental catastrophe in the Gulf of Mexico, many are beginning to ponder the rightness of not just America’s, but the world’s dependence on fossil fuels. Yet large-scale fossil-fuel energy projects continue to march ahead, including one in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo to build a 300 MW […]
With the world’s eyes on the environmental catastrophe in the Gulf of Mexico, many are beginning to ponder the rightness of not just America’s, but the world’s dependence on fossil fuels. Yet large-scale fossil-fuel energy projects continue to march ahead, including one in the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo to build a 300 MW […] Why we get the oil spill we deserve. America, we deserve the oil spill now threatening the beautiful coast of Louisiana. This disaster is not natural, like the earthquake that devastated Haiti or tsunami that swept Southeast Asia in 2006; this disaster is man-made, American-made in fact, pure and simple. So, while in the upcoming […]
Why we get the oil spill we deserve. America, we deserve the oil spill now threatening the beautiful coast of Louisiana. This disaster is not natural, like the earthquake that devastated Haiti or tsunami that swept Southeast Asia in 2006; this disaster is man-made, American-made in fact, pure and simple. So, while in the upcoming […] The Obama Administration has approved the nation’s first offshore wind farm after more than eight years of legal challenges, reports the Associated Press. Speaking Wednesday in Boston, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar said the $2 billion Cape Wind project marks “a new direction in our nation’s energy future.” The 130-turbine, 420-megawatt wind farm will generate […]
The Obama Administration has approved the nation’s first offshore wind farm after more than eight years of legal challenges, reports the Associated Press. Speaking Wednesday in Boston, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar said the $2 billion Cape Wind project marks “a new direction in our nation’s energy future.” The 130-turbine, 420-megawatt wind farm will generate […] Plans for a coal power plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah in northern Borneo have run into stiff opposition. Environmentalists say the coal plant could damage extensive coral reef systems, pollute water supplies, open rainforests to mining, and contribute to global climate change, undercutting Sabah’s image as a ‘green’ destination. The federal government contends […]
Plans for a coal power plant in the Malaysian state of Sabah in northern Borneo have run into stiff opposition. Environmentalists say the coal plant could damage extensive coral reef systems, pollute water supplies, open rainforests to mining, and contribute to global climate change, undercutting Sabah’s image as a ‘green’ destination. The federal government contends […] This year China has become the world’s largest manufacturer of solar panels and wind turbines, doubling its wind capacity since 2005. The economically booming nation—and the world’s most populous—has also invested heavily in nuclear power and the world’s most efficient coal plants, according to the New York Times. Still, even with massive investments in green […]
This year China has become the world’s largest manufacturer of solar panels and wind turbines, doubling its wind capacity since 2005. The economically booming nation—and the world’s most populous—has also invested heavily in nuclear power and the world’s most efficient coal plants, according to the New York Times. Still, even with massive investments in green […] Evaluating 163 nations on their environmental performance, the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) has named Iceland the most environmental nation. Released every two years, the EPI also found that the world’s two largest super-powers—China and the US—have both fallen behind on confronting environmental challenges. Despite being at the top of the list, Iceland continues to face […]
Evaluating 163 nations on their environmental performance, the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) has named Iceland the most environmental nation. Released every two years, the EPI also found that the world’s two largest super-powers—China and the US—have both fallen behind on confronting environmental challenges. Despite being at the top of the list, Iceland continues to face […] For decades industrialized nations have measured their success by the size of their annual GDP (Gross Domestic Product), i.e. economic growth. The current economic model calls for unending growth—as well as ever-rising consumerism—just to remain stable. However, a new report by the New Economics Foundation (nef) states that if countries continue down a path of […]
For decades industrialized nations have measured their success by the size of their annual GDP (Gross Domestic Product), i.e. economic growth. The current economic model calls for unending growth—as well as ever-rising consumerism—just to remain stable. However, a new report by the New Economics Foundation (nef) states that if countries continue down a path of […] Green technology patents will see a year shaved off the average forty month wait time to approve new patents in the US. The US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is implementing a one-year pilot program to push green technology patent applications through the process more quickly, so that the technologies can reach the market faster. […]
Green technology patents will see a year shaved off the average forty month wait time to approve new patents in the US. The US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is implementing a one-year pilot program to push green technology patent applications through the process more quickly, so that the technologies can reach the market faster. […] The Sustainable Sites Initiative has developed the United States’ first rating system for the design, construction, and on-going maintenance of a wide-variety of landscapes, both with and without buildings, including shopping malls, subdivisions, university campuses, corporate buildings, transportation centers, parks and other recreation areas, and single-family homes. “While carbon-neutral performance remains the holy grail for […]
The Sustainable Sites Initiative has developed the United States’ first rating system for the design, construction, and on-going maintenance of a wide-variety of landscapes, both with and without buildings, including shopping malls, subdivisions, university campuses, corporate buildings, transportation centers, parks and other recreation areas, and single-family homes. “While carbon-neutral performance remains the holy grail for […] During the fiscal years of 2002-2008 the United States handed out subsidies to fossil fuel industries to a tune of 72 billion dollars, while renewable energy subsidies, during the same period, reached 29 billion dollars. Conducted by the Environmental Law Institute (ELI) in partnership with the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, the research shows […]
During the fiscal years of 2002-2008 the United States handed out subsidies to fossil fuel industries to a tune of 72 billion dollars, while renewable energy subsidies, during the same period, reached 29 billion dollars. Conducted by the Environmental Law Institute (ELI) in partnership with the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, the research shows […] After attempting to send a memorandum of protest against two dam proposals to the Sarawak Chief Minister Taib Mahmud, fifteen indigenous leaders were arrested in Kuching, Sarawak, reports the non-governmental organization the Burno Manser Fund. Each of the community leaders—including six Penans, four Ibans, three Kenyahs, and two Kayans—were protesting the dams since they will […]
After attempting to send a memorandum of protest against two dam proposals to the Sarawak Chief Minister Taib Mahmud, fifteen indigenous leaders were arrested in Kuching, Sarawak, reports the non-governmental organization the Burno Manser Fund. Each of the community leaders—including six Penans, four Ibans, three Kenyahs, and two Kayans—were protesting the dams since they will […]


 In a Perspectives piece in Science, John R. Regalbuto argues that the world will soon see a revolution in biofuels, but not those made from corn. Instead Regalbuto, program director of Catalysis and Biocatalysis at the National Science Foundation, says that the future of biofuels is in substances that can be converted into liquid hydrocarbons, […]
In a Perspectives piece in Science, John R. Regalbuto argues that the world will soon see a revolution in biofuels, but not those made from corn. Instead Regalbuto, program director of Catalysis and Biocatalysis at the National Science Foundation, says that the future of biofuels is in substances that can be converted into liquid hydrocarbons, […] Wind power may be the key to a clean energy revolution: a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science finds that wind power could provide for the entire world’s current and future energy needs. To estimate the earth’s capacity for wind power, the researchers first sectioned the globe into areas of […]
Wind power may be the key to a clean energy revolution: a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science finds that wind power could provide for the entire world’s current and future energy needs. To estimate the earth’s capacity for wind power, the researchers first sectioned the globe into areas of […] Eight Chinese environmentalists and scientists have composed a letter warning that a new dam under consideration for the Yangtze River could lead to the extinction of several endangered species. The letter contends that Xiaonanhia Dam, which would be 30 kilometers upstream from the city of Chongqing, will negatively impact the river’s only fish reserve. Spanning […]
Eight Chinese environmentalists and scientists have composed a letter warning that a new dam under consideration for the Yangtze River could lead to the extinction of several endangered species. The letter contends that Xiaonanhia Dam, which would be 30 kilometers upstream from the city of Chongqing, will negatively impact the river’s only fish reserve. Spanning […] A fleet of kites could harvest enough energy from high-altitude winds to power New York, report researchers from the Carnegie Institution and California State University. Using 28 years of data from the National Center for Environmental Prediction and the Department of Energy, Ken Caldeira of the Carnegie Institution’s Department of Global Ecology and Cristina Archer […]
A fleet of kites could harvest enough energy from high-altitude winds to power New York, report researchers from the Carnegie Institution and California State University. Using 28 years of data from the National Center for Environmental Prediction and the Department of Energy, Ken Caldeira of the Carnegie Institution’s Department of Global Ecology and Cristina Archer […] Congo biochar initiative wins critical funding to support poverty alleviation, climate change mitigation An initiative using soil carbon enrichment techniques to boost agricultural yields, alleviate poverty, and protect endangered forests in Central Africa was today selected as one of six projects to win funding under the Congo Basin Forest Fund (CBFF). The scientific committee of […]
Congo biochar initiative wins critical funding to support poverty alleviation, climate change mitigation An initiative using soil carbon enrichment techniques to boost agricultural yields, alleviate poverty, and protect endangered forests in Central Africa was today selected as one of six projects to win funding under the Congo Basin Forest Fund (CBFF). The scientific committee of […] Yesterday the Obama Administration established a Biofuels Interagency Working Group to oversee implementation of new rules and research regarding biofuels. On the group’s first day they would do well to look at a new study in Science Magazine comparing the efficacy of ethanol versus bioelectricity. Researchers compared ethanol and bioelectricity in terms of miles per […]
Yesterday the Obama Administration established a Biofuels Interagency Working Group to oversee implementation of new rules and research regarding biofuels. On the group’s first day they would do well to look at a new study in Science Magazine comparing the efficacy of ethanol versus bioelectricity. Researchers compared ethanol and bioelectricity in terms of miles per […]
 Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency mongabay.com November 13, 2008 Limiting global warming to 2-degree rise will require $180/t carbon price says energy think tank
Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency Developing countries must limit emissions to prevent global warming, says energy agency mongabay.com November 13, 2008 Limiting global warming to 2-degree rise will require $180/t carbon price says energy think tank Scientists should not compare biodiversity of rainforests with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief Biodiversity of rainforests should not be compared with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief mongabay.com November 11, 2008 Dr. Yusof Basiron, the controversial CEO of the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC), blogs about the sustainability of palm […]
Scientists should not compare biodiversity of rainforests with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief Biodiversity of rainforests should not be compared with oil palm plantations says palm oil council chief mongabay.com November 11, 2008 Dr. Yusof Basiron, the controversial CEO of the Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC), blogs about the sustainability of palm […] First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe mongabay.com November 10, 2008
First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe First RSPO-certified (“eco-friendly”) palm oil shipment to arrive in Europe mongabay.com November 10, 2008 EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil mongabay.com November 7, 2008
EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil EU’s sustainable biofuels push angers Malaysia, Brazil mongabay.com November 7, 2008 Green New Deal will spark global economy on long-term basis Green New Deal will spark global economy, create jobs mongabay.com October 22, 2008
Green New Deal will spark global economy on long-term basis Green New Deal will spark global economy, create jobs mongabay.com October 22, 2008 Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature mongabay.com October 20, 2008 can be used as a 3.8-billion-year-old R&D lab for technology development is gaining momentum. Benyus, author of
Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature Financial crisis could pave way for greener economy inspired by nature mongabay.com October 20, 2008 can be used as a 3.8-billion-year-old R&D lab for technology development is gaining momentum. Benyus, author of Challenges of starting a green business Challenges facing green business start-ups mongabay.com October 20, 2008
Challenges of starting a green business Challenges facing green business start-ups mongabay.com October 20, 2008 U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels mongabay.com October 2, 2008
U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels U.S. needs environmental standards for biofuels mongabay.com October 2, 2008 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 mongabay.com September 12, 2008 The European Union significantly reduces targets for biofuels produced from food sources, while boosting goals for other renewables The E.U. voted to relax biofuels targets following widespread criticism of […]
Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 Europe cuts biofuel targets to 4% in 2015, 6% in 2020 mongabay.com September 12, 2008 The European Union significantly reduces targets for biofuels produced from food sources, while boosting goals for other renewables The E.U. voted to relax biofuels targets following widespread criticism of […] Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com September 5, 2008 Presidential nominee Barack Obama recently answered fourteen science-related questions for the organization Science Debate 2008. The questions covered a wide-variety of topics, including the importance of innovation, […]
Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Obama talks science: ocean health, water scarcity, climate change, and more Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com September 5, 2008 Presidential nominee Barack Obama recently answered fourteen science-related questions for the organization Science Debate 2008. The questions covered a wide-variety of topics, including the importance of innovation, […] Biofuels up to 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation Biofuels 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation mongabay.com August 27, 2008 The British government should end subsidies for biofuels and instead use the funds to slow destruction of rainforests and tropical peatlands argues a new report […]
Biofuels up to 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation Biofuels 200 times more expensive than forest conservation for global warming mitigation mongabay.com August 27, 2008 The British government should end subsidies for biofuels and instead use the funds to slow destruction of rainforests and tropical peatlands argues a new report […] Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal power production Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal energy mongabay.com August 20, 2008 Geothermal energy got a big boost this week with Google and the Australian government announcing multi-million initiatives that make use of Earth’s heat as a clean and renewable source of power. Tuesday Google.org, the […]
Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal power production Google, Australia give big boost to geothermal energy mongabay.com August 20, 2008 Geothermal energy got a big boost this week with Google and the Australian government announcing multi-million initiatives that make use of Earth’s heat as a clean and renewable source of power. Tuesday Google.org, the […] PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant mongabay.com August 15, 2008 California electricity producer PG&E Thursday announced a plan to build two giant solar photovoltaic power plants that will cover 12.5 square miles and have a peak generating capacity of 800 megawatts. The plants […]
PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant PG&E will build the world’s largest solar power plant mongabay.com August 15, 2008 California electricity producer PG&E Thursday announced a plan to build two giant solar photovoltaic power plants that will cover 12.5 square miles and have a peak generating capacity of 800 megawatts. The plants […] Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests mongabay.com July 22, 2008 Biofuels meant to help alleviate greenhouse gas emissions may be in fact contributing to climate change when grown on converted tropical forest lands, warns a comprehensive study […]
Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests Biofuels can reduce emissions, but not when grown in place of rainforests mongabay.com July 22, 2008 Biofuels meant to help alleviate greenhouse gas emissions may be in fact contributing to climate change when grown on converted tropical forest lands, warns a comprehensive study […] Gore launches second campaign… for Earth Gore launches second campaign mongabay.com July 17, 2008 In a speech Thursday, Al Gore challenged the U.S. to generate 100 percent of its electricity from zero carbon emission sources within 10 years. Speaking at Washington’s Constitution Hall, Gore said America’s security, environmental and economic crises are all related, and […]
Gore launches second campaign… for Earth Gore launches second campaign mongabay.com July 17, 2008 In a speech Thursday, Al Gore challenged the U.S. to generate 100 percent of its electricity from zero carbon emission sources within 10 years. Speaking at Washington’s Constitution Hall, Gore said America’s security, environmental and economic crises are all related, and […] Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com July 10, 2008 The breakthrough scientists have been waiting for to make solar power cheaper, more efficient–and therefore a more […]
Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Breakthrough in solar energy: ten times more effective solar power may be available in three years Jeremy Hance, mongabay.com July 10, 2008 The breakthrough scientists have been waiting for to make solar power cheaper, more efficient–and therefore a more […] Oceans hold vast potential for wind power Oceans hold vast potential for wind power mongabay.com July 9, 2008 The North Pacific, Tasmania, New Zealand, Tierra del Fuego in South America, and the mid-latitudes of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans are potential locations for wind power generation, according to new satellite data from NASA. NASA’s QuikSCAT […]
Oceans hold vast potential for wind power Oceans hold vast potential for wind power mongabay.com July 9, 2008 The North Pacific, Tasmania, New Zealand, Tierra del Fuego in South America, and the mid-latitudes of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans are potential locations for wind power generation, according to new satellite data from NASA. NASA’s QuikSCAT […] Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels mongabay.com July 7, 2008 Britain and the E.U. should exercise caution in pushing for wider use of biofuels, warns a new study commissioned by the U.K. government. The report — dubbed the “Gallagher review” [PDF] for Ed Gallagher, the chair of the government’s […]
Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels Britain urges ‘cautious approach’ on biofuels mongabay.com July 7, 2008 Britain and the E.U. should exercise caution in pushing for wider use of biofuels, warns a new study commissioned by the U.K. government. The report — dubbed the “Gallagher review” [PDF] for Ed Gallagher, the chair of the government’s […] Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines mongabay.com July 7, 2008 By studying and mimicking the characteristics of the flippers, fins and tails of whales and dolphins, engineers have devised more a efficient way to generate wind power, reports a researcher presenting at the Society for Experimental Biology’s Annual Meeting […]
Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines Whale biomimicry inspires better wind turbines mongabay.com July 7, 2008 By studying and mimicking the characteristics of the flippers, fins and tails of whales and dolphins, engineers have devised more a efficient way to generate wind power, reports a researcher presenting at the Society for Experimental Biology’s Annual Meeting […] Clean energy investments rose 60% to $148 billion in 2007 Clean energy gold rush in 2007 mongabay.com July 1, 2008 New investment in renewables and energy efficiency surpassed $148 billion in 2007, rising 60 percent rise from 2006, according to an analysis issued Tuesday July 1 by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). High oil prices […]
Clean energy investments rose 60% to $148 billion in 2007 Clean energy gold rush in 2007 mongabay.com July 1, 2008 New investment in renewables and energy efficiency surpassed $148 billion in 2007, rising 60 percent rise from 2006, according to an analysis issued Tuesday July 1 by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP). High oil prices […] Cellulosic biofuels may be viable alternative to gas within 5 years High fuel prices to make cellulosic biofuels increasingly competitive with gas Madolyn Rogers, special to mongabay.com June 2, 2008 A new institute in the San Francisco Bay Area is seeking to make cellulosic biofuel an economically viable alternative to corn ethanol and gasoline within […]
Cellulosic biofuels may be viable alternative to gas within 5 years High fuel prices to make cellulosic biofuels increasingly competitive with gas Madolyn Rogers, special to mongabay.com June 2, 2008 A new institute in the San Francisco Bay Area is seeking to make cellulosic biofuel an economically viable alternative to corn ethanol and gasoline within […] Will earthquake slow dam-building spree in China? Will earthquake slow enthusiasm for dam-building in China? mongabay.com May 14, 2008 Monday’s 7.9 magnitude earthquake in Sichuan province left more than 15,000 dead, 26,000 missing, and 64,000 injured, according to state media. The quake also “seriously damaged” two hydroelectric stations in Maoxian county, leading authorities to warn […]
Will earthquake slow dam-building spree in China? Will earthquake slow enthusiasm for dam-building in China? mongabay.com May 14, 2008 Monday’s 7.9 magnitude earthquake in Sichuan province left more than 15,000 dead, 26,000 missing, and 64,000 injured, according to state media. The quake also “seriously damaged” two hydroelectric stations in Maoxian county, leading authorities to warn […] China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 mongabay.com April 29, 2008 China aims to expand its wind power generating capacity to 100,000 megawatts by 2020, more than doubling the current world’s installed capacity, according to the Shanghai Daily and The Wall Street […]
China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 China aims for 100 gigawatts of wind power by 2020 mongabay.com April 29, 2008 China aims to expand its wind power generating capacity to 100,000 megawatts by 2020, more than doubling the current world’s installed capacity, according to the Shanghai Daily and The Wall Street […] Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. mongabay.com April 2, 2008 Large-scale solutions intended to help mitigate global warming are harming the very indigenous people who are likely to bear the brunt of climate change, warned the United Nations University (UNU) at a conference […]
Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. Global warming solutions are hurting indigenous people, says U.N. mongabay.com April 2, 2008 Large-scale solutions intended to help mitigate global warming are harming the very indigenous people who are likely to bear the brunt of climate change, warned the United Nations University (UNU) at a conference […] Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech mongabay.com February 21, 2008 The private sector is “pumping hundreds of billions of dollars” into cleaner and renewable energies, says a new publication released yesterday by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The report, The UNEP Year Book 2008, […]
Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech Private sector pumping hundreds of billions into cleantech mongabay.com February 21, 2008 The private sector is “pumping hundreds of billions of dollars” into cleaner and renewable energies, says a new publication released yesterday by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The report, The UNEP Year Book 2008, […] New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency mongabay.com February 13, 2008 Sandia National Laboratories and Stirling Energy Systems (SES) set a new solar-to-grid system conversion efficiency record by achieving a 31.25 percent net efficiency, nearly a 2 point gain of the previous record of 29.4 percent set in […]
New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency New World Record for Solar-to-Grid Conversion Efficiency mongabay.com February 13, 2008 Sandia National Laboratories and Stirling Energy Systems (SES) set a new solar-to-grid system conversion efficiency record by achieving a 31.25 percent net efficiency, nearly a 2 point gain of the previous record of 29.4 percent set in […] Biofuels are worsening global warming Biofuels are worsening global warming Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Converting native ecosystems for production of biofuel feed stocks is worsening the greenhouse gas emissions they are intended to mitigate, reports a pair of studies published in the journal Science. The studies follow a series of reports that have […]
Biofuels are worsening global warming Biofuels are worsening global warming Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Converting native ecosystems for production of biofuel feed stocks is worsening the greenhouse gas emissions they are intended to mitigate, reports a pair of studies published in the journal Science. The studies follow a series of reports that have […] Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Driven by booming economic growth and rapid urbanization, China’s carbon dioxide emissions are surging. At the same time, forecasts suggest climate change will have an immense impact on the […]
Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Carbon tax would make China greener and reduce warming risks Rhett Butler, mongabay.com February 7, 2008 Driven by booming economic growth and rapid urbanization, China’s carbon dioxide emissions are surging. At the same time, forecasts suggest climate change will have an immense impact on the […] E.U. may restrict palm oil biodiesel due to environmental concerns E.U. may ban palm oil biodiesel Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 15, 2008 The E.U. may ban imports of certain biofuel feedstocks that damage the environment, reports The New York Times. While Europe aims to supply 10 percent of all vehicle fuel from biofuels by […]
E.U. may restrict palm oil biodiesel due to environmental concerns E.U. may ban palm oil biodiesel Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 15, 2008 The E.U. may ban imports of certain biofuel feedstocks that damage the environment, reports The New York Times. While Europe aims to supply 10 percent of all vehicle fuel from biofuels by […] Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 7, 2008 Switchgrass yields more than 540 percent more energy than the energy needed to produce and convert it to ethanol, making the grassy weed a far superior source for biofuels than corn ethanol, reports a […]
Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Switchgrass a better biofuel source than corn Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com January 7, 2008 Switchgrass yields more than 540 percent more energy than the energy needed to produce and convert it to ethanol, making the grassy weed a far superior source for biofuels than corn ethanol, reports a […] New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel mongabay.com December 20, 2007 Chemical engineers at the University of Arkansas have devised a way to convert chicken fat into biodiesel fuel. The process advances efforts to “develop commercially viable fuel out of plentiful, accessible and low-cost feedstocks and other agricultural […]
New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel New process turns chicken fat into biodiesel mongabay.com December 20, 2007 Chemical engineers at the University of Arkansas have devised a way to convert chicken fat into biodiesel fuel. The process advances efforts to “develop commercially viable fuel out of plentiful, accessible and low-cost feedstocks and other agricultural […] ? Wind could supply baseline electrical power Wind could supply baseline electrical power American Meteorological Society November 22, 2007 Wind power, long considered to be as fickle as wind itself, can be groomed to become a steady, dependable source of electricity and delivered at a lower cost than at present, according to scientists at Stanford […]
? Wind could supply baseline electrical power Wind could supply baseline electrical power American Meteorological Society November 22, 2007 Wind power, long considered to be as fickle as wind itself, can be groomed to become a steady, dependable source of electricity and delivered at a lower cost than at present, according to scientists at Stanford […] Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation: An interview on BECS with Biopact’s Laurens Rademakers mongabay.com November 6, 2007 A proposed mechanism for generating carbon-negative bioenergy — an energy source that reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide levels — could drive large-scale deforestation in the tropics […]
Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation Carbon-negative bioenergy to cut global warming could drive deforestation: An interview on BECS with Biopact’s Laurens Rademakers mongabay.com November 6, 2007 A proposed mechanism for generating carbon-negative bioenergy — an energy source that reduces atmospheric carbon dioxide levels — could drive large-scale deforestation in the tropics […] Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor mongabay.com September 12, 2007 Clean energy will help people live longer and healthier lives reports a study published in The Lancet. The research recommends a switch from fossil fuels towards renewable energy and improved access to electricity […]
Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor Clean energy will improve health of the world’s poor mongabay.com September 12, 2007 Clean energy will help people live longer and healthier lives reports a study published in The Lancet. The research recommends a switch from fossil fuels towards renewable energy and improved access to electricity […] Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats But learning bat migration patterns may save them from wind turbines Jeremy Hance mongabay.com September 12, 2007 The danger of wind turbines to birds has long been known and well documented. Most recently several studies and articles have attempted […]
Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats Wind power takes a toll on migratory bats But learning bat migration patterns may save them from wind turbines Jeremy Hance mongabay.com September 12, 2007 The danger of wind turbines to birds has long been known and well documented. Most recently several studies and articles have attempted […] Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment mongabay.com August 30, 2007 Environmentalists have long seen biofuels as a means to improve the sustainability of transportation and energy use since they are a renewable source of energy that can be replenished on an ongoing basis. […]
Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment Guidelines to ensure biofuels production won’t hurt the environment mongabay.com August 30, 2007 Environmentalists have long seen biofuels as a means to improve the sustainability of transportation and energy use since they are a renewable source of energy that can be replenished on an ongoing basis. […]