Sites: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
location: Iran
Social media activity version | Lean version
Final cheetah conservationists freed in Iran, but the big cat’s outlook remains grim
- In April, the last four cheetah conservationists from the Persian Wildlife Heritage Foundation jailed in 2018 for alleged espionage were released from prison in Tehran; four of their colleagues had been released earlier, while one had died in custody.
- The case had a chilling effect on scientific collaboration and efforts to save the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), which is today found only in Iran, with fewer than 30 believed to remain in the wild.
- The cheetah faces a range of threats, chief among them vehicle collisions: some 52% of cheetah deaths in Iran are due to road accidents.
- Saving the species will require a comprehensive and coordinated effort, and international scientific cooperation is crucial — but conservation work has been hampered by complex geopolitical dynamics, including sanctions.
Protect Persian leopards, and their defenders, for World Environment Day (commentary)
- For World Environment Day 2022 on June 5, Jane Goodall and 50 other conservationists published a letter urging protection for Persian leopards and and clemency for seven scientists imprisoned for their work studying the cats.
- In an open letter, the scientists highlight the impact of current conflicts, sanctions, and political tensions on the conservation of the leopard, whose range spans 11 countries, including Iran. It was in Iran where nine conservationists associated with the Persian Wildlife Heritage Foundation were arrested in January 2018, accused of spying because they were using camera traps. One of the conservationists, Kavous Seyed-Emami, who died in jail. The rest still sit in prison.
- Goodall and her colleagues call for the release of the imprisoned scientists and actions to facilitate international cooperation beyond recent political circumstances.
- This letter is a commentary containing the opinions of its writers and signers, not necessarily of Mongabay.
Reptile traffickers trawl scientific literature, target newly described species
- The descriptions and locations of new reptile species featured in scientific literature are frequently being used by traders to quickly hunt down, capture and sell these animals, allowing them to be monetized for handsome profits and threatening biodiversity.
- New reptile species are highly valued by collectors due to their novelty, and often appear on trade websites and at trade fairs within months after their first description in scientific journals.
- In the past 20 years, the Internet, combined with the ease and affordability of global travel, have made the problem of reptile trafficking rampant. Some taxonomists now call for restricted access to location information for the most in demand taxa such as geckos, turtles and pythons.
- Once a new species has been given CITES protection (typically a lengthy process), traders often keep the reptiles in “legal” commercial circulation by making false claims of “captive breeding” in order to launder wild-caught animals.
Iran upholds heavy sentences for conservationists convicted of spying
- A court in Tehran this week upheld its guilty verdict for eight Iranian conservationists accused of spying, with sentences ranging from four to 10 years.
- The eight are all affiliated with the Persian Wildlife Heritage Foundation, a Tehran-based conservation organization that works to save the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus) and other species.
- The eight conservationists have been imprisoned since their arrests in January 2018. A colleague arrested at the same time died in custody.
- Rights groups and conservation organizations have condemned the verdict, alleging serious flaws in the judicial process including credible reports of torture and forced confessions.
Iran sentences eight conservationists convicted of spying
- A court in Tehran last week delivered a guilty verdict in the case of eight Iranian conservationists accused of spying, with sentences ranging from four to 10 years.
- The eight were all affiliated with the Persian Wildlife Heritage Foundation, a Tehran-based conservation organization that works to save the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus) and other species. The charges appear to be related to allegations that the conservationists used wildlife camera traps for the purpose of espionage.
- The eight conservationists have been imprisoned since their arrests in January 2018. A colleague arrested at the same time died in custody.
- Rights groups and conservation organizations have condemned the verdict, alleging serious flaws in the judicial process.
Iran’s endangered cheetahs and imperiled conservationists (commentary)
- Eight Iranian wildlife conservationists have been imprisoned by the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps since January 2018, facing charges of espionage. All those in detention — Niloufar Bayani, Taher Ghadirian, Houman Jowkar, Sepideh Kashani, Amirhossein Khaleghi Hamidi, Abdolreza Kouhpayeh, Sam Radjabi and Morad Tahbaz — are among the most knowledgeable, experienced, and capable conservationists working in Iran.
- All are accused of spying under the guise of conducting cheetah surveys by using camera traps to collect sensitive information. But camera-traps are an extremely poor tool for spying. They are indispensable for monitoring shy species like Asiatic cheetahs, but the cat must pass within the sensor’s very limited range — around 5-10 meters — to trigger the unit.
- We hope that their body of excellent work is presented during the trials. We also hope that the Iranian authorities consider their profound contribution to conserving Iran’s magnificent natural heritage, and that these authorities agree with us that the future of the cheetah and of conservation in Iran relies on these very people being able to continue their vital work.
- This post is a commentary. The views expressed are those of the authors, not necessarily Mongabay.
Five wildlife conservationists held by Iran could face the death penalty
- Four conservationists arrested for suspected espionage in Iran in January face charges of “sowing corruption on Earth.”
- The charges stem from the team’s use of camera traps to track the Asiatic cheetah, but Iran’s Revolutionary Guard contends that the accused were collecting information on the country’s missile program.
- If convicted, the conservationists could be sentenced to death.
Conservationist, imprisoned for ‘spying’ with wildlife camera traps, dies in Iranian prison
- Kavous Seyed Emami, a professor of sociology and a director of the Persian Wildlife Heritage Foundation, died in Tehran’s Evin Prison earlier this month.
- Iranian authorities say Seyed Emami committed suicide, an assertion his family doubts.
- Seyed Emami’s arrest and suspicious death appear to be part of a wider crack down on environmentalists in Iran. Authorities arrested at least six other conservationists around the same time.
Cheetah populations crash as fastest-animal disappears from 91% of its range
- The world’s wild cheetah population is down to just 7,100 individuals, a decline of more than 90 percent since the turn of the 20th century
- Cheetah have disappeared across 91 percent of their historic range.
- The findings have led the authors to call for the cheetah to be up-listed from from ‘Vulnerable’ to ‘Endangered’ on the IUCN Red List.
Three murders highlight troubles of Iran’s park rangers
- In the final days of June, three Iranian park rangers were shot by poachers, bringing the tally of rangers killed in such instances in the country to 119.
- At least eight rangers have spent years behind bars after being convicted of murder for killing poachers while on the job.
- The Iranian Department of Environment claims the rangers were released during the last year. But the conditions of their release concern environmentalists, who point to flaws in the system meant to protect both rangers and the country’s rich biodiversity.
2015 Equator Prize winners span 19 countries
- The United Nations today announced 21 winners of the 2015 Equator Prize, a prestigious award that recognizes community-led environmental initiatives.
- The winners, selected from a pool of 1,461 nominations across 126 countries, include a wide range of groups from around the world.
- The winners were announced during a ceremony hosted by actor Alec Baldwin
Asiatic cheetahs: on the road to extinction?
 New road projects imperils Critically Endangered cheetah subspecies Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are unique among large cats. They have a highly specialized body, a mild temperament, and are the fastest living animals on land. Acinonyx jubatus venaticus, the Asiatic subspecies, is unique among cheetahs and the only member of five currently living subspecies to occur outside […]
New road projects imperils Critically Endangered cheetah subspecies Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are unique among large cats. They have a highly specialized body, a mild temperament, and are the fastest living animals on land. Acinonyx jubatus venaticus, the Asiatic subspecies, is unique among cheetahs and the only member of five currently living subspecies to occur outside […]
Animal picture of the day: rare image of Asiatic cheetah and cubs
 A rare image of a mother Iranian cheetah and its three cubs. Photo by: Javad Shokouhi/Yazd DOE-CACP. The Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), also known as the Iranian cheetah, is one the world’s rarest cat subspecies with somewhere between 70-110 individuals left. No surprisingly it is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN Red List. “This […]
A rare image of a mother Iranian cheetah and its three cubs. Photo by: Javad Shokouhi/Yazd DOE-CACP. The Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), also known as the Iranian cheetah, is one the world’s rarest cat subspecies with somewhere between 70-110 individuals left. No surprisingly it is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN Red List. “This […]
World nations see six all-time record high temperatures, no lows so far in 2011
 Eight months into the year, six nations have seen record high temperatures, including Kuwait, Iraq, Armenia, Iran, and Republic of the Congo, reports Jeff Master’s Wunderblog. To date no record lows have been recorded in any country in the world so far. This is similar, though not quite as extreme, to last year when twenty […]
Eight months into the year, six nations have seen record high temperatures, including Kuwait, Iraq, Armenia, Iran, and Republic of the Congo, reports Jeff Master’s Wunderblog. To date no record lows have been recorded in any country in the world so far. This is similar, though not quite as extreme, to last year when twenty […]
Half a trillion spent on fossil fuel subsidies mostly “a complete waste of money”
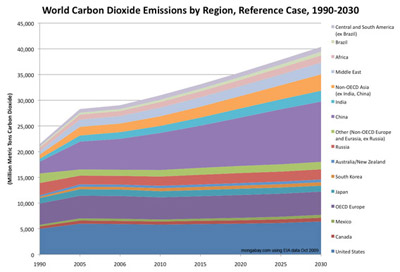 Despite a warming planet linked to the burning of fossil fuels, governments around the world still spend 500 billion US dollars a year subsidizing fossil fuel industries. A new study from the Global Subsidies Initiative (GSI) of the International Institute for Sustainable Development looks at the difficult political situation behind ending fossil fuel subsidies. “Fossil […]
Despite a warming planet linked to the burning of fossil fuels, governments around the world still spend 500 billion US dollars a year subsidizing fossil fuel industries. A new study from the Global Subsidies Initiative (GSI) of the International Institute for Sustainable Development looks at the difficult political situation behind ending fossil fuel subsidies. “Fossil […]
Forgotten Species: the fiery Luristan Newt
 Everyone knows the tiger, the panda, the blue whale, but what about the other five to thirty million species estimated to inhabit our Earth? Many of these marvelous, stunning, and rare species have received little attention from the media, conservation groups, and the public. This series is an attempt to give these ‘forgotten species‘ some […]
Everyone knows the tiger, the panda, the blue whale, but what about the other five to thirty million species estimated to inhabit our Earth? Many of these marvelous, stunning, and rare species have received little attention from the media, conservation groups, and the public. This series is an attempt to give these ‘forgotten species‘ some […]
Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers
 Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers An interview with Dr. Laurie Marker,founder of the Cheetah Conservation Fund Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com October 2, 2008 Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers
Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers An interview with Dr. Laurie Marker,founder of the Cheetah Conservation Fund Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com October 2, 2008 Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers
Feeds: news | india | latam | brasil | indonesia
 New road projects imperils Critically Endangered cheetah subspecies Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are unique among large cats. They have a highly specialized body, a mild temperament, and are the fastest living animals on land. Acinonyx jubatus venaticus, the Asiatic subspecies, is unique among cheetahs and the only member of five currently living subspecies to occur outside […]
New road projects imperils Critically Endangered cheetah subspecies Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) are unique among large cats. They have a highly specialized body, a mild temperament, and are the fastest living animals on land. Acinonyx jubatus venaticus, the Asiatic subspecies, is unique among cheetahs and the only member of five currently living subspecies to occur outside […] A rare image of a mother Iranian cheetah and its three cubs. Photo by: Javad Shokouhi/Yazd DOE-CACP. The Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), also known as the Iranian cheetah, is one the world’s rarest cat subspecies with somewhere between 70-110 individuals left. No surprisingly it is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN Red List. “This […]
A rare image of a mother Iranian cheetah and its three cubs. Photo by: Javad Shokouhi/Yazd DOE-CACP. The Asiatic cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus), also known as the Iranian cheetah, is one the world’s rarest cat subspecies with somewhere between 70-110 individuals left. No surprisingly it is considered Critically Endangered by the IUCN Red List. “This […] Eight months into the year, six nations have seen record high temperatures, including Kuwait, Iraq, Armenia, Iran, and Republic of the Congo, reports Jeff Master’s Wunderblog. To date no record lows have been recorded in any country in the world so far. This is similar, though not quite as extreme, to last year when twenty […]
Eight months into the year, six nations have seen record high temperatures, including Kuwait, Iraq, Armenia, Iran, and Republic of the Congo, reports Jeff Master’s Wunderblog. To date no record lows have been recorded in any country in the world so far. This is similar, though not quite as extreme, to last year when twenty […] Despite a warming planet linked to the burning of fossil fuels, governments around the world still spend 500 billion US dollars a year subsidizing fossil fuel industries. A new study from the Global Subsidies Initiative (GSI) of the International Institute for Sustainable Development looks at the difficult political situation behind ending fossil fuel subsidies. “Fossil […]
Despite a warming planet linked to the burning of fossil fuels, governments around the world still spend 500 billion US dollars a year subsidizing fossil fuel industries. A new study from the Global Subsidies Initiative (GSI) of the International Institute for Sustainable Development looks at the difficult political situation behind ending fossil fuel subsidies. “Fossil […] Everyone knows the tiger, the panda, the blue whale, but what about the other five to thirty million species estimated to inhabit our Earth? Many of these marvelous, stunning, and rare species have received little attention from the media, conservation groups, and the public. This series is an attempt to give these ‘forgotten species‘ some […]
Everyone knows the tiger, the panda, the blue whale, but what about the other five to thirty million species estimated to inhabit our Earth? Many of these marvelous, stunning, and rare species have received little attention from the media, conservation groups, and the public. This series is an attempt to give these ‘forgotten species‘ some […] Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers An interview with Dr. Laurie Marker,founder of the Cheetah Conservation Fund Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com October 2, 2008 Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers
Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers An interview with Dr. Laurie Marker,founder of the Cheetah Conservation Fund Rhett A. Butler, mongabay.com October 2, 2008 Cheetah population stabilizes in Namibia with support from farmers